[ad_1]
Web zero society: eventualities and pathways
How might societal modifications have an effect on the trail to web zero?
April 2023
Foreword
Local weather change presents a menace to humanity that we can not ignore. Within the UK, we now have dedicated to reaching web zero emissions by 2050. Decreasing emissions just isn’t solely the appropriate factor to do for the well being of our planet and its inhabitants however additionally it is a key financial alternative for the twenty first century. This Foresight report signifies that, relying on the course of societal change and associated modifications in vitality demand, the vitality system prices of assembly web zero might be decrease for the UK than not assembly web zero, as a proportion of GDP. The potential financial, environmental and well being prices of doing nothing are substantial. In the meantime, the trail to web zero offers alternatives, together with for creating inexperienced jobs and fostering new applied sciences for which there will probably be a considerable market.
This report attracts collectively proof from local weather science, social science, and vitality methods modelling. It units out 4 eventualities for what UK society might be like in 2050 after which examines how these might have an effect on vitality demand and the trail to web zero, together with the composition of the vitality system and the associated prices. The eventualities developed usually are not predictions of what’s going to occur. They need to really feel difficult and, maybe, even excessive. It’s unlikely that anyone of those eventualities will come to go in its entirety, however we do know that society in 30 years will look very completely different from at present and is more likely to embrace some options of those eventualities. I hope that organisations can use these eventualities to mirror on their long-term technique, contemplating questions reminiscent of: What if society modified in a number of the methods described? What about assembly web zero turns into tougher, and the way might we reply? What new alternatives might this current? The solutions to those questions sign the necessity to work outdoors of siloes; our findings counsel that the trail to web zero can’t be paved by one organisation alone.
Our report provides to the proof base exhibiting that societal modifications can have an effect on future vitality demand and emissions. Situations with decrease vitality demand might have decrease prices for taxpayers and companies, in addition to lowered reliance on new applied sciences, however after all include different challenges. To satisfy web zero, financial progress must proceed to be decoupled from demand and emissions, and we must always not assume that as-yet-unproven know-how will present a easy reply. A fancy problem like local weather change requires a mix of novel applied sciences, the infrastructure to embed these in society, and for us all to make extra sustainable selections the place we will.
Our public dialogue allowed us to carry a larger variety of thought to the questions being posed. After we spoke with members of the general public in regards to the eventualities, they had been open to the thought of great societal modifications, understood the necessity for these to occur, and had been extra constructive about futures that maximised the well being and fairness co-benefits of assembly web zero. My thanks to those volunteers. I’d additionally prefer to thank the wide selection of educational, authorities and {industry} specialists who supported this work in addition to the good staff within the Authorities Workplace for Science.
Sir Patrick Vallance
Authorities Chief Scientific Adviser
Govt abstract
The UK is dedicated to reaching web zero by 2050. Future societal norms and behaviours could have a big affect on how emissions are lowered, however they’re additionally extremely unsure. Society in 2050 is more likely to be very completely different from at present. Testing in opposition to a wider set of assumptions about how society might look ought to make the UK’s web zero technique extra resilient and able to tackle dangers and alternatives as they come up.
This report exhibits that if society modified in ways in which cut back demand for vitality, the vitality system prices of a state of affairs assembly web zero might be decrease by 2% of GDP than a baseline case the place the UK fails to satisfy web zero. There are additionally dangers and prices related to eventualities with larger ranges of vitality demand, which must be deliberate for. The twelve key findings of this report may be discovered on the backside of this part.
Goal
Commissioned as a part of the federal government’s web zero technique in 2021, the web zero society report goals to reply the next questions:
- What does proof on previous societal modifications inform us about how future modifications might unfold, and might we spot early indicators of this occurring?
- Knowledgeable by this proof, how would possibly society plausibly change by 2050, and the way might this have an effect on our pathway to web zero?
The report doesn’t discover or make suggestions for HM Authorities’s web zero technique. It focuses on how society would possibly change, the affect (constructive or unfavourable) on the prices and feasibility of assembly web zero, and the potential drivers of this past authorities local weather coverage. Whereas our evaluation is in depth, it was not technically possible to quantify all related impacts of every state of affairs, such because the financial impacts of being a profitable exporter of inexperienced applied sciences or lowering imports of fossil fuels.
Background
The UK’s unbiased Local weather Change Committee (CCC) has revealed a spread of proof exhibiting that assembly web zero within the UK is each technologically possible and inexpensive, with a predicted price of about 1–2% of GDP.
Many modifications wanted for web zero have upfront funding prices. Nonetheless, these could also be absolutely or partially offset by lowered working prices, reminiscent of decreased want for heating in better-insulated properties. Increased fossil gasoline costs would additionally enhance such financial savings. If gasoline costs don’t fall from their 2022 ranges, that are traditionally very excessive, then the CCC has estimated the web zero programme would offer a price saving of 0.5% of GDP per 12 months.
Most of the applied sciences wanted to satisfy web zero are already obtainable in some kind, which reduces a number of the uncertainty over how web zero will probably be met. For instance, most eventualities for assembly web zero depend on important rollout of electrical automobiles, warmth pumps and renewable electrical energy (predominantly wind and photo voltaic). , , ,6 Different applied sciences have been demonstrated at a small scale however are but to be confirmed on the scale wanted.
There’s additionally rising proof of the co-benefits of assembly web zero, together with for the financial system and for well being. For instance, creating and exporting new inexperienced applied sciences from the UK would assist meet web zero whereas being a driver of UK jobs and progress. Such direct advantages from mitigating local weather change and reaching web zero have been proven to outweigh the prices in HM Authorities’s Carbon Price range 6 Impression Evaluation.
Regardless of this proof base on the general prices, advantages and feasibility of assembly web zero, there stay some key uncertainties round points reminiscent of vitality demand, consumption patterns and the provision of sure applied sciences out to 2050, which this challenge explores.
Strategy
The report has been knowledgeable by the next analysis:
- Latest societal traits evaluate: A high-level evaluate of latest traits within the behaviours that straight affect emissions, with evaluation of the underlying societal drivers of these traits, to offer a baseline on which the challenge builds.
- Societal change proof evaluate: A evaluate of proof on previous societal modifications, together with a sequence of case research overlaying completely different classes (together with consumer-led, market-led and government-led) and completely different timescales. This has knowledgeable the event of the state of affairs narratives.
- Situation narrative growth: A set of believable eventualities designed to stretch occupied with how society would possibly change, developed by way of workshops with stakeholders from completely different sectors, together with authorities, enterprise, and academia, delivered to life by way of written narratives and illustrations. Situations usually are not predictions. They’re a software designed to help web zero coverage makers in contemplating how they might reply to a variety of circumstances. There isn’t any ‘proper reply’ inside the eventualities, as an alternative they illustrate the impacts of various potential modifications.
- Vitality system modelling: Representing every state of affairs in a set of vitality system fashions, together with the important thing mannequin used for HM Authorities’s web zero technique, to grasp what kind of vitality system is perhaps required to satisfy web zero in every state of affairs. This contains an evaluation of the prices, feasibility, and a few wider impacts (for instance, well being) of assembly web zero in every state of affairs.
- Public dialogue: A sequence of workshops with members of the general public to check the plausibility of the eventualities and perceive their views on the implications of various eventualities for assembly web zero.
Situations
This report presents 4 eventualities which discover crucial uncertainties in patterns of societal vitality use, consumption and know-how availability out to 2050. The 4 eventualities differ when it comes to:
- Financial progress and technological change,
- Institutional belief and social cohesion, and
- What these variations imply for exercise throughout society and the financial system.
Chapter 2 describes how these eventualities had been made. The eventualities have been delivered to life in a sequence of descriptive narratives (abstract overleaf), infographics, illustrations, and quantitative assumptions. These are all set out in Chapter 3.
The quantitative assumptions in every state of affairs had been then fed into an vitality system mannequin. This enabled an evaluation of how web zero would probably be met in every state of affairs, taking account of the vitality infrastructure and carbon elimination applied sciences that might be wanted. Excessive stage outcomes from this evaluation are set out within the subsequent part.
The eventualities had been every designed to incorporate difficult outcomes, to make them helpful for testing web zero coverage in opposition to. When you learn them and discover you don’t want any of those futures to occur, that’s the eventualities working as supposed. They’re intentionally provocative and draw out a number of the points authorities would want to deal with in every case. Take into consideration what you wish to be completely different and learn how to make that occur. Actuality in 2050 is more likely to embrace some points from all our eventualities, in addition to modifications not thought of right here.
Determine 1. Abstract of the 4 web zero society future eventualities
The textual content from Determine 1 is laid out under:
-
The atomised society: Technological change has fuelled progress. Particular person freedoms are prioritised, with folks capable of get pleasure from new experiences enabled by know-how. Nonetheless, extra wealth has been amassed by the richest and society is split alongside earnings traces; the wealthy reside in protected bubbles and the poor are extra uncovered to the consequences of local weather change.
-
The self-preservation society: financial progress and technological progress have didn’t reside as much as expectations for wealthy and poor alike. Folks do this they should get by, usually utilizing conventional strategies and out-dated know-how. Society is fragmented into many various teams. Some are extra comfy with the sluggish tempo of change, significantly older and rural communities.
-
The sluggish lane society: Financial and technological progress are sluggish which means there’s much less cash to put money into helpful infrastructure and restricted new know-how obtainable. Nonetheless, with excessive ranges of social cohesion and institutional belief, persons are prepared to contribute extra to enhance their communities. There’s additionally a rising tradition of restore, recycling and the sharing financial system.
-
The metropolitan society: Financial progress and technological change have delivered enhancements in dwelling requirements for many, by way of inequalities stay. Geography shapes identification, with sturdy communities within the metropolis areas which have pushed progress. There’s rising resentment in rural populations as they see funding directed in the direction of city areas however restricted funding within the countryside.
Implications for assembly web zero
Our modelling offers an in depth evaluation of how web zero may be met in every state of affairs, overlaying vitality provide, know-how rollout and infrastructure necessities. Full particulars may be present in Chapter 4. Determine 2 under exhibits whole ultimate vitality use by state of affairs. All eventualities see a fall in vitality use because of the rollout of vitality environment friendly applied sciences and measures, however variation is important. Increased vitality calls for consequence from components like extra long-distance journey, larger consumption of products, and dwelling in larger properties.
Determine 2. Complete ultimate vitality use in 2020–2050 (Petajoule/12 months) within the 4 web zero society eventualities

Determine 2 knowledge: Complete ultimate vitality use, PJ/12 months
| 2020 | 2025 | 2030 | 2035 | 2040 | 2045 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At Soc | 5600 | 5500 | 5000 | 4600 | 4500 | 4500 | 4600 |
| Met Soc | 5600 | 5300 | 4700 | 4200 | 3900 | 3700 | 3500 |
| SP Soc | 5700 | 5300 | 4600 | 4000 | 3600 | 3400 | 3300 |
| SL Soc | 5700 | 5200 | 4500 | 3800 | 3300 | 3000 | 2800 |
Determine 3 under exhibits residual emissions in 2050. All eventualities have roughly the identical emissions trajectory, assembly legislated carbon budgets and the 2050 web zero goal. In all circumstances assembly web zero requires carbon elimination applied sciences. Nonetheless, the eventualities with larger vitality use rely extra closely on these applied sciences. The affect of agriculture and land use can be important, because the eventualities with much less meat consumption have extra land obtainable for afforestation and bioenergy crops. Land-based carbon removals additional cut back reliance on engineered carbon removals.
Determine 3. Greenhouse gasoline emissions by sector (MtCO2e/12 months) in 2020 and for the 4 web zero society eventualities in 2030 and 2050

Determine 3 knowledge.Greenhouse gasoline emissions, MtCO2e/12 months
| Energy | Trade | Gasoline provide | Warmth and buildings | Home transport | Worldwide aviation and transport | Agriculture and land use | Waste and F-gases | Removals | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 47 | 56 | 29 | 100 | 99 | 28 | 50 | 34 | 0 | |
| At Soc | 2030 | 3 | 42 | 20 | 84 | 52 | 30 | 48 | 18 | 0 |
| At Soc | 2050 | -4 | 7 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 19 | 36 | 14 | -78 |
| Met Soc | 2030 | 3 | 43 | 23 | 72 | 63 | 29 | 43 | 22 | 0 |
| Met Soc | 2050 | 0 | 18 | 6 | 10 | 5 | 18 | 8 | 14 | -80 |
| SP Soc | 2030 | 3 | 42 | 22 | 76 | 62 | 27 | 46 | 19 | 0 |
| SP Soc | 2050 | 0 | 11 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 21 | 14 | -62 |
| SL Soc | 2030 | 3 | 36 | 23 | 78 | 61 | 29 | 42 | 22 | 0 |
| SL Soc | 2050 | 0 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 14 | -6 | 13 | -45 |
The implications of the eventualities for vitality system prices (together with gasoline prices and different working bills, and capital funding) are proven in Determine 4, which presents the system prices in every state of affairs:
- as a proportion of GDP (which varies by state of affairs), reflecting the truth that larger funding prices are extra inexpensive to a society with larger actual incomes and related tax income; and likewise
- relative to the system prices in a baseline state of affairs by which web zero just isn’t met (recognising that constructing, sustaining and working an vitality system will at all times characterize a big nationwide expenditure). Whereas every state of affairs’s prices are calculated as a direct proportion of the state of affairs’s particular person GDP projection, the baseline state of affairs makes use of the OBR’s 2020 forecasts.
Determine 4. Annual vitality system prices (2019 costs, undiscounted) as a proportion of GDP for the 4 web zero society eventualities, relative to these within the baseline state of affairs (expressed as a proportion level distinction)

Determine 4 knowledge. Annual vitality system price as a proportion of GDP, relative to baseline state of affairs
| The atomised society | The metropolitan society | The self-preservation society | The sluggish lane society | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | -0.0055 | -0.0055 | -0.0055 | -0.0055 |
| 2020 | -0.0084 | -0.0083 | -0.0084 | -0.0086 |
| 2021 | -0.0046 | -0.0059 | -0.0053 | -0.0072 |
| 2022 | -0.0026 | -0.0047 | -0.0028 | -0.0058 |
| 2023 | -0.0016 | -0.0042 | -0.00059 | -0.0044 |
| 2024 | -0.0014 | -0.0044 | 0.0011 | -0.0034 |
| 2025 | -0.0014 | -0.0047 | 0.0027 | -0.0025 |
| 2026 | -0.0019 | -0.0058 | 0.0033 | -0.0031 |
| 2027 | -0.0027 | -0.0071 | 0.0035 | -0.0041 |
| 2028 | -0.0036 | -0.0084 | 0.0037 | -0.005 |
| 2029 | -0.0044 | -0.0097 | 0.0039 | -0.0059 |
| 2030 | -0.0052 | -0.011 | 0.0041 | -0.0067 |
| 2031 | -0.0028 | -0.0099 | 0.0067 | -0.0049 |
| 2032 | -0.00058 | -0.009 | 0.0093 | -0.0031 |
| 2033 | 0.0015 | -0.0082 | 0.012 | -0.0013 |
| 2034 | 0.0034 | -0.0074 | 0.014 | 0.00043 |
| 2035 | 0.0052 | -0.0066 | 0.017 | 0.0022 |
| 2036 | 0.0031 | -0.0089 | 0.016 | 0.0014 |
| 2037 | 0.0011 | -0.011 | 0.016 | 0.00076 |
| 2038 | -0.00078 | -0.013 | 0.015 | 0.00021 |
| 2039 | -0.0026 | -0.015 | 0.015 | -0.00028 |
| 2040 | -0.0044 | -0.017 | 0.015 | -0.00073 |
| 2041 | -0.0044 | -0.017 | 0.016 | -0.00016 |
| 2042 | -0.0044 | -0.018 | 0.016 | 0.00044 |
| 2043 | -0.0045 | -0.018 | 0.017 | 0.001 |
| 2044 | -0.0046 | -0.019 | 0.018 | 0.0017 |
| 2045 | -0.0047 | -0.02 | 0.019 | 0.0023 |
| 2046 | -0.0033 | -0.02 | 0.024 | 0.0034 |
| 2047 | -0.002 | -0.02 | 0.03 | 0.0044 |
| 2048 | -0.0008 | -0.02 | 0.035 | 0.0055 |
| 2049 | 0.00031 | -0.02 | 0.041 | 0.0066 |
| 2050 | 0.0013 | -0.02 | 0.046 | 0.0077 |
Assembly web zero is most inexpensive within the metropolitan society, the place 2050 system prices as a proportion of GDP are 2% decrease than within the baseline state of affairs, which means it’s extra inexpensive than not assembly web zero. Vitality demand and financial progress have been decoupled most importantly on this state of affairs, by way of modifications reminiscent of shifting journey patterns and shifting to a ‘round financial system’ which makes use of sources extra effectively. Regardless that the metropolitan society wants a bigger vitality system than the sluggish lane society, the upper GDP makes this extra inexpensive.
Assembly web zero can be inexpensive within the sluggish lane and atomised societies, at lower than 1% above the baseline state of affairs in 2050. Within the sluggish lane society it is because societal modifications have led to decrease ranges of vitality demand, whereas within the atomised society it is because larger GDP helps to pay for the excessive ranges of know-how adoption and infrastructure wanted to satisfy web zero on this state of affairs.
In distinction, the self-preservation society assumes neither the societal modifications to cut back demand, nor the technological innovation and financial sources to pay for it. Consequently, the 2050 system prices are 5% larger than the baseline.
You will need to word that we now have not modelled the constructive impacts on GDP that assembly web zero could be more likely to have. Such advantages have been set out beforehand by the CCC and in HM Authorities’s Carbon Price range 6 Impression Evaluation and Web Zero Technique. 6, Nor have we factored within the important prevented prices of extra adaptation to the consequences of local weather change from assembly web zero at a world stage. Each are mentioned in additional element in Chapter 4.
Public dialogue
We couldn’t talk about the way forward for society with out speaking straight with the individuals who form it: UK residents. The challenge staff, with help from Sciencewise, commissioned the analysis firm Ipsos to hold out a public dialogue based mostly on the 4 eventualities.
A gaggle of 29 contributors from throughout the UK (Determine 5) took half within the public dialogue. This group, whereas small, was broadly reflective of UK inhabitants demographics (together with age, earnings stage, geographical location, ethnicity and gender).
Determine 5. Areas of contributors on a map of the UK (places in massive cities, reminiscent of London, characterize multiple participant)

The general public dialogue explored:
- Plausibility and pathways: The points of the eventualities that contributors felt had been least believable and the modifications they believed could be wanted between now and 2050 to make the state of affairs believable.
- Cross-cutting themes: The areas that contributors felt had been essential throughout all eventualities.
- Tensions and trade-offs: The tensions and trade-offs concerned in choice making round web zero, as recognized by contributors.
- Reactions to the person eventualities: Preliminary reflections regarding the sectors mentioned above.
Extra element on the general public dialogue method and findings may be present in Chapter 5.
Key findings
- Web zero may be met in all of the eventualities we modelled. Even in eventualities the place societal modifications result in larger ranges of vitality demand, there are pathways to web zero. Nonetheless, these larger demand eventualities depend on in depth use of carbon elimination applied sciences which are but to be confirmed at scale, which might be tough and/or costly to roll out on the tempo required, introducing larger threat to this path to web zero.
- Societal change will have an effect on the long run stage of demand for vitality and items and what applied sciences can be found. There’s round a 65% distinction in 2050 vitality demand between our eventualities. However precisely how society will change is, after all, unsure. Many equally believable eventualities exist, however ours characterize a number of the key potential modifications that governments ought to concentrate on as they plan.
- If societal modifications cut back vitality demand, assembly web zero might be cheaper than failing to take action. In comparison with a baseline state of affairs, which fails to satisfy web zero and has restricted societal modifications, our state of affairs with larger financial progress and demand-reducing societal modifications has 2050 vitality system prices which are decrease by 2% of GDP. On this state of affairs, modifications to journey patterns and new fashions for consuming items cut back vitality demand. This in flip reduces the scale, complexity and funding wants of the vitality system.
- In eventualities the place societal modifications cut back vitality demand, reliance on carbon elimination applied sciences is lowered, much less land is required for infrastructure, and well being co-benefits are larger. Situations that see decrease vitality demand and consumption, as a result of components reminiscent of these outlined within the earlier discovering, have lowered reliance on direct air seize (DAC) know-how to deal with residual emissions. These eventualities additionally require much less land for vitality infrastructure, which might make the vitality system simpler to ship and permit the land for use for different functions. Vital well being advantages might additionally circulation from lowered meat consumption and elevated bodily exercise.
- In distinction, in eventualities the place societal modifications do little to cut back demand, assembly web zero will probably be tougher to ship. That is partially because of the want for a bigger vitality system to be constructed quickly to satisfy the demand. It’s also because of the elevated reliance on costly know-how reminiscent of DAC to compensate for larger vitality use and emissions. Such massive vitality methods may be extra inexpensive in eventualities with stronger financial progress. Nonetheless, if financial progress is weak then this will likely imply web zero is much less inexpensive (as much as 5% of GDP costlier than the baseline).
- Financial progress and technological innovation are correlated. There’s a threat {that a} low progress, low innovation world would have fewer technological choices for assembly web zero. It’s potential to satisfy web zero with out additional technological breakthroughs. Nonetheless, with out them, the path to web zero would require extra important societal modifications, reminiscent of larger reductions within the ranges of flying and lowered consumption of meat and dairy. We’ve got not explicitly estimated the potential financial advantages of the UK being a frontrunner in inexperienced know-how in our evaluation. Nonetheless, this might plausibly additional improve the relative price discount in some eventualities.
- Financial progress and vitality demand may be additional decoupled if different societal modifications reminiscent of useful resource effectivity and different ‘round financial system’ measures happen in parallel. Our evaluation means that assembly web zero in a excessive financial progress state of affairs with such societal modifications might be round 2% of GDP less expensive in 2050 than in a excessive financial progress state of affairs with out them. All else being equal, financial progress is more likely to enhance general vitality demand, rising the scale and complexity of the vitality system, with related supply challenges. With bettering financial progress as a constant authorities aim, web zero planning ought to account for a way web zero may be met in a world with larger progress.
- Excessive ranges of innovation might result in extra quickly falling unit price reductions than assumed right here. Value reductions for key web zero applied sciences might come about extra quickly in eventualities the place the UK is main technologically or the place international decarbonisation drives quicker innovation. This can be extra more likely to occur within the eventualities with larger ranges of technological growth, by which case we is perhaps understating the affordability of assembly web zero in these eventualities.
- The trail to web zero will probably be affected by a variety of societal components that might be tracked as a part of planning for web zero, together with earnings distribution, sectoral combine within the financial system, adoption of digital applied sciences, the extent of city versus rural dwelling, and ranges of cohesion between completely different social teams. Authorities will greatest have the ability to adapt its method to web zero — seizing alternatives and mitigating a number of the prices — with early alerts of the course of journey. To enhance the resilience of its web zero technique, the federal government might observe these developments and adapt its method to web zero accordingly.
- Public help for technological innovation is more likely to have to be actively cultivated when it creates extremely seen modifications in folks’s day by day lives. As these eventualities display, know-how could have a giant position to play in assembly web zero. Nonetheless, members of the general public we spoke to had been apprehensive of excessive ranges of seen technological change, reminiscent of automation of jobs or novel meals manufacturing applied sciences. Concern centred on the well being impacts of applied sciences in addition to guaranteeing they didn’t introduce inequalities. The place a authorities’s chosen path to web zero would possibly contain extremely seen applied sciences, public help will have to be maintained. Elevated affordability, extra information in regards to the know-how, and reassurances round reliability and security had been all seen as key to making sure public help.
- Members of the general public we spoke to had been open to the concept there could also be important societal modifications by 2050. Nonetheless, they recognized some tensions between the modifications which may happen and the affect on their lives. These included tensions between sustaining selection however encouraging sustainability and between rising funding in know-how however guaranteeing prices had been manageable and pretty distributed.
- Sustainable selections are solely potential for most individuals when underpinned with supportive insurance policies and infrastructure. The members of the general public that we spoke to recommended that people’ ambitions to make sustainable selections had been restricted by the choices obtainable and their private circumstances. Contributors recommended that there have been methods to assist folks make extra sustainable selections, together with: elevated funding in infrastructure (reminiscent of public transport or lively journey), reskilling these liable to being ‘left behind’ by modifications, supporting the general public in creating their information of various choices, and incentivising companies to maneuver in the direction of a round financial system.
How can our report be used?
The outputs of the report present insights into the overall dangers and alternatives related to completely different pathways to web zero, however the proof and eventualities may also be utilized by coverage makers to assist develop and refine particular web zero insurance policies. Approaches that might be used embrace:
- Stress-testing: Coverage makers might stress-test coverage choices in opposition to the potential future eventualities set out right here, to establish the choices which are most resilient to completely different outcomes, or to assist adapt insurance policies in order that they grow to be extra resilient. You will need to recognise that there’s not a ‘appropriate state of affairs’; they’re merely an illustrative set of discrete potentialities. The Authorities Workplace for Science offers sources that can be utilized to help stress-testing workshops.
- Horizon scanning: Authorities might observe indicators to evaluate whether or not the UK is headed extra in the direction of a world which resembles one or different of the eventualities, offering intelligence on whether or not web zero is perhaps tougher or simpler to satisfy than at the moment assumed, or the technique might have to adapt in another method. You will need to word that these are solely 4 potential eventualities, and it’s unlikely that that the UK will observe precisely in the direction of any one in all them particularly. However the train can nonetheless assist to make sure coverage makers are on the entrance foot in getting ready for potential outcomes.
- Additional public engagement: By gathering extra intelligence on societal attitudes and related info on how society is altering, authorities might be outfitted with higher knowledge in regards to the probably course of journey for society. This might embrace new surveys or public dialogue actions.
Information to utilizing our report:
Would you prefer to stress take a look at your organisation’s web zero plan?
If sure, please confer with: Our futures (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4), implications for web zero (4.2, 4.3, 4.4), public dialogue (5.3, 5.4, 5.5) & subsequent steps.
Would you want to observe alerts that we’re on a sure state of affairs?
If sure, please confer with: Our futures (3.3, 3.4, 3.5), implications for web zero (4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.5), public dialogue (5.3) & subsequent steps.
Would you prefer to discover how a web zero society would possibly really feel for various teams?
If sure, please confer with: Our futures (3.1, 3.2, 3.3), implications for web zero (4.3), public dialogue (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6) & annex 6.
Would you prefer to create partaking studying supplies on web zero?
If sure, please confer with: Our futures (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4), implications for web zero (4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.5), public dialogue (5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6) & annex 6.
Would you prefer to: perceive extra about futures work and state of affairs growth?
If sure, please confer with: Our method (2.1, 2.2, 2.3), eventualities (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4), public dialogue (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5), annex 1, annex 2 & annex 3
Would you want to check mannequin outputs to different modelling work?
If sure, please confer with: Our method (2.3), our futures (3.3, 3.4), implications for web zero (4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.5), annex 4 & annex 5.
1. Introduction
What might the UK be like in 2050 when it has achieved its emissions targets? A web zero society is one the place there’s a stability between the greenhouse gases emitted and people faraway from the ambiance. There are questions on what is going to change over the subsequent few many years on the UK’s journey to changing into a web zero society. How will buildings be completely different? What’s going to journey be like at house and overseas? What jobs will there be? What meals will probably be eaten and the way will they be made? UK society is a continuously altering and complicated system made up of tens of millions of people, every pushed by their very own beliefs, values and circumstances. With such complexity, it’s inconceivable to foretell precisely how society will change. Nonetheless, it’s potential to consider a number of the completely different paths that UK society might absorb a scientific, evidence-informed method. This report is meant to assist coverage makers and shapers plan by contemplating a spread of potential societal modifications that would occur by 2050.
1.1 Background
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are compounds launched into our ambiance that entice the solar’s warmth, contributing to international warming and local weather change. A few of these gases are produced by dwelling beings; for instance, many animals launch methane throughout digestion. GHGs may also be produced by human actions, together with by way of vitality technology, manufacturing, agriculture, and waste administration. , For a lot of many years, international web emissions of those gases have been going up. , Because of this the quantity of GHGs being launched into the ambiance far exceeds the quantity that may be eliminated by pure processes or human know-how.
In 2019, the UK dedicated in laws to reaching ‘web zero’ by 2050, which means the UK’s GHG emissions could be equal to the emissions the UK removes from the ambiance. This goal adopted a suggestion by the Local weather Change Committee (CCC) and made the UK the primary main financial system to go a web zero emissions legislation. In its progress experiences to Parliament on this goal, the CCC notes that attaining web zero by 2050 is as a lot a societal problem as a technical one.2, Progress has been made within the UK in lowering emissions by way of infrastructure and industry-focused initiatives, reminiscent of transitioning to much less polluting energy sources and rising vitality effectivity. Most of those modifications have been considerably invisible to shoppers. Nonetheless, the subsequent section of lowering emissions will probably require extra seen and in depth modifications, reminiscent of how we journey or warmth our properties.2
Social norms (the shared requirements for acceptable behaviour) will probably have a big affect on the effectiveness of emissions-reducing insurance policies; proof means that those who align with pre-existing social norms might be extra profitable. , Future social norms, attitudes and behaviours are tough to foretell precisely. For instance, a coverage maker within the UK within the Nineteen Nineties occupied with tobacco use within the 2020s may need struggled to envisage a future society the place most individuals not smoke in automobiles, many former people who smoke favour digital cigarettes (which had been solely simply rising available on the market within the Nineteen Nineties), and the social acceptability of smoking is low throughout all age teams. Social norms usually are not immutable and might change dramatically over time. They are often influenced by many components, together with social actions, media campaigns, mounting analysis proof, and authorities insurance policies. , , Returning to the instance of smoking, proof from a examine on the impact of the smoking ban in indoor public areas within the 2000s (which adopted many years of public well being campaigns) discovered that the coverage preceded a rise in folks’s help for smoke-free laws and a lower in how acceptable they deemed smoking to be.
Societies are extraordinarily advanced methods made up of tens of millions of people, every pushed by their very own values, wants and ambitions. It’s inconceivable to foretell precisely what UK society will probably be like in 2050. Nonetheless, it’s potential to consider a number of the completely different paths UK society might take, and what this would possibly imply for assembly web zero, to assist coverage makers think about how they could want to answer a spread of potential future circumstances.
1.2 Scope
The analysis undertaken to supply this report has been constructed on the stable foundations of earlier work from throughout a spread of sectors (together with academia, non-public {industry}, the general public sector, and the third sector).
Extremely related earlier work on this space contains the 2021 Vitality Methods Catapult analysis on the direct emissions impacts of various societal and behavioural modifications. This challenge mapped 39 particular person behaviours (reminiscent of lowering meals waste or carpooling) and 11 societal modifications (reminiscent of elevated working from house) to grasp how these work together and contribute to general emissions. The challenge additionally used modelling and evaluation to discover the emissions and prices implications of behavioural and societal modifications in numerous sectors.
The Centre for Analysis into Vitality Demand Options’ (CREDS) 2021 report on the position of vitality demand discount in attaining web zero has additionally knowledgeable this report. CREDS envisaged 4 future eventualities for the UK in 2050 and modelled how completely different ranges of vitality demand discount might have an effect on future emissions. Its method is distinct from a lot different analysis on this space as a result of it didn’t assume substantial technological improvements and funding.
Components of each the Vitality Methods Catapult analysis and CREDS work have fed into the strategies used within the web zero society report. Nonetheless, this report is distinct from earlier work in the way it:
- considers the affect of a number of mixed societal modifications in every state of affairs, together with how numerous actors inside society behave and use know-how,
- co-creates eventualities with authorities coverage makers and exterior specialists to make sure they had been believable, but in addition sufficiently divergent and difficult to stress-test coverage and technique,
- contains the impacts of potential societal shifts throughout a spread of sectors (particularly these outdoors of the normal decarbonisation coverage area) that would both lower or enhance emissions and vitality use, and
- offers recent perception on the important thing interdependencies, trade-offs, and spill-over results of various behavioural and societal modifications on the trail to web zero.
This method is meant so as to add worth to the discussions round future vitality wants and emissions by exploring how the behaviour of people and organisations would possibly mix sooner or later to kind completely different potential societies. This challenge was commissioned by the Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique (BEIS) of their 2021 Web Zero Technique: Construct Again Greener.3
Within the technique, HM Authorities set out its method to assembly web zero and proposed to go ‘with the grain’ of societal traits to help progress in the direction of web zero. This Foresight report is meant to assist coverage makers and shapers think about the other ways these societal traits would possibly develop between now and 2050. It explores the query of how societal modifications might have an effect on the best way the UK achieves web zero.
This challenge cuts throughout many interrelated analysis and coverage areas. Due to this fact, it is very important make clear what this report will (and won’t) cowl, as follows:
- Web zero: This report primarily considers future emissions and progress in the direction of the UK’s home web zero goal. Recognising the significance of cumulative emissions, this contains the dedication to legislated carbon budgets between now and 2050. The report additionally recognises that UK society has a wider worldwide carbon footprint, which incorporates emissions ensuing from the manufacturing of products imported from different international locations. The UK’s worldwide carbon footprint is taken into account throughout the eventualities however just isn’t the main focus of our evaluation. There are different associated points (reminiscent of biodiversity loss or plastic air pollution), which might be affected by the societal modifications within the eventualities. The report features a high-level consideration of those impacts by state of affairs, however not an in depth evaluation. Moreover, the main focus of this work is mitigation (making local weather change impacts much less extreme) reasonably than adaptation (altering how folks reside to deal with the consequences of local weather change).
- UK in a world context: The eventualities developed on this challenge think about the UK. There are some concerns for a way international traits and occasions might affect progress in the direction of web zero. Nonetheless, the eventualities don’t try and estimate emissions ranges in different international locations. It’s potential that in these eventualities different nations have additionally met their web zero targets but in addition conceivable that there was slower progress internationally in the direction of web zero.
- Goal achievement: All of the eventualities offered on this report present the UK assembly its web zero goal by 2050. Nonetheless, the pathways taken to web zero differ, as do the prices, technical challenges, outcomes and impacts of the pathways chosen. For instance, in some eventualities the pathway to web zero could also be extra pricey or tough.
1.3 The best way to use this report
This report doesn’t make suggestions however can be utilized in a wide range of methods to organize for potential futures. The first viewers is coverage makers in authorities engaged on web zero or not directly related insurance policies, but it surely also needs to be usable by a spread of different organisations with web zero methods (reminiscent of companies or native authorities).
To assist guarantee this relevance and usefulness, the report has obtained steerage and recommendation from a various group of educated people together with, however not restricted to, those that gave time to develop the eventualities on this report and people who reviewed numerous elements of the challenge in our working group, steering group and professional group. A listing of people and organisations who helped form this work may be discovered within the acknowledgements part.
To help usability, there are options under for which sections is perhaps of most relevance for these wanting to have interaction with the report for various means.
Information to utilizing our report:
Would you prefer to stress take a look at your organisation’s web zero plan?
If sure, please confer with: Our futures (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4), implications for web zero (4.2, 4.3, 4.4), public dialogue (5.3, 5.4, 5.5) & subsequent steps.
Would you want to observe alerts that we’re on a sure state of affairs?
If sure, please confer with: Our futures (3.3, 3.4, 3.5), implications for web zero (4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.5), public dialogue (5.3) & subsequent steps.
Would you prefer to discover how a web zero society would possibly really feel for various teams?
If sure, please confer with: Our futures (3.1, 3.2, 3.3), implications for web zero (4.3), public dialogue (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6) & annex 6.
Would you prefer to create partaking studying supplies on web zero?
If sure, please confer with: Our futures (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4), implications for web zero (4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.5), public dialogue (5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6) & annex 6.
Would you prefer to: perceive extra about futures work and state of affairs growth?
If sure, please confer with: Our method (2.1, 2.2, 2.3), eventualities (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4), public dialogue (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5), annex 1, annex 2 & annex 3
Would you want to check mannequin outputs to different modelling work?
If sure, please confer with: Our method (2.3), our futures (3.3, 3.4), implications for web zero (4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.5), annex 4 & annex 5.
2. Our method
Anybody can take into consideration what UK society would possibly seem like in 2050. Some folks may think conditions the place society has not modified very a lot from how it’s now. Others would possibly image worlds with large technological improvements or societal shifts. Certainly, occupied with, and planning for, the long run is one thing that coverage makers and shapers do on a regular basis. Nonetheless, taking a scientific method to producing future eventualities could also be much less acquainted to some. This chapter units out the method used on this challenge, together with explanations of the strategies used to generate our eventualities and to translate these into fashions.
2.1 Overview
The web zero society eventualities have been developed utilizing strategies from the Authorities Workplace for Science (GO-Science) Futures Toolkit.10 It is a set of strategies designed to assist authorities officers with long-term, strategic coverage making. It contains three levels:
- Proof gathering, which makes use of horizon scanning strategies to establish traits (common actions throughout society in an identifiable course) and weak alerts (early indicators of change or rising points that will grow to be extra important) that point out potential future societal modifications. The drivers (causes or causes for change) for these traits are then recognized.
- Driver mapping, which explores the relative significance and uncertainty of those drivers of future societal change and identifies crucial uncertainties.
-
Situation narrative growth, which brings collectively numerous these crucial uncertainties right into a set of coherent, believable and various depictions of the long run.
This challenge additionally launched a fourth stage to discover the eventualities additional: - Vitality system modelling, which interprets qualitative state of affairs narratives into quantitative inputs for fashions to think about the implications for assembly web zero in every state of affairs.
Determine 6. A schematic exhibiting the 4 levels utilized in creating the eventualities and their emissions implications

Determine 6. Textual content model
| Step | 1. What are the rising societal modifications that would affect emissions | 2. Which of those societal modifications are crucial uncertainties for web zero? | 3. How might potential modifications mix into coherent eventualities? | 4. What are the implications for assembly web zero? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | Proof gathering: Utilizing PESTLE to seek out drivers and proof for change | Driver mapping workshop: rating recognized drivers when it comes to uncertainty and significance | Situation narratives workshop | Vitality system modelling and wider evaluation |
2.2 Ideas
Why use eventualities?
Situations are brief narratives that describe other ways a system and its surroundings would possibly develop sooner or later. A system might be an organisation, native space, financial system, or entire society, and the surroundings is the exterior components that affect the way it capabilities. For instance, a hospital might be a system and the surroundings might embrace the bodily location it’s in, the investments it receives, and the variety of sufferers it serves. Situations usually are not predictions however are a solution to think about completely different variations of the long run. They discover how completely different futures might emerge, establish dangers and alternatives, and take a look at what may be finished to realize numerous aims in numerous future circumstances. By definition, they are typically discrete alternate options and actuality will almost certainly lie in some mixture of eventualities.
The web zero society eventualities have been developed by figuring out crucial uncertainties regarding how society will use vitality and devour items between now and 2050. Crucial uncertainties are potential future modifications which are more likely to be essential, however it’s at the moment unclear which course the change will go in and/or what the magnitude of change is more likely to be. As a result of it isn’t potential to know the modifications that can occur, this implies there are a number of believable future ‘finish states’. These finish states can embrace opposing extremes when crucial uncertainties might go both of two very other ways. A state of affairs is constructed from a mix of finish states which are coherent and potential however nonetheless current completely different and fascinating circumstances.
The narrative eventualities offered on this report embrace some rationalization of how a selected finish state has occurred, based mostly on obtainable proof on how wider societal modifications (reminiscent of financial progress) might affect behaviours related to lowered emissions (reminiscent of driving much less or utilizing merchandise for longer). The benefits of this method are:
- It helps choice makers perceive which wider modifications would possibly result in such eventualities.
- It acknowledges proof on correlations between components which may not be represented in a less complicated sensitivity evaluation of particular person components. For instance, a excessive know-how world might result in larger vitality calls for in some areas (reminiscent of manufacture of electronics as a result of larger client demand) however decrease demand in others (reminiscent of journey for work as a result of improved digital communication). It might additionally speed up the event of applied sciences to realize web zero.
- It permits a wider set of indicators to be developed to trace in opposition to the eventualities, together with wider societal components that would have an effect on pathways to web zero.
In fact, it is very important acknowledge that the relationships assumed in our eventualities usually are not set in stone, and that causality in society is never provable (that’s to say, demonstrably true) or immutable (which means unable to alter). Situations might counsel {that a} explicit occasion might set off a selected change. Nonetheless, that doesn’t imply the occasion would positively trigger the change, nor that the occasion could be the one method for the change to occur, nor that the change would final. Because of this, we now have stored explanations of a number of the points of state of affairs finish states extra open to interpretation.
What are the ideas for our eventualities?
Some key ideas for the web zero society eventualities embrace that they’re:
2.3 Course of
Stage one: Proof gathering
Historical past and traits
Trying again over the previous 30 years, we will see how societal modifications (reminiscent of pervasive web use or low-cost air journey) have had widespread impacts on vitality use and GHG emissions. As a part of the proof gathering stage of the challenge, a latest societal traits report was produced (Annex 1). It explored historic relationships between drivers of change, societal traits, and emissions inside 4 sectors: the constructed surroundings, journey and transport, work and {industry}, and meals and land use. This proof informs the assumptions in regards to the future relationships between these components, which have been used to construct the eventualities. An instance of how drivers of change had been mapped to latest societal traits and the probably affect may be seen in Determine 7, under.
Determine 7. Relationships between chosen drivers of change, societal traits, and emissions

Determine 7. Textual content model
| Societal driver of change | Ensuing web zero behavioural traits from drivers of change | Impression on web zero |
|---|---|---|
| Digital communications | Demand for journey & demand for house heating | Vitality and emissions |
| UK financial progress | Demand for journey & demand for UK manufactured items | Vitality and emissions |
| Reshoring of producing | Demand for UK manufactured items | Vitality and emissions |
Though we present the causal impacts of societal modifications on vitality demand and emissions right here in Determine 7, there are additionally suggestions loops that exist, significantly in relation to calls for spurring innovation in new applied sciences.
The latest societal traits report targeted on an illustrative set of traits that had been chosen based mostly on: their significance for emissions, the general public availability of datasets, and sector specialists’ views. The report reviewed over 100 related items of analysis literature to establish and examine the underlying societal drivers and disruptors of those traits.
Of the recognized societal drivers of change, many are acquainted and longstanding, together with authorities insurance policies, the state of the financial system, and the related prices and efficiency of low emission selections. Nonetheless, different drivers that had been recognized have emerged extra not too long ago, together with provide chain disruptions, availability of crucial uncooked supplies and elements, and restricted familiarity with new applied sciences reminiscent of warmth pumps. The highest three drivers discovered to have an effect on a lot of traits (reminiscent of site visitors flows, house insulation charges and meals waste) had been:
- Financial progress, which is the rise within the worth of products and companies produced inside a inhabitants. It’s associated to the provision of latest merchandise/companies and to family incomes. Increased financial progress is related to larger ranges of consumption and journey. For instance, pre-pandemic, rising incomes and falling airfares had been the principle drivers of demand for aviation; distance flown internationally grew by 20% from 2010 to 2019.
- Environmental consciousness, which is the understanding of the significance of the pure surroundings and its safety. Environmental consciousness can usually be a moderating power on the will increase in consumption related to financial progress. For instance, environmental concerns are one of many major drivers for switching to plant-based diets, alongside well being and private moral causes. The variety of folks reporting following a meat-free weight loss plan elevated by 11% between 2016 and 2022.
- Demographics, which incorporates inhabitants traits reminiscent of family dimension, age and earnings. Demographic modifications in society are strongly correlated with traits in general consumption of meals, companies and items, though the course of the affect varies for various demographic modifications.
The complexity of those drivers is illustrated by Determine 8, which exhibits these drivers on the left, the traits they have an effect on within the center and the contribution of those traits to sectors on the appropriate. This determine doesn’t present particular impact sizes; the load of the traces from the drivers are stored even and don’t embrace details about the scale of the contribution to the traits as these usually are not reliably quantifiable.
Determine 8. Societal drivers affecting the most important variety of traits throughout the 4 sectors

Determine 8. Textual content model
| Sectoral driver: environmental consciousness | |
|---|---|
| Sub-driver | Sector utilized in modelling |
| Residence insulation charges | The constructed surroundings |
| Good meters | The constructed surroundings |
| New EV gross sales | Journey and transport |
| Charging factors | Journey and transport |
| Low-traffic neighbourhoods | Journey and transport |
| Rooftop photo voltaic PVs | The constructed surroundings |
| Non-residential vitality effectivity | The constructed surroundings |
| Meat-free consuming | Meals and land use |
| Meals waste | Meals and land use |
| Sectoral driver: financial progress | |
|---|---|
| Sub-driver | Sector utilized in modelling |
| Visitors circulation | Journey and transport |
| Loading components for freight | Journey and transport |
| Demand for aviation | Journey and transport |
| Meals waste | Meals and land use |
| Building and demolition waste | Work and {industry} |
| Consumption and commerce | Work and {industry} |
| Non-residential ground space | The constructed surroundings |
| Sectoral driver: demographics | |
|---|---|
| Sub-driver | Sector utilized in modelling |
| Consumption and commerce | Work and {industry} |
| Non-residential ground space | The constructed surroundings |
| Family dimension | The constructed surroundings |
| Residential ground space | The constructed surroundings |
| Calorie consumption | Meals and land use |
Figuring out drivers of change
Horizon scanning is the method of on the lookout for early warning indicators of change within the coverage and technique surroundings. A horizon scanning train was performed to try to reply the query ‘What are the principle drivers of societal and behavioural change that can straight or not directly have an effect on UK GHG emissions between now and 2050?’. Given the necessity to produce eventualities that can be utilized to check UK web zero coverage, this train primarily targeted on drivers of change outdoors of the decarbonisation coverage area that would affect emissions. Nonetheless, some drivers had been thought of that might be influenced by each insurance policies and different exterior components, such because the relative prices of ‘inexperienced’ selections (that are affected by insurance policies and components like inflation or technological innovation).
Candidate drivers of change had been recognized through desk-based analysis. Sources included educational literature, gray literature , and information articles. These had been structured utilizing a PESTLE framework , then sifted right into a shortlist of 40 drivers (Annex 3).
Proof on the extent to which drivers affect social traits, thereby resulting in general societal change, was thought of in an proof evaluate (Annex 2). This evaluate explored how change in advanced methods (which UK society may be thought of) works and what components can drive change. It explores circumstances research from earlier societal modifications to point out how system change may be initiated at numerous ranges (together with by way of top-down authorities coverage and bottom-up social actions) and the way numerous components might work together to supply completely different outcomes. Typically these could also be outcomes that coverage makers or shapers don’t predict, particularly when it comes to the velocity of modifications. For instance, some interventions might expertise surprising resistance from the system whereas others might choose up velocity, trigger spill-over results or set off a social tipping level. The evaluate additionally supplied supporting proof for the challenge’s prior assumption that it is very important think about a variety of traits and drivers when occupied with future societal change. Different insights from this proof evaluate had been used to check the plausibility of the proposed results of potential drivers, the interior coherence of state of affairs narratives and the setting of modelling inputs in later levels.
Stage two: Driver mapping
Figuring out crucial uncertainties
The following stage was to think about which drivers had been most essential and unsure. To make sure the ultimate eventualities had been usable by a spread of stakeholders, it was essential to usher in a wide range of related experience and various views at this stage. A workshop was held that introduced collectively 35 people from nationwide authorities, native authorities, {industry}, third sector organisations, citizen teams, and academia.
First, drivers had been mapped when it comes to significance and uncertainty, outlined as follows:
-
Significance: Contributors had been requested to think about the potential scale and length of affect of the driving force on UK GHG emissions and/or vitality consumption between now and 2050. In addition to long-term impacts, short-term impacts had been thought of. In circumstances the place the driving force was unsure, contributors had been requested to consider excessive believable outcomes for that driver earlier than deciding on its significance.
-
Uncertainty: Contributors had been requested whether or not they might think about a number of completely different believable outcomes for this driver, both due to a scarcity of proof on the course of journey, or due to deep uncertainty inherent in advanced methods over lengthy timescales. Uncertainty and significance weren’t essentially correlated. For instance, elevated use of renewable electrical energy will probably be essential for web zero targets however it’s low in uncertainty (traits and present insurance policies point out a comparatively clear path). Uncertainty was interpreted as the extent of distinction between these believable outcomes (the broader the hole between believable outcomes of a driver, the extra unsure it’s).
Contributors scored every driver when it comes to significance and uncertainty. Common scores are proven in Determine 9 under. This train helped to establish crucial uncertainties, that are drivers which are each extremely essential and likewise extremely unsure. Eighteen crucial uncertainties had been recognized utilizing significance/uncertainty scores and qualitative suggestions from specialists (see Determine 9 and Desk 1 under).
Determine 9. Significance/uncertainty scores for shortlisted drivers of change

Determine 9 knowledge
| PESTLE issue | Driver label | Uncertainty Rating (vary: -4 to 4) | Significance Rating (vary: -4 to 4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Political | P4: Enterprise backlash in political choice making | -1 | 3 |
| Political | P5: Polarising belief in authorities | 0 | 1 |
| Political | P6: more and more controversial and fractious geopolitics | 1 | 2 |
| Financial | Ec1: Macro-economic stability and progress | 0 | 3 |
| Financial | Ec2: Relative prices of ‘making the inexperienced selection’ | 0 | 4 |
| Financial | Ec6: Potential for elevated localisation of manufacturing and financial exercise | 2 | 1 |
| Societal | S1: Shifts in the place and the way folks reside – locations, housing, and households | 0 | 1 |
| Societal | S2: Altering nature of labor | 0 | 1 |
| Societal | S5: Actual and perceived unfairness of impacts of local weather change and paying for web zero | -1 | 3 |
| Technological | T1: Potential for web zero know-how price or efficiency modifications that transfer the aim posts | 1 | 4 |
| Technological | T3: Rising use of linked and autonomous automobiles | 0 | -1 |
| Technological | T4: Rising use of synthetic intelligence in vitality methods and throughout the financial system | 0 | 1 |
| Legislative | L2: Rising circumstances of local weather change litigation | 0 | 2 |
| Legislative | L3: Rising monetary prices for emissions | -1 | 3 |
| Legislative | L4: Different international locations legislate to cease UK outsourcing its emissions | 0 | 3 |
| Environmental | En2: Improve in growth and greening of habitable cities | 0 | 1 |
| Environmental | En3: Lowering property worth and elevated inside displacement as a result of environmental issues/excessive climate | -1 | 1 |
| Environmental | En5: Rising pressure in how land is used – housing, farming, energy technology, afforestation, and so on. | 0 | 3 |
Whereas these 18 crucial uncertainties kind the premise for the eventualities, the opposite 22 drivers are nonetheless of relevance and in some circumstances had been used to tell the ultimate state of affairs narratives.
Creating axes of uncertainty
The crucial uncertainties had been then developed into ‘axes of uncertainty’. This includes exploring two different outcomes for every crucial uncertainty which are each believable and divergent from one another. The workshop contributors developed these in breakout teams, and ensuing concepts had been then additional refined by the web zero society challenge staff. The total set of axes is included in Annex 3.
Desk 1. Crucial uncertainties sorted by PESTLE class
| Class | Crucial uncertainty | Description |
| Political | P4: Enterprise affect on political choice making | Reaching web zero requires change from the inhabitants, non-public sector, and public sector organisations. Nonetheless, the extent of company involvement in these processes is unclear and will probably affect political choice making. Understanding the general course of this as both an enabler or barrier to assembly web zero is important sooner or later. |
| Political | P5: Polarising belief in authorities and establishments | In 2022, the ONS discovered 35% of the inhabitants said that they belief the nationwide authorities, though completely different ranges are reported in numerous companies supplied by authorities. When folks don’t belief that choices are being made with their pursuits at coronary heart, they’re much less more likely to be accepting of coverage change. Due to this fact, polarised belief within the authorities, significantly throughout completely different sections of society, creates uncertainty in regards to the extent that change can occur because of web zero insurance policies. |
| Political | P6: Fractiousness of geopolitics | The UK’s geopolitical alliances are more and more essential within the context of ongoing conflicts, risky vitality costs and the impacts of local weather change the world over. This context drives uncertainty in how efficient multilateralism may be and will affect the implementation of worldwide decarbonisation agreements (positively or negatively) relying on the fluctuating geopolitical state of play. |
| Financial | Ec1: Macro-economic stability and progress | A rising financial system can drive manufacturing and consumption of extra items and companies, and rising family incomes are related to elevated ranges of journey. Though the precise affect on vitality demand and emissions will depend upon how rapidly vitality and emissions intensities are falling, extra progress will imply extra vitality demand, all else equal. However, financial progress can be related to funding and technological innovation, each of that are wanted to satisfy web zero. The OBR has tended to forecast decrease long-term progress for the reason that 2008 monetary disaster, which has been ‘baked into’ web zero pathways. The strain between this assumption and a want to extend financial progress leads to unsure implications for emissions into the long run. |
| Financial | Ec2: Relative prices of ‘making the inexperienced selection’ | The ‘inexperienced hole’ describes the hole between shoppers’ said intention to behave sustainably and their precise behaviours, usually because of the perceived or precise price of creating a sustainable selection. A wide range of components affect this, reminiscent of rising prices, inflation, and ease of entry/use. It’s unclear how modifications in these components will play out over the long run and affect societal traits in sustainable (‘inexperienced’) selections. This driver is targeted on components outdoors of presidency local weather coverage. |
| Financial | Ec6: Potential for elevated localisation of manufacturing and financial exercise | Pushed by provide chain disruptions through the COVID-19 pandemic, it has been estimated that the manufacture of £4.2 billion value of merchandise might be reshored by UK retailers between 2020 and 2021. A UCL evaluation highlighted a spread of things that might decide the affect of this on emissions, on each the provision and demand facet. For instance, UK home vitality use and emissions would probably be larger in a state of affairs with elevated reshoring relative to a state of affairs with decrease ranges of reshoring, however this might probably result in the UK’s general carbon footprint being decrease as a result of the usage of much less carbon-intensive vitality within the UK. There may be traits in the direction of localisation of financial exercise inside the UK, pushed by know-how and societal traits, and triggered by such shifts through the pandemic. |
| Societal | S1: Shifts in the place and the way folks reside – locations and housing | The ONS has discovered that household and family constructions have been continuously altering. For instance, there was a rise in single-person households and multi-family households. These modifications, together with how folks work (see under driver), can have a spread of impacts on emissions, sophisticated by the various vary within the kinds of housing they inhabit, which influences vitality effectivity. |
| Societal | S2: Altering nature of labor (together with distant working and altering sector combine) | Advances in automation and distant communication know-how, in addition to modifications spurred on by the COVID-19 pandemic, have modified the character of how and the place folks work. The altering price of vitality might also affect whether or not folks select to work from home or within the workplace. Ongoing uncertainty in these traits creates uncertainty in vitality use and emissions in associated sectors, reminiscent of buildings and transport. |
| Societal | S5: Actual and perceived unfairness of impacts of local weather change and paying for web zero | There’s a rising emphasis on learn how to mitigate the unequal impacts of local weather change. If web zero insurance policies disproportionately have an effect on the much less well-off and consumption will increase for the richest segments of society, this would possibly result in a backlash in opposition to such insurance policies. On the identical time, teams experiencing the worst results of local weather change would possibly put strain on governments to speed up emission reductions. |
| Technological | T1: Potential for web zero know-how price or efficiency modifications that transfer the aim posts | If low carbon applied sciences are adopted extra quickly than anticipated, reminiscent of as a result of decrease prices and efficiency enhancements, emissions might drastically cut back. Different applied sciences, reminiscent of geoengineering or direct air seize options, might additionally change authorities priorities in tackling local weather change. Nonetheless, it’s unsure (each on the demand and provide facet) the extent to which these modifications will happen, and whether or not they are going to be balanced out by different components each home and internationally. |
| Technological | T3: Use of linked and autonomous automobiles (CAVs) | Consultants predict that new cars could have autonomous capabilities underneath most circumstances inside 10-20 years. Automation facilitates the adoption of energy-saving driving practices and modifications in automobile design that allow emissions reductions. Nonetheless, heavy uptake of CAVs might enhance demand for journey by automotive, together with by non-drivers. There’s additionally uncertainty over their impacts on reconfiguration of streetscapes and the impact this might have on public transport and lively journey choices. |
| Technological | T4: Use of synthetic intelligence in vitality methods and throughout the financial system | Rising deployment of AI in electrical energy methods might optimise energy grids and enhance vitality effectivity, thereby lowering emissions. Nonetheless, powering and coaching AI within the first place is vitality intensive, and there’s appreciable societal scepticism of AI, elevating the query of how this pressure will probably be balanced to optimise vitality effectivity with public belief. |
| Authorized | L2: Potential circumstances of local weather change litigation | The cumulative variety of local weather change-related litigation circumstances has greater than doubled from 2015 to 2022. Strategic litigation that targets governments, companies and monetary actors is on the rise. More and more, litigation is used as a software to encourage a ‘simply transition’, but in addition as a method for fossil gasoline corporations to litigate in opposition to governments. Relying on the supply, quantity and worth of those litigations, the affect on authorities actions and societal emissions might be substantial. |
| Authorized | L3: Monetary prices for emissions | Civil penalties issued to companies by the Setting Company for non-compliance with local weather change laws elevated from £1.4 million to £2.1 million between 2018 and 2021. UK carbon credit have been rising for the reason that UK Emissions Buying and selling Scheme (ETS) began and are retailing at the next price than these within the EU ETS. All else equal, this would possibly enhance the monetary incentive for corporations to cut back their emissions, however it isn’t recognized to what extent this might occur, or if they might flip to offshore emission will increase as an alternative. |
| Authorized | L4: Adjustments to the worldwide carbon accounting regime | As of 2019, the UK is the largest web importer of carbon dioxide emissions per capita within the G7. , Had been the worldwide accounting regime to alter considerably it might result in modifications in how nationwide insurance policies have to answer completely different sources of emissions. |
| Environmental | En2: Improvement and greening of habitable cities | A pattern in the direction of inexperienced and habitable cities is being seen in an effort to facilitate climate-friendly city areas. Rising city tree cowl, for instance, improves resilience to local weather change and improves perceived aesthetics and liveability of neighbourhoods. Enhancements in metropolis infrastructure additionally encourage lively journey and discourage automotive use. Nonetheless, it stays to be seen how widespread these developments will probably be within the UK and the way important an affect they’ll have on the behaviour of metropolis residents. |
| Environmental | En3: Affect of environmental issues / excessive climate on property values and inside migration | Financial principle means that climate-related dangers (reminiscent of flooding and rising sea ranges) ought to lower property values in at-risk areas however, the connection has been discovered to differ relying on the frequency and severity of maximum occasions. How this relationship develops with the rising traits in excessive climate occasions and the fluctuating property market is unsure. |
| Environmental | En5: Pressure in how land is used – housing, farming, energy technology, afforestation, and so on | There’s more likely to be rising competitors between renewable vitality technology, growth, and urbanisation as a result of inhabitants growth, afforestation, peatland restoration, and rising crops for bioenergy. Nonetheless, there’s uncertainty over how this may play out and the way land will finally be used, significantly the place makes use of reminiscent of photo voltaic, onshore wind and housing face opposition from the general public being affected. |
Axis clustering and correlation evaluation
Following the workshop to establish crucial uncertainties, the web zero society challenge staff assessed widespread themes and relationships between the 18 axes of uncertainty and recognized two dominant axes of uncertainty which kind the premise of the 4 eventualities:
- Social cohesion and institutional belief: This axis is anxious with long-term uncertainty over the power of connections between completely different social teams together with the degrees of belief in establishments (together with companies, native/nationwide governments and intergovernmental organisations).
- Financial progress and technological progress: This axis is anxious with long-term uncertainty over the extent and stability of financial progress (mirrored in employment and productiveness) together with the tempo of growth and adoption of latest applied sciences.
The mapping of the 18 authentic axes of uncertainty is proven in Determine 10 under. These 18 had been then used as ‘sub-axes’ to assist present additional element and nuance to the eventualities.
Determine 10. Mapping of the sub-axes of uncertainty in opposition to the 2 dominant axes of uncertainty: social cohesion and institutional belief (high) and financial progress and technological progress (backside)


Determine 10 textual content
| Low social cohesion & institutional belief | Excessive social cohesion & institutional belief |
|---|---|
| The low social cohesion & institutional belief course is related to weak connections between completely different social teams and low belief in establishments | The excessive social cohesion & institutional belief course is related to sturdy connections between completely different social teams and excessive belief in establishments |
| Financial centralisation | Financial decentralisation |
| Companies act in opposition to targets and regulation | Companies agree and act on strict emissions targets |
| Folks really feel disproportionate impacts as a result of price distribution | Folks belief the prices of motion are pretty distributed |
| Elevated variety of authorized losses for the surroundings | Elevated variety of authorized wins for the surroundings |
| Much less inhabitants strain on city centres | Excessive city inhabitants pressures |
| Extra dispersed inhabitants | Extra concentrated city polarisation |
| Declining belief in authorities and its communications | Resurgence in belief in authorities and its communications |
| Targets of countries are in direct opposition | Frequent settlement between international locations on priorities for humanity and the world |
| Low occupancy non-public possession | Excessive occupancy sharing with communal possession |
| AI position is lively and controlling with larger threat | AI position is primarily informative/ advisory with sturdy oversight |
| Flawed participatory mechanism leading to no settlement on land use priorities | Nicely developed participatory mechanism to find out land use priorities |
| Low progress & tech progress | Excessive progress & tech progress |
|---|---|
| The low progress & technological progress course is related to low financial progress and slower technological progress | The excessive progress & technological progress course is related to larger financial progress and quicker technological progress |
| Excessive carbon transport is least expensive selection | Low carbon transport is cheaper and extra fascinating |
| Financial prices of CC are largely ignored in choice making | Financial prices of CC thought of are in choice making |
| Society depends on guide tech for day by day duties | Society depends on AI and automatic processes |
| Low and fluctuating productiveness progress | Excessive and regular productiveness progress |
| No funding into new builds, leading to badly insulated outdated housing inventory | Funding into new builds which are web zero compliant |
| Mercantilism (emissions) | International commons (emissions) |
| Unregulated growth planning with low funding in low carbon infrastructure and inexperienced areas | Sturdy growth management rising funding in low carbon infrastructure and inexperienced area |
| Unmet guarantees by know-how | Aggressive web zero know-how growth and adoption |
To include points of those 18 sub-axes into the eventualities in a constant and evidence-based method, the challenge staff explored analysis literature for the proof on the relationships between the 2 dominant axes and key themes represented inside the sub-axes.
First, specializing in the sub-axis of ‘institutional belief’, key themes embrace:
- Social cohesion: Proof means that social cohesion and institutional belief are extremely correlated, with researchers suggesting that institutional belief is a element of social cohesion. , , , Information additionally present that these two components usually are not simply correlated at society-level but in addition inside people; individuals who categorical larger institutional belief additionally understand there to be larger social cohesion. Due to the excessive correlation between these components, this can be very tough to disentangle them and, subsequently, they’ve been thought of collectively as one axis.
- Polarisation: Decrease belief and interplay between completely different teams is related to larger polarisation. They’re correlated and work together in numerous methods, with neither being the particular driver for the opposite. For instance, having stronger (extra polarised) viewpoints might imply that a person trusts fewer sources of data and, subsequently, solely depends on info inside an ‘echo chamber’. Nonetheless, the reverse might also be true, the place a person might discover themselves inside a sure restricted group (on-line or in actual life) and solely getting access to one viewpoint creates distrust of others and leads to larger polarisation.
- Interpersonal belief: There’s a correlation between people trusting establishments and them trusting others (with those that have larger ranges of institutional belief additionally having larger charges of interpersonal belief). Proof suggests that there’s a causal hyperlink, the place a rise in institutional belief leads to a rise in interpersonal belief, particularly the place there are constructive interactions with representatives of establishments (for instance, healthcare employees, cops or authorities officers).20,65, Analysis means that the reverse impact (the place larger interpersonal belief precipitates larger institutional belief) is both weak or unattested.65
- Isolation: Prolonged intervals of social isolation is related to decrease belief in establishments. Loneliness and isolation are additionally correlated with decrease interpersonal belief. , Proof suggests each that being remoted makes folks much less trusting of others, but in addition that being much less trusting (of establishments and people) might result in changing into socially remoted. It has additionally been discovered such results are reversable and that elevating folks’s belief of their neighbours can cut back loneliness and emotions of isolation.
- Urbanisation: Some analysis has proven that these dwelling in cities have larger institutional belief than these dwelling in rural areas and that when institutional belief is low, belief between teams (reminiscent of between city dwellers and rural dwellers) can be low. , , Causality is much less clear as it’s tough to determine whether or not larger belief results in larger urbanisation (with extra folks selecting to maneuver into cities) or whether or not extra folks dwelling in shut proximity will increase belief.
-
Decentralisation: Proof means that administrative and monetary decentralisation (the place tasks and/or revenues are cascaded to extra native/regional ranges of presidency) is related to larger ranges of institutional belief. ,
Specializing in the sub-axis of ‘financial progress’, key themes embrace: - Technological progress: Proof exhibits that financial progress and technological progress are carefully linked, with some analysis indicating that technological progress is essentially the most important driver for financial progress. , , Indications are that it’s tough, and certain counterproductive, to attempt to disentangle these two components.
- Urbanisation: An elevated proportion of the inhabitants of a rustic dwelling in cities and cities (versus in rural areas) is related to larger financial progress. , Proof exhibits that individuals shifting into city areas can enhance financial progress. This impact is taken into account to be pushed by economies of agglomeration (the place prices decline and advantages enhance when people and companies are introduced geographically nearer collectively) and by rising productiveness in city areas. , , , , Different associated components additionally contribute to the elevated financial progress correlated with urbanisation, reminiscent of funding in transport infrastructure. Nonetheless, the connection between urbanisation and financial progress is non-linear and proof means that larger results are probably for international locations with low city populations and smaller results are probably the place important urbanisation has already occurred.80, The scale of an city space additionally doesn’t straight predict the productiveness or financial exercise in that space; bigger cities usually are not essentially extra productive or affluent cities.86,87
- Inhabitants well being: Increased financial progress means extra money obtainable for companies reminiscent of well being. GDP (gross home product) per capita and life expectancy are correlated. The same correlation can be discovered between expenditure on healthcare and each life expectancy and wholesome life expectancy (common years spent dwelling in ‘good’ well being).90 Nonetheless, the connection between a nation’s GDP and its inhabitants’s well being is sophisticated and international locations with decrease GDP per capita have comparable well being outcomes to the UK. Proof has lengthy proven that a rise in GDP delivers the largest impact on life expectancy for the least economically developed international locations with diminishing returns in additional economically developed international locations. , Isolating particular person causal components for elevated life expectancy can be tough. There are quite a few components that usually co-occur with rising GDP that contribute to elevated well being and life expectancy, together with higher dwelling requirements, entry to medical improvements (in therapy, analysis and prevention), improved schooling and better incomes.90, , , , , Analysis exhibits that a person’s earnings straight impacts their general well being, together with their wholesome life expectancy. There’s additionally some restricted proof suggesting that earnings inequality inside a rustic can contribute to hostile well being outcomes. Due to this fact, though progress might make constructive well being outcomes simpler, we now have not handled decrease financial progress and higher well being as utterly incompatible in our eventualities.
- Vitality demand and GHG emissions: Elevated financial progress has traditionally been correlated with elevated vitality demand and ensuing GHG emissions inside a rustic. , , , Nonetheless, many international locations, together with the UK, have began to ‘decouple’ these components by findings methods to extend financial progress whereas stabilising or lowering vitality demand and GHG emissions.55, , As soon as web zero emissions has been achieved, GHG emissions will successfully be absolutely decoupled from financial progress, however on this case, society will nonetheless want to make use of a finite quantity of vitality, so the long run relationship between financial progress and vitality use stays unsure. Vitality demand within the UK has been lowering during the last decade and most projections assume demand will proceed to fall. Nonetheless, the extent of demand discount by 2050 will differ and depend upon a spread of things, together with financial progress. One of many key indicators used for financial progress is GDP. Increased GDP progress may be related to larger consumption; rising consumption can enhance GDP, but in addition having larger incomes (usually associated to financial progress) will increase consumption. , Nonetheless, the connection between consumption and GDP is weaker in excessive earnings international locations. , Due to this fact, the connection between future financial progress and future vitality demand (each within the UK and globally) can’t be assumed with out contemplating the kinds of exercise/know-how which are driving the financial progress and the vitality system getting used to help these actions.
Stage three: Situation narrative growth
Creating and refining state of affairs narratives
As a part of stage three, a second workshop was held with the identical group of contributors, who had been despatched descriptions of how the 2 axes had been mixed to supply 4 high-level eventualities. The descriptions had been preliminary sketches of every future world, aiming to offer sufficient element for contributors to have the ability to visualise what they could feel and appear like, however not a lot element that their creativity was constrained in serving to carry the eventualities to life by way of workshop workouts. Three workshop workouts had been designed to assist reply three questions:
- What would a 2050 society seem like in every state of affairs? How will folks reside, work, play and devour?
- What’s going to these eventualities imply for the best way we use vitality and sources in key emissions sectors (the constructed surroundings, journey and transport, work and {industry}, and meals and land use)?
- What are believable timelines for these eventualities between now and 2050? What must occur for us to finish up on this world?
The workshop generated a wealthy set of outputs with options from specialists for components to think about and potential interdependencies. These had been captured on an internet collaboration platform.
Finalising the eventualities
The ultimate step was to construct extra element into the state of affairs narratives, enhancing their plausibility and coherence as described above. This concerned the next levels:
- Producing the narratives: Situation narratives had been drafted to explain what every 2050 society would seem like and what the implications is perhaps for a way folks within the UK reside their lives. The narratives had been additionally delivered to life by way of illustrations.
- Figuring out names: Situation names had been chosen from workshop options to assist succinctly summarise every state of affairs and make it simpler to confer with them in subsequent workstreams.
- Comparative evaluation: Situations had been in contrast side-by-side on a spread of variables of curiosity to make sure they had been sufficiently completely different from each other and serving to to discover completely different coverage points.
- Consulting stakeholders: Key stakeholders inside and outdoors authorities had been consulted on the drafts to make sure the outputs appropriately mirrored the workshop contributors’ views and tackled the problems the eventualities had been anticipated to discover.
- Balancing constructive and unfavourable points: Work was undertaken to make sure the narratives and state of affairs names had been comparatively impartial and included a mixture of constructive and unfavourable points. This was partly to reinforce plausibility. It was additionally to make sure that all of the eventualities create comparable ranges of curiosity. Ideology and particular person preferences might make sure eventualities extra interesting to some people, however nobody state of affairs is meant to be ‘preferable’ or ‘higher’ than another.
The ultimate state of affairs narratives are offered within the subsequent chapter.
Stage 4: Vitality system modelling
This part offers a high-level overview of the modelling stage, with additional particulars supplied in Chapter 3 (modelling inputs abstract), Chapter 4 (outcomes), and Annex 4 (full modelling inputs).
The modelling framework
The qualitative state of affairs narratives give a sign of what a future UK society might seem like by 2050. The challenges in attaining the web zero goal differ by state of affairs and this implies every state of affairs has a definite vitality system that meets the wants of its society. To translate the eventualities into fashions to discover the implications for vitality, land and different sources, the web zero society challenge staff labored with modellers from the Centre for Analysis into Vitality Demand Options (CREDS).
The CREDS modelling framework’s depth, breadth and overlap with authorities fashions made it an appropriate software for representing the web zero society eventualities. The CREDS modelling framework (Determine 11) contains 4 sectoral fashions (Desk 2).8 The UK TIMES mannequin integrates these right into a UK-wide vitality system. The fashions have been harmonised by way of constant high-level assumptions, reminiscent of future modifications in inhabitants, financial progress, and family dimension (various by state of affairs). As well as, interactions between the sectors have been captured by way of evaluating demand profiles inside particular sectoral fashions. For instance, manufacturing ranges in every state of affairs is dependent upon the quantity of building exercise within the constructed surroundings and the variety of automobiles manufactured to be used within the journey and transport sector.
Determine 11. CREDS modelling framework

Determine 11 textual content model
| Step | 1. Improvement of a state of affairs narrative supplied to the modelling groups | 2. Sector stage modelling counting on essentially the most applicable construction for every sector | 3. Identification of inter-linkages | 4. Integration right into a central modelling system | 5. Coherent eventualities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motion | Contemplating components reminiscent of digitalisation, sharing & round financial system, vitality effectivity, wholesome society, environmental consciousness, globalisation, work & automation | Fashions used: •Work and industry- UK MRIO •Journey and transport – TEAM UK •Non-domestic constructed surroundings– TEAM UK •Meals and land use – UK MRIO •Home constructed surroundings – Nationwide Family Mannequin | For instance, home constructed surroundings impacts: •Non-domestic constructed surroundings •Journey and transport •Work and {industry} Non-domestic constructed surroundings impacts: •Home constructed surroundings •Work and {industry} Work and {industry} impacts: •Journey and transport Journey and transport impacts: •Work and {industry} Meals and land use impacts: •Land use (bespoke evaluation) •Work and {industry} | All 5 fashions combine into UKTM | 4 eventualities which are internally constant and have a transparent widespread narrative: •Atomised •Metropolitan •Self-preservation society •Sluggish lane |
Desk 2. Fashions used for every of the sectors
| Modelling focus | Mannequin |
| Total vitality system | UKTM (UK TIMES mannequin) |
| The constructed surroundings | UK NHM (Nationwide Family Mannequin) and a bespoke non-residential buildings mannequin |
| Journey and transport | TEAM-UK (Transport Vitality Air Air pollution Mannequin for UK) |
| Work and {industry} | Hybrid UK MRIO (Multi-Regional Enter Output mannequin) |
| Meals and land use | Hybrid UK MRIO (Multi-Regional Enter Output mannequin) |
Translating state of affairs narratives into fashions
The state of affairs narratives present a high-level description of every believable future together with options of what 4 completely different sectors (the constructed surroundings, journey and transport, work and {industry}, and meals and land use) might be like in 2050. Utilizing these qualitative descriptions as a place to begin, the web zero society challenge staff labored with modellers to develop a set of evidence-based mannequin inputs for every sector, various by state of affairs (Annex 4). Excessive-level assumptions relevant throughout the sectors, reminiscent of financial and inhabitants progress, had been additionally outlined for every state of affairs, drawing on completely different projections from the Workplace for Price range Accountability and the Workplace for Nationwide Statistics. , The sectoral inputs had been used to run sectoral fashions. These fashions, alongside the pre-defined high-level assumptions, had been fed into the UK TIMES Mannequin (UKTM). UKTM is a technology-rich cost-optimisation mannequin of the UK vitality system developed by UCL and BEIS for decarbonisation eventualities.
The quantitative inputs for the sectoral fashions and the high-level assumptions by state of affairs are offered alongside the state of affairs narratives within the following part (Chapter 3). The parameters include a set of assumptions for every of the 4 sectors described earlier, in addition to cross-cutting macro-economic assumptions that affect a number of sectors. For instance, modifications in family dimension and earnings have an effect on: automotive possession, demand for housing, and the composition of diets. 4 sector-specific teams of parameters had been recognized within the state of affairs narratives as qualitative components that would probably be translated into quantitative inputs for modelling. Not all qualitative assumptions had been finally represented within the fashions (as a result of they didn’t match into the desired fashions or there was a scarcity of sturdy proof obtainable to quantify these components appropriately). Nonetheless, the total set thought of are listed under.
Every parameter might be set at one in all 5 ranges: low, medium-low, medium, medium-high, and excessive. The parameters for every state of affairs had been:
- Cross-cutting: 1) Progress in GDP per capita: fee of change within the UK’s gross home product divided by its inhabitants. 2) Family dimension: the common variety of people dwelling in a UK family. 3) Family disposable earnings: the common earnings per family after taxes and different deductions. 4) Variety of households: the full variety of households within the UK.
- Constructed surroundings: 1) Floorspace per particular person: the UK’s constructing ground space divided by its inhabitants. 2) Residence working: the usage of computer systems to work remotely reasonably than from the workplace, rising vitality use per family, expressed as whole variety of enterprise journeys. 3) Insulation and vitality effectivity: measures to forestall warmth loss from a constructing and cut back vitality use per family for a given vitality service reminiscent of area heating. 4) Information processing demand: use of computing significantly by way of knowledge centres rising whole ultimate vitality demand. 5) One particular person households: the variety of households occupied by only one particular person.
- Journey and transport: 1) Worldwide journey and aviation: journey that crosses the UK borders expressed in journeys per capita and journey lengths. 2) Digital interactions: communication by way of the usage of distant and digital media, ensuing within the general discount in motorised miles per particular person, expressed as proportion lower in journeys per capita. 3) Autonomous automobile uptake and use: the speed of adoption of autonomous automobiles in addition to their occupancy, their dimension, and whether or not automobiles are shared. Increased uptake can enhance journey size, as a result of decrease prices, and likewise affect automobile dimension and occupancy, relying on how every society is probably going to make use of the know-how. 4) Energetic existence: methods of dwelling that contain a number of bodily exercise reminiscent of biking and strolling, lowering motorised miles per particular person, expressed as a shift in distance travelled from x to y modes, by journey size class. 5) Shared journey choices: sharing of transportation by a bunch of individuals, mirrored in automobile occupancy charges, expressed as a shift in distance travelled from x to y modes, by journey size class. 6) Urbanised populations: the variety of folks dwelling in cities, which impacts journey size and mode share.
- Work and {industry}: 1) Sharing financial system: a system the place sources reminiscent of tools, automobiles and land are shared amongst people, lowering the share of producing within the UK’s GDP. 2) Make do and mend: sustaining the situation of products in order that they’re in use for so long as potential, lowering the share of producing within the UK’s GDP, expressed as product longevity. 3) Reshoring of producing: returning the manufacturing of products again to the UK, mirrored as an elevated share of producing in home GDP accompanied by lowered imports. 4) Automation: use of digital applied sciences to regulate equipment with out, or with much less, human enter (this parameter was not used within the modelling). 5) Useful resource consumption: the nation’s use of sources (reminiscent of vitality, water and supplies) divided by the nation’s inhabitants. 6) Rebound results: behaviours rising in response to energy-saving measures that negate or cut back these vitality financial savings (this parameter was not used within the modelling).
- Meals and land use: 1) Meat consumption: modifications within the quantity of meat consumed as a proportion of whole day by day energy. 2) Reliance on meals imports: the power of the UK’s personal meals manufacturing to satisfy home demand for meals, measured as the worth of meals manufacturing divided by the worth of meals consumption. 3) Various proteins uptake: alternative of pink meat with cultured equivalents, measured because the market share of cultured meat. 4) Afforestation: the annual fee of tree-planting. 5) Greenfield growth: property building on beforehand undeveloped land (this parameter was not used within the modelling). 6) Meals waste: the quantity of discarded meals that was in any other case appropriate for consumption expressed as proportion change within the quantity of meals wasted (of the waste that’s avoidable).
The total set of modelling inputs by sector and state of affairs, together with a rationale for a way the assumptions differ by state of affairs, is out there in Annex 4. Examples of how levers had been set inside every sector are supplied in tables all through Chapter 3.
Along with concerns for particular person sectors, we used qualitative methods pondering maps to discover interactions between sectors to make sure the eventualities had been represented as coherently as potential. Extra element on that is supplied on the finish of Chapter 3.
All through the modelling course of, high quality assurance procedures had been adopted to test for errors and be certain that modelling inputs and outputs had been appropriate and supported by specialists. The method included conferences with authorities officers with experience in particular sectors to evaluate levers and assumptions, discussions with authorities analysts to pick applicable state of affairs assumptions (reminiscent of financial progress and end-use calls for), and each inside and exterior critiques of modelling assumptions and outputs.
We’ve got carried out the modelling train utilizing state-of-the-art and technically sturdy instruments and strategies, utilized by each main educational teams and authorities departments, however as with all modelling train there are some limitations and points that might be accounted for in future work. As a key instance, one limitation is that know-how price reductions are the identical throughout all eventualities and usually are not pushed by elevated uptake, regardless of there being proof of this, not less than on the international stage. That is mentioned additional in Chapter
3. Our futures
What would possibly life within the UK be like in 2050? What are the implications of various futures for 4 key sectors in society (the constructed surroundings, journey and transport, work and {industry}, and meals and land use)? How would possibly occasions over the subsequent few many years have an effect on the trail to web zero? This part goals to reply these questions by describing and illustrating the 4 web zero society eventualities. It units out the eventualities in narrative kind, which may help the reader conceptualise these completely different believable futures. These narratives, and the implications mentioned within the subsequent chapter, may help coverage makers and shapers anticipate the completely different expectations, attitudes, and behaviours of the long run UK inhabitants.
3.1 Introduction
As mentioned within the earlier part, the web zero society eventualities had been generated to create 4 believable futures spanning two axes:
- Social cohesion and institutional belief: This axis is anxious with long-term uncertainty over the power of connections between completely different social teams together with the degrees of belief in establishments (together with companies, native/nationwide governments and intergovernmental organisations).
- Financial progress and technological progress: This axis is anxious with long-term uncertainty over the extent and stability of financial progress together with the tempo of growth and adoption of latest applied sciences.
A abstract of the 4 eventualities that had been developed are proven in relation to those axes under in Determine 12. You will need to word that these positions throughout the 2 axes had been a place to begin for creating the eventualities; every potential future encompasses a wider vary of crucial uncertainties (extremely essential however extremely unsure potential future modifications) so the illustration under is a simplified two-dimensional plot of a extra advanced multi-dimensional area.
3.2 Situation summaries
Beneath are narrative summaries of the eventualities adopted by visible representations of ranges of progress for key points of society for every state of affairs.
Determine 12. Abstract of the 4 web zero society future eventualities

The textual content from Determine 12 is laid out under:
-
The atomised society: Technological change has fuelled progress. Particular person freedoms are prioritised, with folks capable of get pleasure from new experiences enabled by know-how. Nonetheless, extra wealth has been amassed by the richest and society is split alongside earnings traces; the wealthy reside in protected bubbles and the poor are extra uncovered to the consequences of local weather change.
-
The self-preservation society: financial progress and technological progress have didn’t reside as much as expectations for wealthy and poor alike. Folks do this they should get by, usually utilizing conventional strategies and out-dated know-how. Society is fragmented into many various teams. Some are extra comfy with the sluggish tempo of change, significantly older and rural communities.
-
The sluggish lane society: Financial and technological progress are sluggish which means there’s much less cash to put money into helpful infrastructure and restricted new know-how obtainable. Nonetheless, with excessive ranges of social cohesion and institutional belief, persons are prepared to contribute extra to enhance their communities. There’s additionally a rising tradition of restore, recycling and the sharing financial system.
-
The metropolitan society: Financial progress and technological change have delivered enhancements in dwelling requirements for many, by way of inequalities stay. Geography shapes identification, with sturdy communities within the metropolis areas which have pushed progress. There’s rising resentment in rural populations as they see funding directed in the direction of city areas however restricted funding within the countryside.




| Atomised society | Metropolitan society | Self-preservation society | Sluggish lane society | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue progress for the richest | Excessive | Medium-high | Medium-low | Low |
| Revenue progress for the poorest | Medium-low | Medium-low | Low | Medium-low |
| Availability of superior tech | Excessive | Excessive | Medium-low | Low |
| Availability of web zero tech | Medium-high | Medium | Medium-low | Low |
| Belief inside the UK | Low | Excessive | Low | Excessive |
| Belief globally | Medium-low | Excessive | Low | Medium-high |
| Inhabitants in city areas | Low | Excessive | Medium-low | Medium-high |
| Inhabitants in rural areas | Medium-high | Low | Low | Excessive |
| Inhabitants in suburbs | Medium-high | Low | Medium-high | Medium-low |
| Localisation of financial exercise | Low | Medium-high | Medium-low | Excessive |
| Reshoring of producing | Excessive | Low | Medium-low | Low |
| Ranges of automation | Excessive | Medium-high | Low | Medium-low |
3.3 Full eventualities
This part contains the 4 full eventualities combining each the qualitative narratives and the quantitative parameters derived from these narratives.
Situation narratives
The narratives for every state of affairs embrace an outline, an outline of what UK society might be like in 2050 in that state of affairs, and an exploration of how completely different sectors (the constructed surroundings, journey and transport, work and {industry}, and meals and land use) might have developed by 2050. Every state of affairs additionally contains some visualisations of the parameters derived from the narratives for every of those 4 sectors.
As talked about beforehand, the eventualities had been developed to satisfy three core ideas:
- Believable: Situation finish states ought to really feel like they might occur by 2050 and the long run modifications depicted in a person state of affairs ought to really feel coherent. This requires narratives to think about what would possibly occur between now and 2050.
- Stretching: Situations ought to really feel stretching and, in some circumstances, uncomfortable, diverging from what coverage makers think about to be the ‘enterprise as typical’ trajectory.
- Reply essential questions: The eventualities must be designed to assist reply key questions for presidency, reminiscent of:
- What are the potential vary of outcomes that would come from recognized crucial uncertainties and the way can these be taken under consideration throughout planning?
- What if society begins to evolve in a method that will increase (or decreases) vitality demand considerably past present assumptions? What would the implications be for assembly web zero if that pattern continues?
- What do choice makers who’re contemplating supporting a selected societal change have to know in regards to the wider advantages and prices?
- What will probably be wanted within the wider system to make sure that potential unfavourable impacts of any transitions are abated and constructive impacts augmented?
To satisfy these ideas and to assemble a sensible view of potential future societies, the narratives are intentionally broad and embody areas outdoors of the everyday decarbonisation coverage areas. Because the societal change proof evaluate (Annex 2) signifies, taking a large view of a posh system may help to establish parts that would have a big, and typically surprising, affect. Some societal modifications outdoors of these sometimes receiving best focus (often vitality technology, manufacturing and transport) might have main implications on emissions. For instance, an increase in cryptocurrency might end in larger vitality calls for, if present designs for them stay.
As these eventualities are designed to stretch and take a look at coverage pondering, they’re intentionally excessive and divergent. The eventualities are neither predictions nor aspirations. It’s probably that future UK society will comprise a mix of parts from throughout the eventualities. There are additionally many permutations that haven’t been offered which are equally believable and certain. All of the eventualities described are illustrative of potential future societal modifications. Though there are typically some options for what might trigger the modifications being described, these usually are not thought of particular nor the one method such a change might happen.
Home and worldwide occasions can affect society and the chance of reaching web zero targets. The eventualities under don’t depend on the prevalence (or lack of) particular crucial occasions to achieve their 2050 finish state. Nonetheless, there are such occasions that would expedite the trail in the direction of a future just like these offered within the eventualities and different occasions that would make a number of the eventualities implausible. Moreover, every state of affairs varies in how resilient it’s to shocks (reminiscent of excessive climate occasions or provide chain disruption).
Situation notes
As talked about beforehand, the eventualities developed for this report deal with two major axes (social cohesion and institutional belief and financial progress and technological progress) however mix different recognized crucial uncertainties to create a richer and extra cohesive future world. For the total set of drivers of modifications and axes of uncertainty recognized for this report, see Annex 3.
We created every state of affairs by assuming completely different theoretically potential mixtures of axes. These eventualities don’t characterize the one potential mixtures of axes, nor are they at all times essentially the most believable. As a substitute, they’re designed to be very completely different from one another, so are helpful for testing our assumptions. Extra optimistic eventualities, the place all societal modifications are constructive, are potential. Nonetheless, we now have intentionally included some points in every state of affairs that most individuals will discover unfavourable to make them helpful to stress-test coverage in opposition to.
At the beginning of every state of affairs narrative, we offer some element on the uncertainties included and the how we selected the mixtures included. Importantly, these eventualities usually are not predictions and make no claims about what might trigger the societal modifications outlined. As a substitute, they’re an train in asking: what if X and Y had been true in 2050? There isn’t any ‘proper reply’ inside the eventualities, as an alternative they illustrate the impacts of various potential modifications.
Embedded inside the state of affairs narratives are a sequence of infographics exhibiting how key parameters change in every state of affairs relative to the opposite eventualities (low, medium-low, medium, medium-high, or excessive). In some circumstances, the place quantification is easy and values are simple to specific (as a mean, proportion share, or proportion progress by 2050), we now have supplied the numbers utilized in our evaluation. That is supplied for the comfort of readers eager to grasp in additional element what assumptions have been made whereas they’re studying these narratives, however a extra complete set of data on these parameter values is supplied in Part 3.5 and in Annex 4.
The atomised society
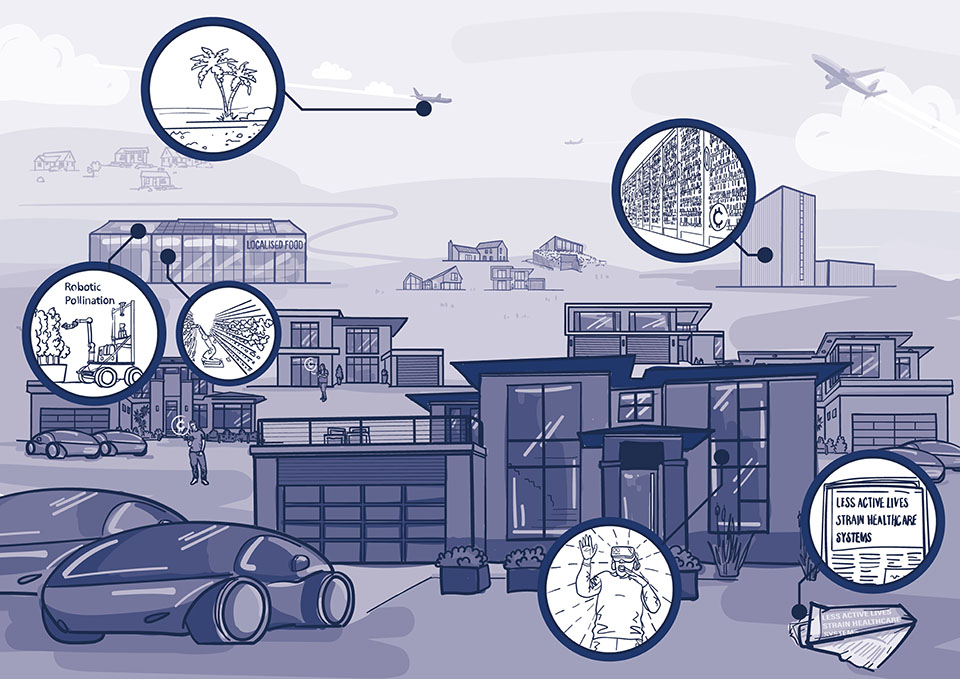
How we developed this state of affairs
We created this state of affairs by assuming larger financial progress occurred concurrently decrease institutional belief and extra individualistic attitudes. The specialists who participated in our state of affairs growth workshops recommended that larger financial progress on this state of affairs might have been pushed by fast technological change and better consumption. Extra dispersed dwelling in bigger suburban properties might be in line with larger financial progress and households being extra separated from their native communities, significantly when mixed with use of superior digital communications platforms that permit folks to socialize from their house. Our specialists additionally felt that, whereas everybody was more likely to see some earnings progress, the decrease ranges of belief on this state of affairs had been extra more likely to be related to larger ranges of inequality, with diverging existence between low- and high-income households. When it comes to what this mix of axes means for vitality use, folks usually get pleasure from extra inexpensive items, companies and experiences (reminiscent of international journey) usually enabled by know-how. Individualistic attitudes imply persons are much less involved with any downsides of consumption.
Life within the atomised society
The UK has skilled a interval of financial progress, fuelled by technological innovation. For folks on larger incomes, life in 2050 is nice, however these with decrease incomes have been disproportionately affected by the impacts of local weather change. Those that are struggling financially categorical deep resentment in the direction of these with larger wealth. The inhabitants has grow to be extra broadly dispersed throughout city, suburban and rural areas as a result of larger digital connectivity. Persons are more and more dwelling in digital ‘bubbles’, which has lowered the number of people they encounter; this has created mutual suspicion between teams.
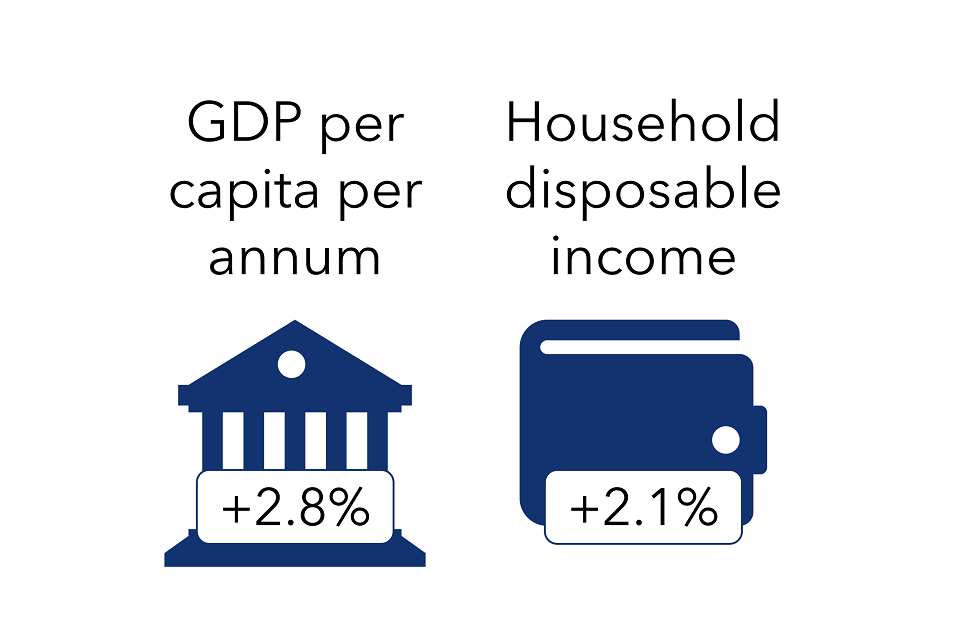
Dwelling circumstances have usually improved, however enhancements have been maintained on the expense of the surroundings. Reducing emissions just isn’t a precedence and, even when it had been, there is no such thing as a consensus on how to take action. This has resulted in excessive ranges of consumption, which have positioned a pressure on sources. Technological progress and customarily benign financial circumstances have led to improved dwelling requirements for the higher off (who account for the majority of vitality use) and the center courses. These on decrease incomes haven’t skilled the identical advantages and earnings inequality has elevated within the many years main as much as 2050. Different inequalities, together with regional inequality and digital inequality (unequal entry to and/or familiarity with know-how for some teams), additionally stay. Nonetheless, new know-how has pushed enhancements in public sector companies (together with the advantages methods, healthcare and social care). Digital literacy has additionally improved, with most people managing to maintain up with the fast tempo of change.
Society is spending extra time on-line and this has led to fragmentation and fewer lively existence, with those that are unable to afford to journey utilizing the immersive metaverse as a type of digital escapism. This has had some knock-on impacts on the general well being of the inhabitants, with extra sedentary existence and time spent on-line in digital environments impacting on each bodily (primarily cardiovascular and metabolic) and psychological well being, inserting pressure on healthcare methods, and impacting the productiveness of the workforce. Once more, the poorest in society are disproportionately affected, with these with larger wealth having the ability to entry therapies that enhance longevity.
Automation of labor has additionally been widespread, however the advantages of automation haven’t been distributed evenly, largely accruing to the homeowners of know-how reasonably than the entire workforce. Upskilling and retraining initiatives have principally didn’t maintain tempo with the march of automation, resulting in important ranges of precarity in work for the poorest.
Worldwide concerns: A breakdown in worldwide cooperation has led to faltering international local weather motion with states prioritising the safety of their very own societies and important infrastructure over international commons. This has in flip led to elevated ranges of worldwide battle, significantly round competitors for scarce sources and tensions of migration triggered by accelerated local weather breakdown within the international south. Inside this context of a scarcity of belief and worldwide cooperation, many inside society are blaming ‘the system’ (each governments and multinational corporations) for the dearth of equitable societal change.
Sectors
The constructed surroundings: The inhabitants has grow to be comparatively dispersed, with the wealthy more and more dwelling in bigger properties in self-contained ‘bubbles’ in suburban and rural areas. There has additionally been a rise in folks dwelling alone. There was some funding in new construct properties, which has led to discount in housing strain and improved affordability. Many individuals are working from house and spending extra time on-line, resulting in elevated demand for connectivity and knowledge processing infrastructure. Folks have usually been spending much less time of their native communities, leading to a sluggish decline in native facilities.
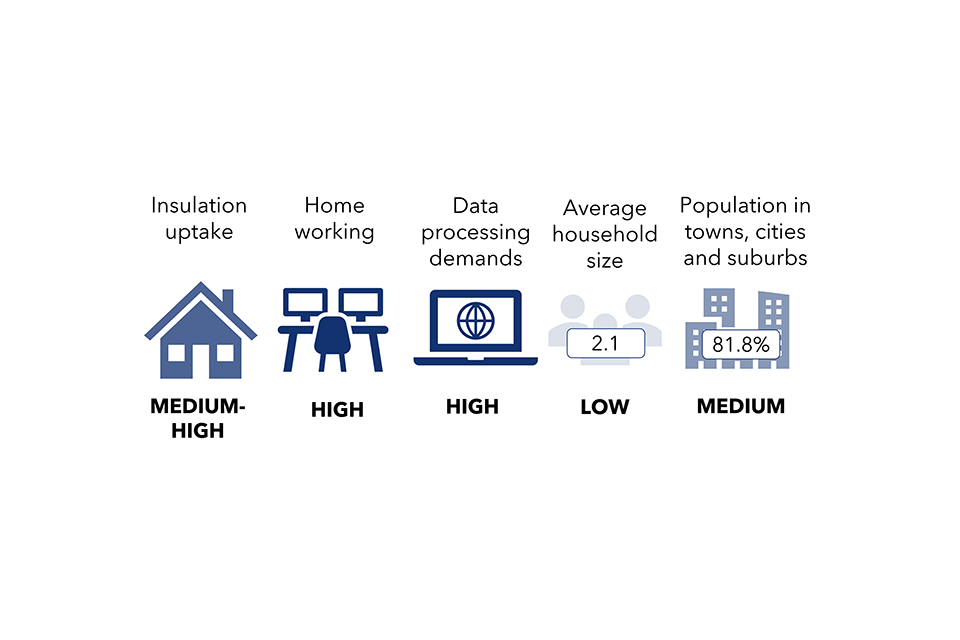
| Insulation uptake | Residence working | Information processing calls for | Common family dimension | Inhabitants in cities, cities and suburbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-high | Excessive | Excessive | Low (2.1) | Medium (81.8%) |
Journey and transport: Uptake of CAVs has been sturdy, significantly among the many wealthy. The non-public possession mannequin continues to dominate, with solely restricted traction achieved for shared journey. Public transport has improved considerably over time, significantly between areas by high-speed rail. Nonetheless, excessive fares have excluded the poorest from the community and competitors from CAVs means utilization just isn’t as excessive because it might be. Flying (for leisure, particularly) has grown, offsetting a number of the advantages of decrease carbon applied sciences in aviation. The wealthy are travelling additional afield, however poorer persons are exploring new locations in neighbouring international locations. Among the conventional ‘vacation within the solar’ locations of the 2020s have grow to be more and more unappealing as a result of excessive warmth.
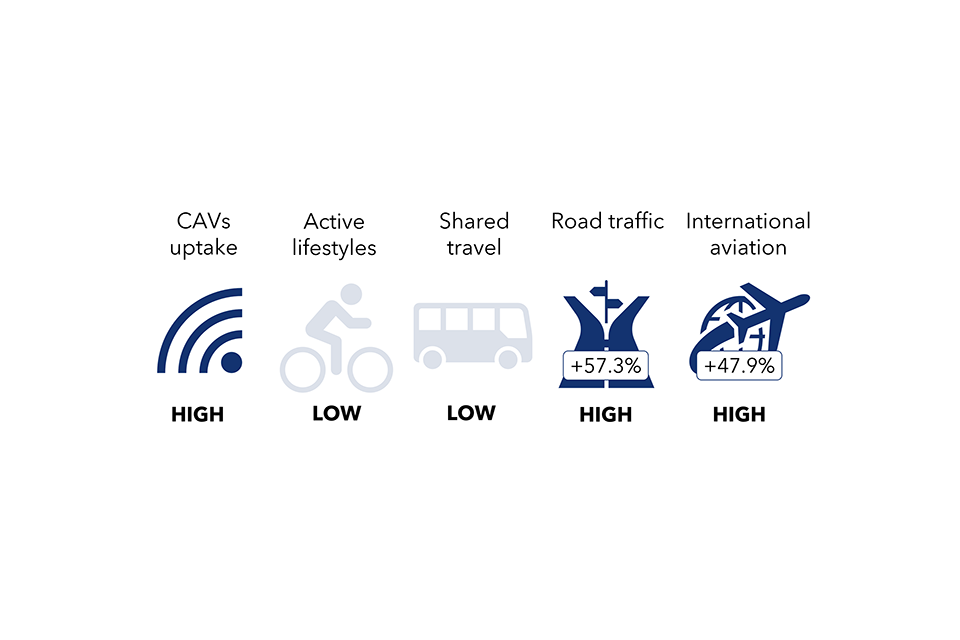
| CAVs uptake | Energetic existence | Shared journey | Street site visitors | Worldwide aviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excessive | Low | Low | Excessive (+57.3%) | Excessive (+47.9%) |
Work and {industry}: Though there’s higher administration of merchandise throughout their whole lifecycle, consumption has remained excessive and technological obsolescence stays. Partially, this is because of livid worldwide competitors to create the ‘subsequent large client tech’. It’s also attributable to folks changing into much less involved about throwaway tradition thanks to raised recycling options. Worldwide conflicts and progress in automation have led to some reshoring of producing. There’s a thriving financial system for items and companies in the actual and digital worlds, with cryptocurrencies enjoying a rising position amongst these with much less confidence within the international monetary system and central banks.
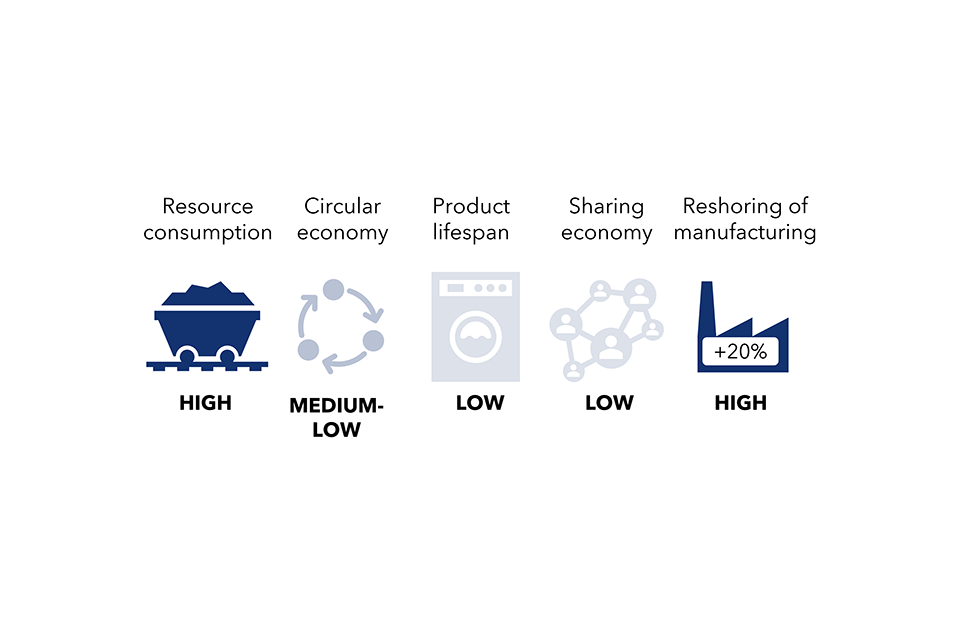
| Useful resource consumption | Round financial system | Product lifespan | Sharing financial system | Re-shoring of producing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excessive | Medium-low | Low | Low | Excessive (+20%) |
Meals and land use: Tech advances have ushered in larger dietary selections, together with for meat-free protein. Cultured meat is broadly obtainable and, after preliminary hesitance, has been broadly accepted by shoppers as a suitable different to farm-reared meat. In some wealthier city areas, vertical farming has been adopted to offer domestically grown meals. Environmental degradation has considerably impacted biodiversity and there’s much less productive land obtainable. Nonetheless, tech options, reminiscent of genome-edited crops or robotic pollination, have preserved some self-sufficiency in meals manufacturing.
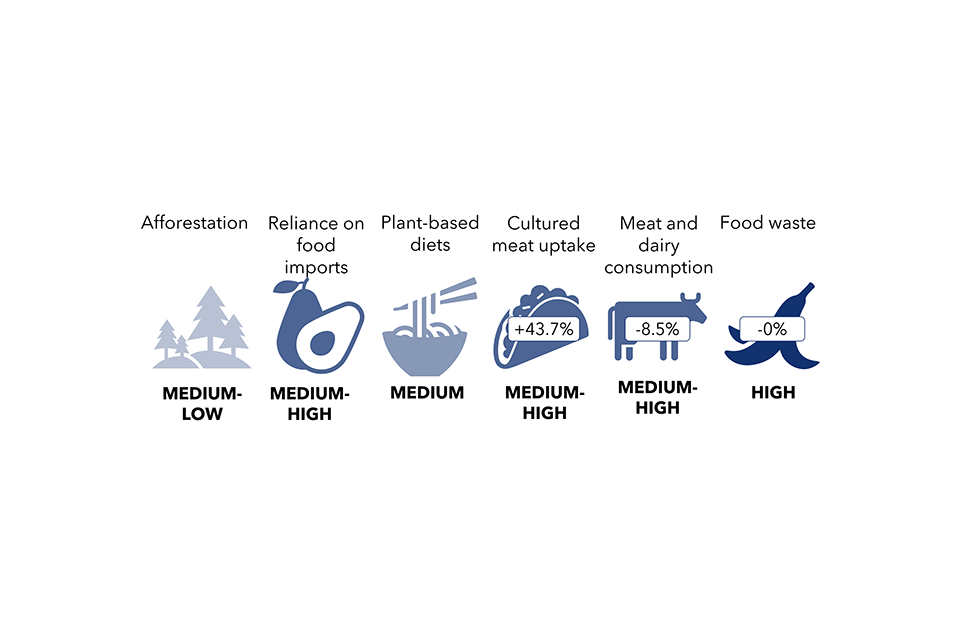
| Afforestation | Reliance on meals imports | Plant-based diets | Cultured meat uptake | Meat and dairy consumption | Meals waste |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-low | Medium-high | Medium | Medium-high (+43.7%) | Medium-high (-8.5%) |
Excessive (-0%) |
The metropolitan society

How we developed this state of affairs
We created this state of affairs by assuming larger financial progress, elevated availability of know-how, larger institutional belief, and larger social cohesion inside geographical areas all coincide in 2050. The specialists who participated in our state of affairs growth recommended that this might be a state of affairs by which dense, habitable cities thrive, offering each financial progress (by way of agglomeration) and a way of local people. Extra infrastructure could be wanted to help this city densification, however this funding could be supported by larger ranges of financial progress. Our specialists additionally recommended {that a} believable dynamic on this world might be these dwelling in rural areas feeling ‘left behind’, leading to a scarcity of cohesion between areas however excessive ranges of belief inside native communities. When it comes to what this mix of axes means for vitality use, there’s a pressure between the sustainable existence enabled by cities (reminiscent of low automotive use) and the upper ranges of consumption facilitated by larger incomes. This recommended that there could be a common desire for modifications to exercise which are facilitated by infrastructure or ‘behind the scenes’ processes (reminiscent of material-efficient provide chains), reasonably than folks selecting to devour much less.
Life within the metropolitan society
Financial progress and technological change have delivered enhancements in dwelling requirements for many, though inequalities stay. There’s a sturdy sense of neighborhood inside the rising, various city inhabitants and likewise inside rural areas. Nonetheless, there are divisions between these two communities, as rural populations resent the elevated funding for city areas (the place new infrastructure is assumed to have the largest financial affect), which isn’t matched by comparable funding within the countryside.
Via technological developments, focussed on effectivity, GDP progress has been more and more ‘decoupled’ from emissions, vitality demand and useful resource extraction. An agenda of infrastructure renewal has been largely realised, with important upskilling programmes to help the transition in the direction of ‘inexperienced financial system’ sectors and to deal with the impacts of widespread adoption of automation applied sciences throughout many industries. Nonetheless, the deal with building, larger ranges of disposable earnings and availability of thrilling new client applied sciences imply vitality consumption and materials use is comparatively excessive.
Centralised authorities makes use of well-regulated and totally examined synthetic intelligence to help choice making. Widespread perception that this makes choices fairer and extra impactful, alongside different efforts to enhance equality, has led to larger political engagement. Nonetheless, some older folks discover the fast tempo of change exclusionary.

There’s a higher stability between useful resource consumption and charges of replenishment. A lot useful resource discount is data-driven and automatic, making it simple for people to decide on merchandise that decrease their materials and carbon footprints. However this doesn’t take away the temptation to purchase extra merchandise (particularly these with well-publicised sustainable manufacturing and provide chains). This results in a rebound impact, with useful resource consumption initially dropping earlier than rising once more.
Worldwide societal concerns: This world is characterised by usually sturdy ranges of worldwide belief and collaboration round assembly local weather targets and accommodating these displaced by local weather impacts. States have labored in cooperation to drive and scale a spread of applied sciences to mitigate essentially the most extreme impacts of local weather change and minimise battle round scarce sources. There’s a sturdy and globalised financial system served by advanced international provide webs, with little reshoring of producing to the UK, however provide chains stay considerably fragile, fragmented, and susceptible to exterior shocks.
Sectors
The constructed surroundings: Apart from ongoing devolution to massive metropolis areas, choice making stays largely centralised. Funding is channelled in the direction of city areas to drive financial progress with important funding within the ‘greening of cities’, designed to permit easy accessibility to important companies near house. This attracts many to compact city dwelling, usually in smaller households, however these in rural areas really feel that they’ve been uncared for and are sometimes dwelling in older homes with much less entry to modernised companies and facilities. Most city and rural properties are served by good and efficient digital infrastructure, with some folks doing hybrid work from their properties and native hubs.
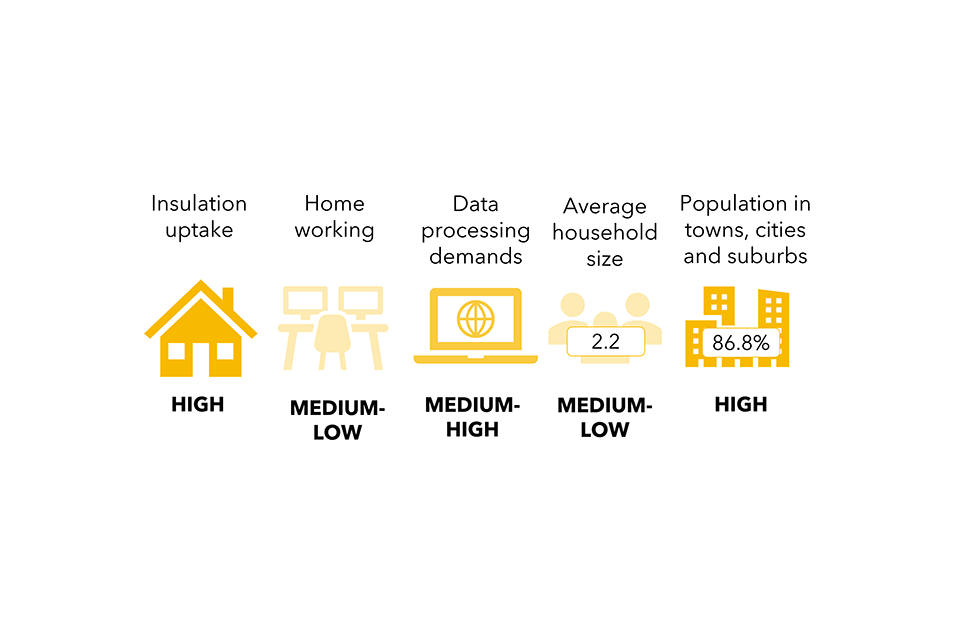
| Insulation uptake | Homeworking | Information processing calls for | Common family dimension | Inhabitants in cities, cities and suburbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excessive | Medium-low | Medium-high | Medium-low (2.2) | Excessive (+86.8%) |
Journey and transport: Funding in handy and low-cost micro-mobility and public transport encourages city dwellers to forgo brief automotive journeys. CAVs are broadly obtainable in city and rural areas and, though some non-public possession stays, they are typically used as on-demand shared companies for home journey. Flying continues to be used, principally internationally. Nonetheless, it’s much less financially aggressive and fewer socially acceptable for home journey. Zero carbon flying know-how has not too long ago grow to be obtainable however continues to be comparatively excessive price. There are higher built-in rail companies, making journey cheaper and simpler, though primarily inside or between cities. Distant working and telepresence know-how can be found and used broadly, however many individuals nonetheless worth face-to-face interactions in each work and leisure.
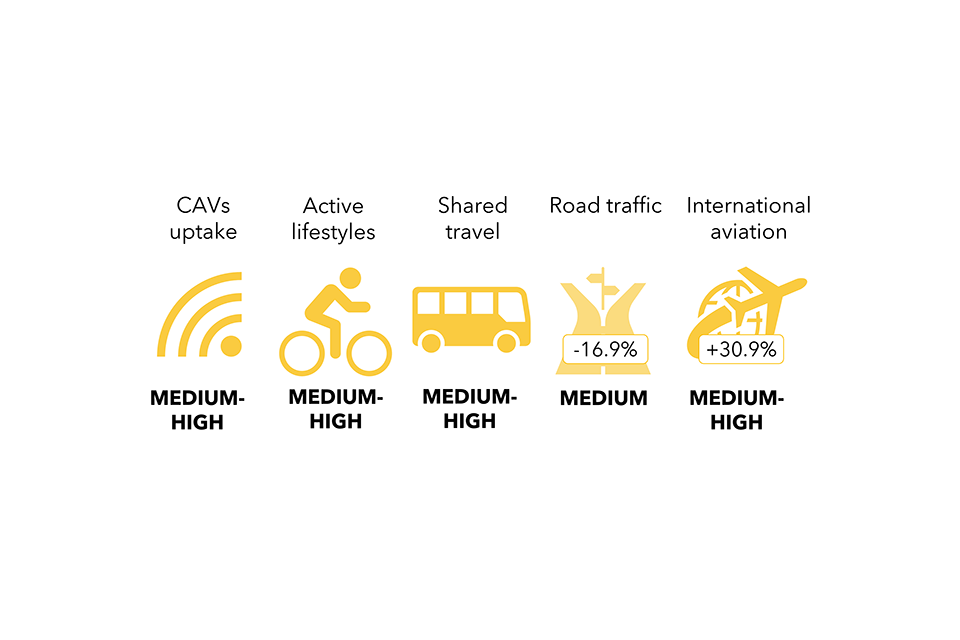
| CAVs uptake | Energetic existence | Shared journey | Street site visitors | Worldwide aviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-high | Medium-high | Medium-high | Medium (-16.9%) | Medium-high (+30.9%) |
Work and {industry}: Consumption continues to drive financial progress, through a mix of bodily merchandise and intangible companies. Though restore and mend tradition has not taken off, round financial system measures are broadly in place behind the scenes. Services and products are knowledge wealthy, and it’s potential to trace provenance and product lifecycles utilizing revolutionary know-how mixtures reminiscent of blockchains, AI and the web of issues, lowering the environmental impacts of continued consumption. AI know-how is now embedded throughout the financial system to drive effectivity in useful resource utilization and all new merchandise are required to account for full lifecycle useful resource and emissions implications. Folks don’t usually make consciously sustainable selections, however algorithms assist make ‘greener choices’ simpler.
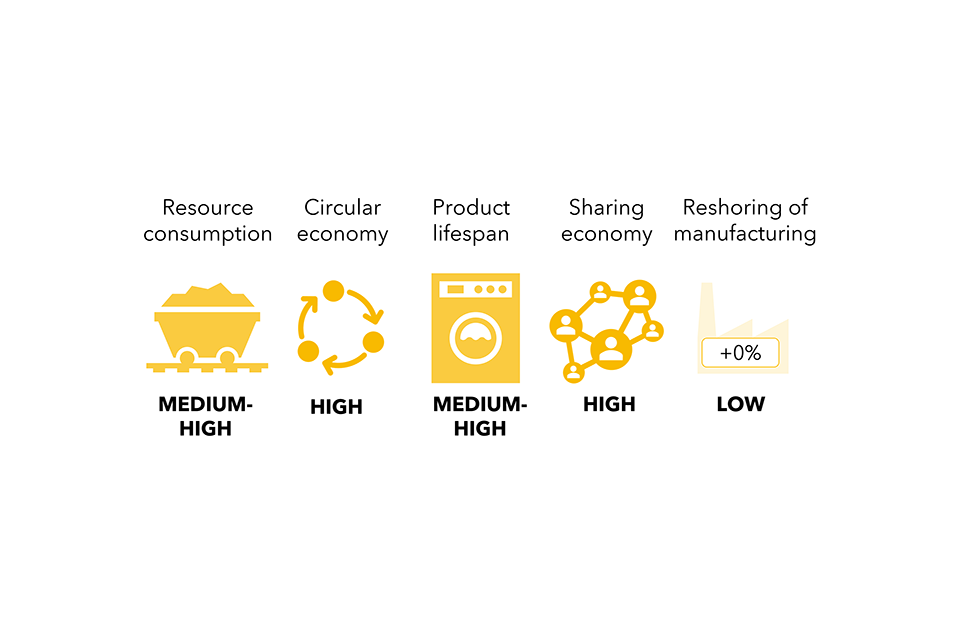
| Useful resource consumption | Round financial system | Product lifespan | Sharing financial system | Reshoring of producing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-high | Excessive | Medium-high | Excessive | Low (+0%) |
Meals and land use: A larger deal with defending the pure surroundings has supplied co-benefits, together with for public well being and the financial system (for instance, by way of will increase in ecotourism and larger availability of pure sources, reminiscent of water). Progress with rewilding has been blended, with tensions between supportive city elites and rural communities who really feel threatened by lack of what they see as ‘their’ property. Vital advances in agricultural tech, reminiscent of genome modifying and agricultural robotics, have led to reductions in land and pesticide use. Natural farming has additionally seen some progress with the mixture of low- and high-tech approaches bettering meals self-sufficiency. Diets have broadly adjusted for improved sustainability with elevated uptake of extra plant-based diets and, after preliminary public hesitancy, cultured meat. There are issues over the medium to long run implications of a shift to extra artificial diets, significantly round lack of micronutrients. Organically farmed meat is a uncommon, considerably unaffordable, luxurious merchandise. Many livestock farmers have discovered their companies are not worthwhile and have made use of reskilling programmes to maneuver into different careers.
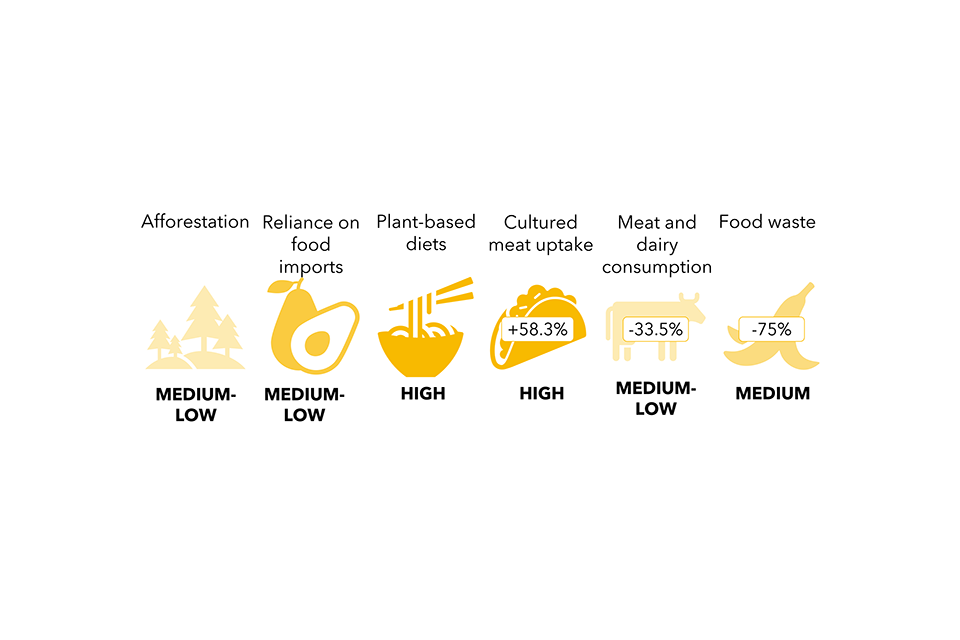
| Afforestation | Reliance on meals imports | Plant-based diets | Cultured meat uptake | Meat and dairy consumption | Meals waste |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-low | Medium-low | Excessive | Excessive (+58.3%) | Medium-low (-33.5%) | Medium (-75%) |
The self-preservation society
How we developed this state of affairs
We created this state of affairs by assuming decrease financial progress happens alongside decrease institutional belief and social cohesion. The specialists who participated in our state of affairs growth felt it was potential that the UK might fail to realize larger financial and technological progress than skilled not too long ago for numerous causes. Sooner or later, our specialists noticed this contributing to reductions in social cohesion and decrease belief in establishments. Though social cohesion general is low on this society, our specialists recommended that this might result in stronger bonds inside smaller teams and households, which might have sure advantages, reminiscent of for caregiving. In addition they felt that this state of affairs might have some positives for these inside society who might really feel overwhelmed by fast change, and {that a} state of affairs by which not a lot has modified since at present might be engaging to some, significantly some older folks. When it comes to what this mix of axes means for vitality use, consumption ranges could be more likely to keep comparatively excessive in a state of affairs reminiscent of this, with out broader societal modifications reminiscent of neighborhood infrastructure or technological efficiencies which may help consumption reductions.
Life within the self-preservation society
For the reason that early 2020s, there was low general progress and restricted technological development. Social divisions have emerged following a interval of political, societal and financial turbulence. Centralised governance dominates and there are areas that really feel disenfranchised. Voter turnout is low and politics has grow to be extremely polarised. Some have been interested in excessive political positions. Folks acquire a way of neighborhood and identification from these fragmented teams that they battle to seek out in wider society.
GDP progress continues to be prioritised as a key measure, however there’s a failure to realize it. There have been cycles of increase and bust, recessions and stagflation to deal with over three many years. Revenue distribution is just like that of 2020s with comparatively excessive ranges of inequality. There’s restricted general progress, so the wealthy haven’t grow to be vastly richer as everybody has seen their incomes squeezed.
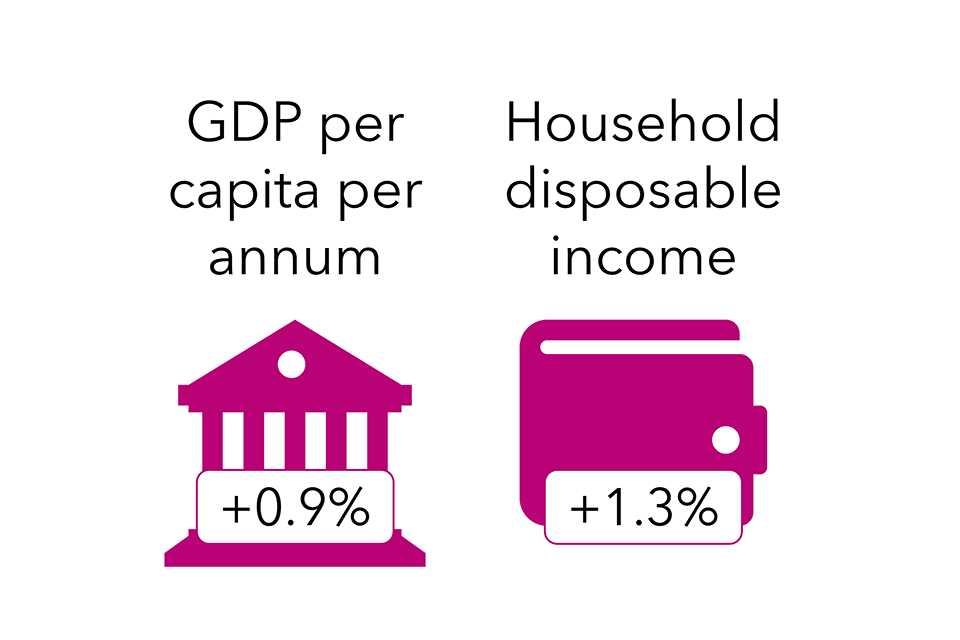
There was sluggish technological progress. For some in society, there was rising unease across the services of ‘large tech’ corporations. This was fuelled by rising incidents of knowledge breaches, fraud, misinformation, and different problematic on-line behaviours that characterised a lot of the 2020s and triggered more and more widespread backlashes through the 2030s. Synthetic intelligence is tightly regulated and has its makes use of rigorously managed following a sequence of high-profile circumstances of misuse, discrimination, and accidents. Some have deserted large tech in favour of smaller area of interest (and infrequently much less regulated) communication and collaboration platforms, which has in some circumstances elevated fragmentation and perception in conspiracy theories.
Whereas some assume extra extremist political candidates might carry change, others are opting to remain disconnected and reside their lives offline, particularly youthful generations, who’re disillusioned by perceived stagnation. Though the many years to 2050 have been difficult for society as a complete, the relative lack of radical change has felt extra comfy for some in older generations.
Worldwide societal concerns: Ongoing distrust and geopolitical and financial tensions between nations has acted as a brake on attaining the worldwide consensus on the safety of environmental commons. Many inside society are blaming multinational corporations for the dearth of equitable societal change. The UK stays reliant on imported items, however geopolitical tensions have resulted in a world protectionist financial system and provide chains are susceptible to exterior shocks. Though plans are in place to reshore manufacturing, this has up to now been restricted.
Sectors
The constructed surroundings: Excessive crime and lack of funding in infrastructure have made metropolis centres much less engaging, however the inhabitants within the suburbs round cities grows so the general city inhabitants stays excessive. The difficult financial backdrop has impacted the tempo of constructing new properties, with demand usually outstripping provide in lots of areas. Total, there are fewer folks dwelling alone than in earlier many years. Whereas older generations favor rural areas, youthful ones are more and more shifting to the suburbs. Though incipient, youthful generations are more and more choosing off-grid and self-sufficiency dwelling, and there was some enhance in cohabitation and multigenerational dwelling to make ends meet.
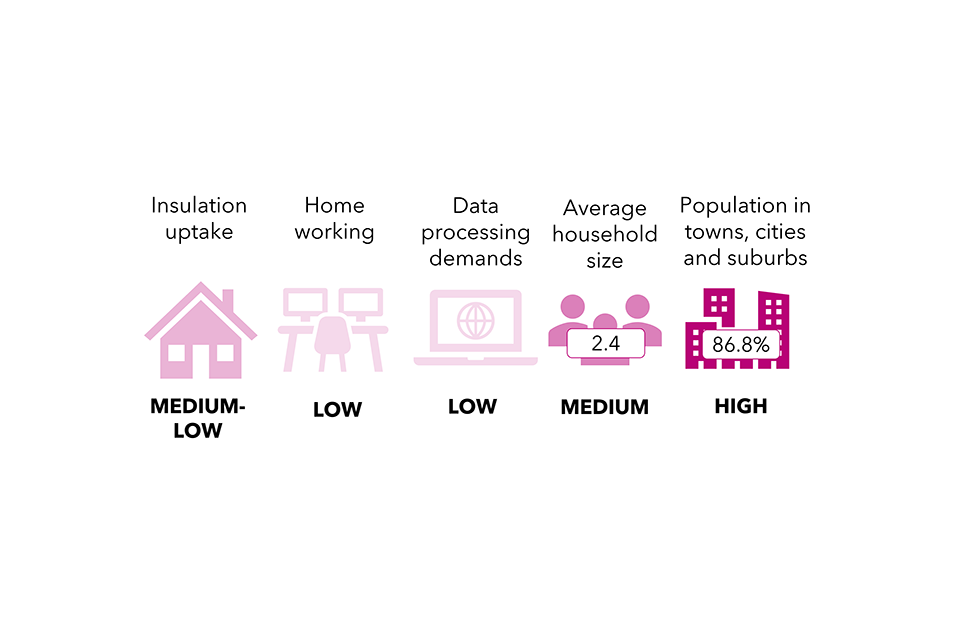
| Insulation uptake | Homeworking | Information processing calls for | Common family dimension | Inhabitants in cities, cities and suburbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-Low | Low | Low | Medium | Excessive |
Journey and transport: Transport choices are fragmented and disconnected outdoors of main cities. Inside cities, city transport is positioned underneath pressure by way of lack of funding. Some cities and cities have seen reasonable progress in low-tech transport infrastructure, particularly for strolling and biking as many extra residents have opted for these as their main technique of transport. This has primarily been pushed by folks making an attempt to decrease their price of dwelling. By 2050, CAVs have simply grow to be obtainable to the extra prosperous and personal possession stays the dominant mannequin. Flying has not been decarbonised and, though it stays engaging for these that may afford it, some persons are changing into more and more priced out.
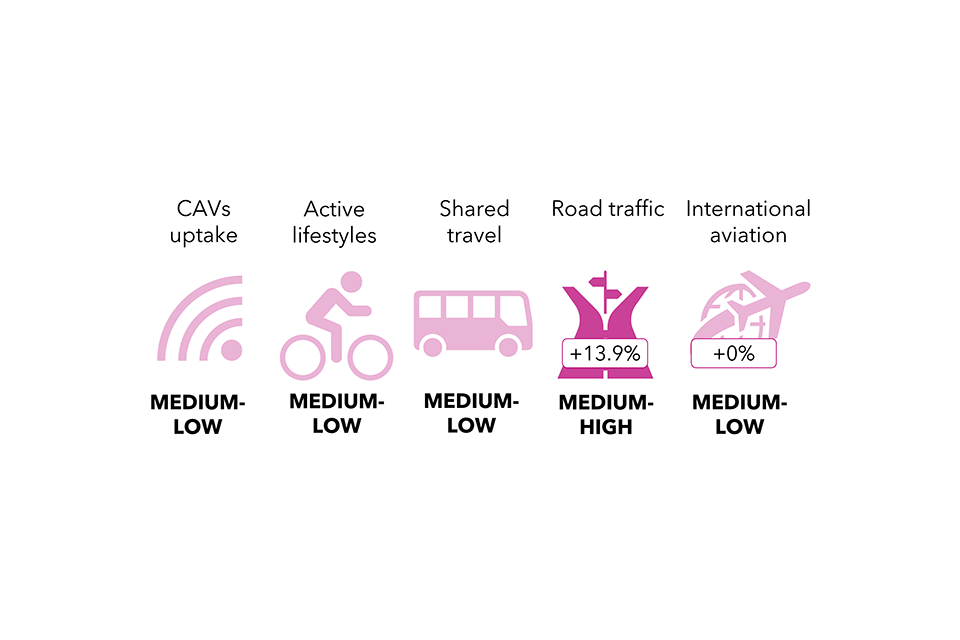
| CAVs uptake | Energetic existence | Shared journey | Street site visitors | Worldwide aviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-low | Medium-low | Medium-low | Medium-high (+13.9%) | Medium-low (+0%) |
Work and {industry}: Some kinds of work have been automated, however a big proportion of the inhabitants continues to be working in face-to-face service and guide roles. Some elements of the financial system have embraced mutual trade of products and companies as a substitute for conventional funds. Distant working continues to be an choice for these employed in larger paid ‘information work’ and that is finished each from house and from native shared workspaces. Repairability stays low. Many items are nonetheless designed with inbuilt obsolescence and ‘greenwashing’ persists. Many individuals choose to purchase new merchandise as a result of restore stays extra pricey than alternative, however a ‘make do and mend’ angle is prevalent amongst those that have chosen to undertake extra off-grid existence.
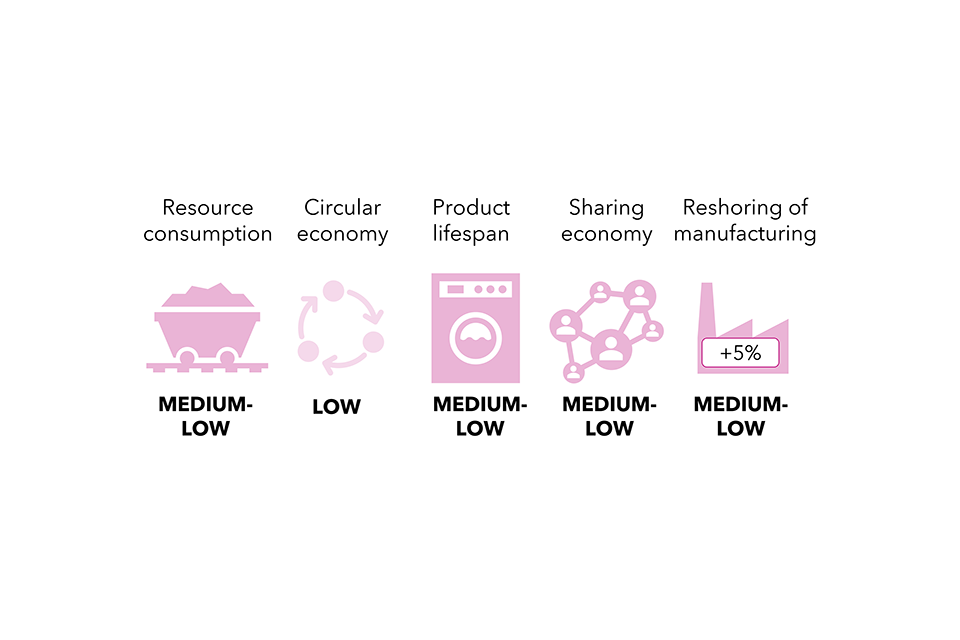
| Useful resource consumption | Round financial system | Product lifespan | Sharing financial system | Reshoring of producing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-low | Low | Medium-low | Medium-low | Medium-low (+5%) |
Meals and land use: Local weather occasions and lack of progress on new applied sciences have put larger strain on agriculture. Some farms have grow to be unviable (exacerbated by excessive climate occasions like drought and flooding), rising the UK’s reliance on imports. However deserted British farms have additionally created alternatives for constructive land use change reminiscent of rewilding and afforestation. Consequently, extra folks can get pleasure from leisure use of land and rural communities in some areas are higher capable of help themselves by way of ecotourism and elevated availability of some pure sources (reminiscent of lumber or foraged meals). Meat consumption has remained comparatively secure for the reason that 2020s and cultured alternate options have largely didn’t take off. Demand is primarily being crammed by intensively farmed meat, however natural choices can be found for these that may afford them.
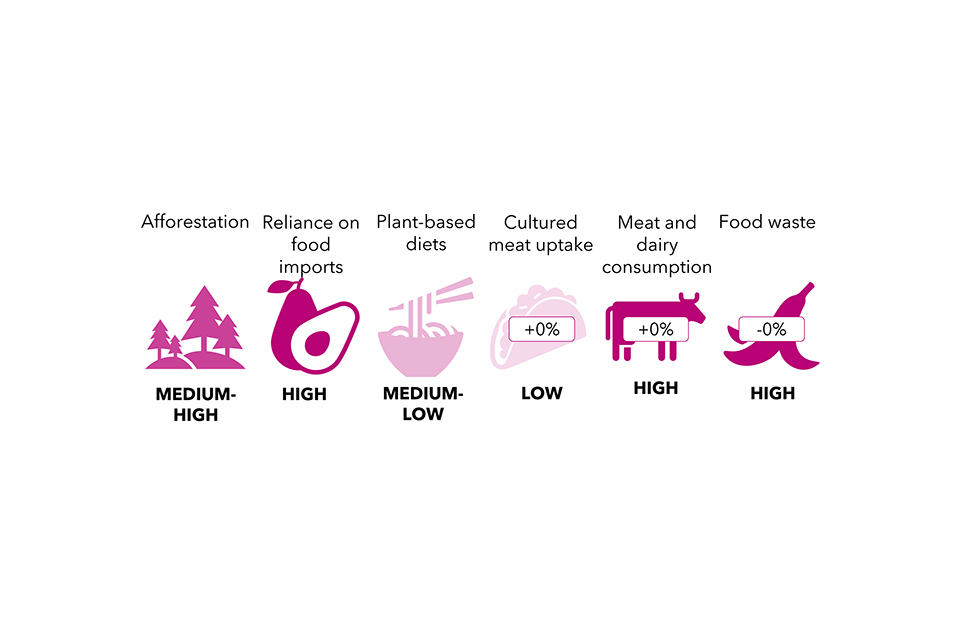
| Afforestation | Reliance on meals imports | Plant-based diets | Cultured meat uptake | Meat and dairy consumption | Meals waste |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-high | Excessive | Medium-low | Low (+0%) | Excessive (+0%) | Excessive (-0%) |
The sluggish lane society
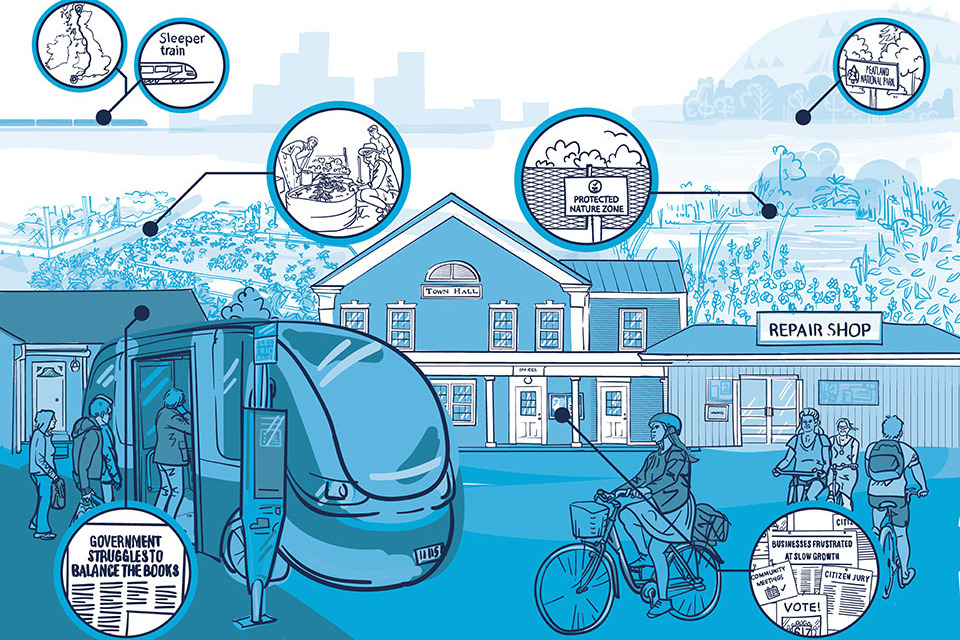
How we developed this state of affairs
We created this state of affairs by assuming decrease financial progress coincides with larger institutional belief and decrease individualistic attitudes. Our specialists felt decrease progress might have been induced, partially, by antipathy in the direction of consumption, which is perceived by some as linked to local weather change. To create this state of affairs, we imagined what would possibly have to be true for low progress and better cohesion to occur on the identical time. Usually this meant assuming modifications which improved residents wellbeing however didn’t price rather a lot. For instance, this state of affairs assumes a well being system that makes use of extra low-cost, preventative public well being measures as a result of there are restricted new therapies obtainable (each due to a scarcity of technological development and lowered public sector spending energy). Our specialists additionally recommended a ‘make do and mend’ tradition might emerge as a response to financial constraints, particularly given the excessive ranges of local people cohesion.
Life within the sluggish lane society
Financial progress within the UK has slowed over the previous few many years. Public funds have been squeezed by low progress, lowering the UK’s potential to make important strides in know-how, innovation or infrastructure (together with in transport, healthcare or schooling). This has additionally pressured a deal with lower-tech, decrease price options in public companies. The stalling of financial progress was significantly tough for residents within the first decade, particularly once they in contrast dwelling requirements to these in different international locations experiencing continued progress. Some folks have continued to seek out the sluggish tempo of change, and low availability of latest client items, irritating. Nonetheless, many voters have come to just accept low progress as long as the restricted obtainable sources are focussed on rising well being and wellbeing, bettering planetary well being, and lowering inequality.
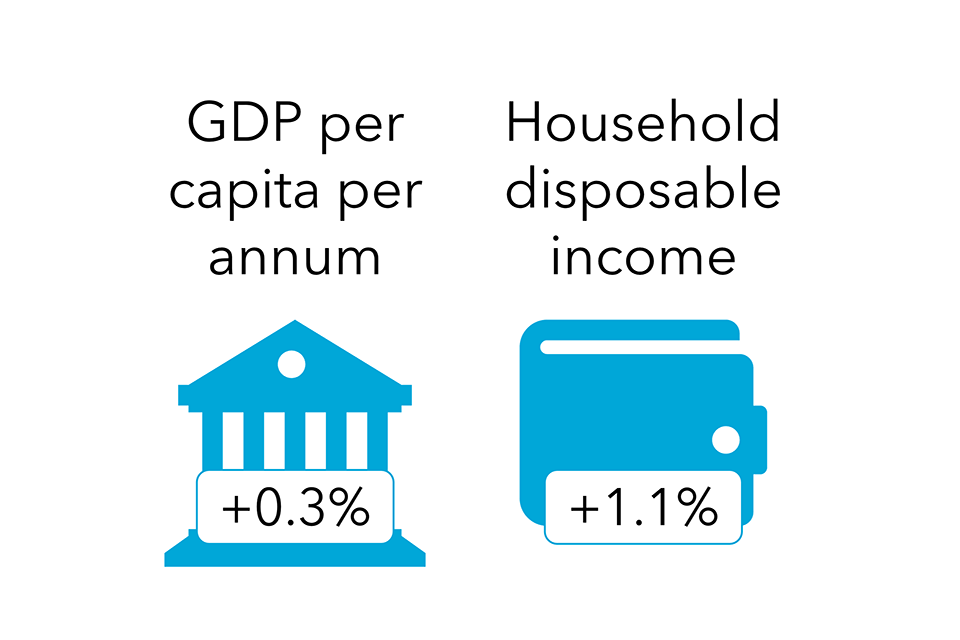
Wage stagnation and unfavourable financial circumstances have led to lowered consumption and have contributed to a resurgence of a ‘make do and mend’ tradition. Given the unaffordability of products for a lot of people, native areas have established a shared financial system for dearer gadgets; for instance, family home equipment or modes of transport (reminiscent of on-demand electrical mini-buses) are rented reasonably than owned.
Technological advances in all areas have been sluggish on this state of affairs. This implies there’s comparatively little web zero know-how obtainable, but in addition restricted advances in different fascinating areas, reminiscent of healthcare. The place there was technological progress, efforts have been largely directed in the direction of addressing sustainability and the wellbeing of society. Synthetic intelligence, for instance, is tightly regulated and used primarily for enhancements in environmental monitoring, delivering extra environment friendly public transport, and guaranteeing fairer prioritisation and allocation of sources.
Within the late 2030s, governments started devolving extra accountability to native areas and areas, starting with an growth of metropolis mayors, however finally filtering right down to smaller cities. Given this state of affairs’s place on our key axes, we now have assumed larger political engagement and voting on the native stage, the place folks can clearly see that their selection makes a distinction. This has additionally boosted localism and native engagement with methods being shared, unfold, and adopted between native governance and advocacy teams.
Worldwide societal concerns: By the early 2030s, international cooperation round web zero and the local weather agenda made progress with the institution of a brand new settlement for pure sources safety programme and international warming limits. Nonetheless, regardless of improved worldwide collaboration, large emitters reminiscent of China and Russia noticed their efforts restricted as a result of lack of technological progress.
Sectors
The constructed surroundings: The inhabitants is unfold throughout metropolis centres and rural areas dwelling localised existence. To compensate for continued wage stagnation, many companies have adopted shorter working weeks for workers. Working from house additionally turned broadly adopted throughout many industries within the 2020s, permitting many to maneuver out of cities and into rural areas. The plan to decentralise the federal government and provides extra accountability to native areas within the 2030s supported extra compact existence inside cities and cities. The rising rural inhabitants reside as sustainably as they’ll, however journey additional and reside in larger homes, usually constructed on greenfield websites. Infrastructure funding programmes weren’t carried out within the late 2030s, making it difficult to ship new properties on the tempo and scale required. Though pricey, many properties embrace ‘sensible’ AI options, which have been normalised. This has resulted in higher vitality and useful resource consumption administration.
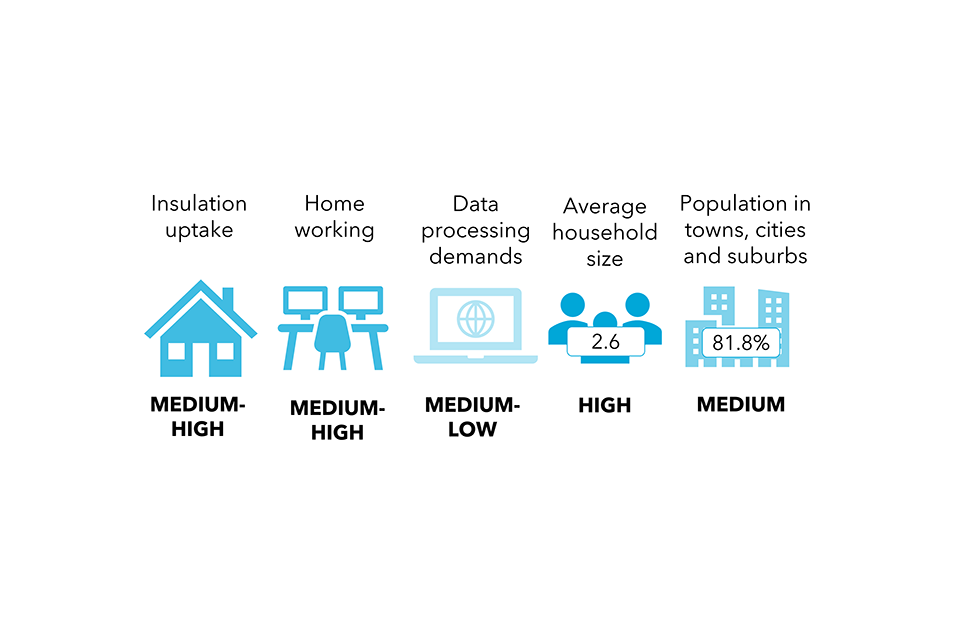
| Insulation and vitality effectivity | Residence working | Information processing calls for | Common family dimension | Populations in cities, cities and suburbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-Excessive | Low | Medium-low | Excessive (2.6) | Medium (81.8%) |
Journey and transport: The growth of unpolluted air zones and the event of extra environment friendly public transport made non-public possession of automobiles much less engaging. Due to this fact, most people stroll or cycle to work. There was a short-lived dip in short- and long-haul journey through the COVID-19 pandemic however worldwide journey resumed extra intensely within the 2030s. Nonetheless, the comparatively excessive price of flying alongside preferences for a ‘slower’ tempo of life prompted extra folks to decide on to trains and boats for long-haul journey. Even airships have seen a renaissance. Some persons are pissed off by this slower tempo, significantly the place it holds again enterprise productiveness.
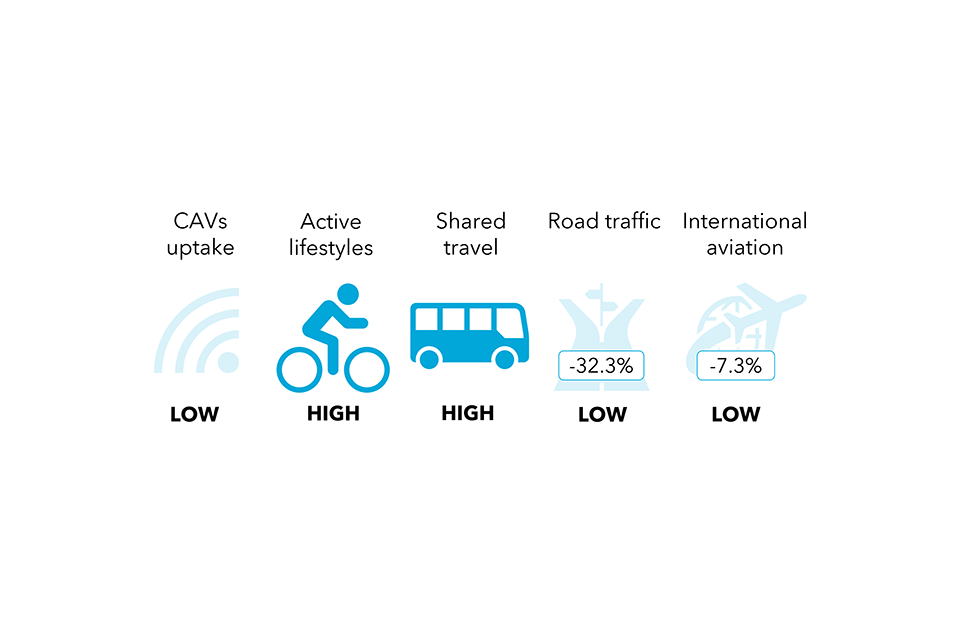
| CAVs uptake | Energetic existence | Shared journey | Street site visitors | Worldwide aviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Excessive | Excessive | Low (-32.3%) | Low (-7.3%) |
Work and {industry}: Larger companies have more and more begun selling constructive societal values, though many multinational corporations have lowered buying and selling within the UK given the low spending energy of its residents. The ensuing hole out there, mixed with the deal with neighborhood and spending domestically, has created a friendlier working surroundings for smaller companies. Nonetheless, given the backdrop of low progress, no enterprise of any dimension is flourishing, and wages comply with. There’s a lowered selection of latest merchandise and people which are obtainable are unaffordable to many individuals. This has led to a ‘restore first’ mannequin and widespread adoption of sharing of products and companies. Many native areas at the moment are served by restore outlets with some additive manufacturing capabilities which are geared in the direction of extending the helpful lifetime of merchandise and serving the wants of native economies.
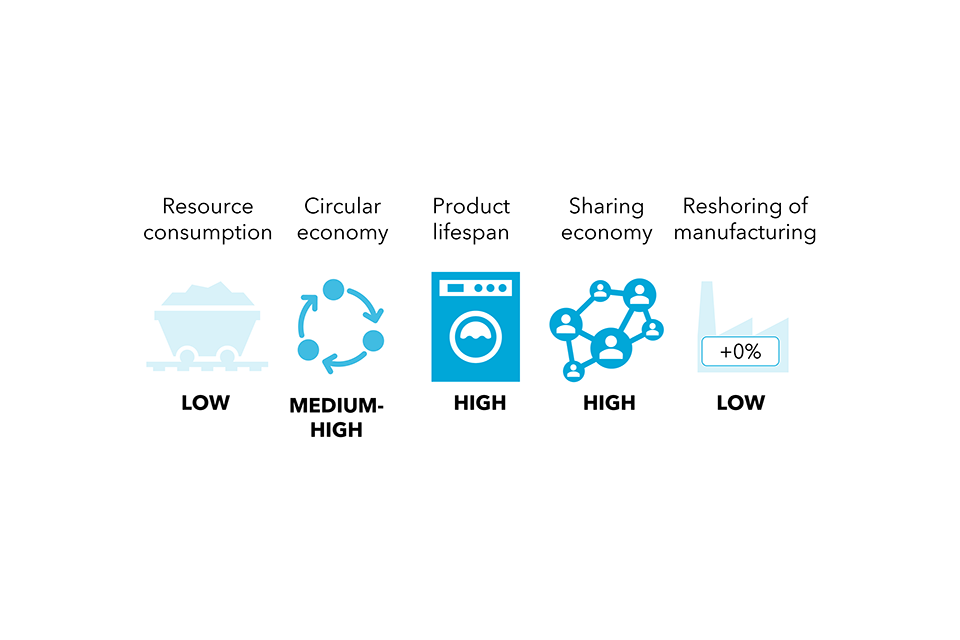
| Useful resource consumption | Round financial system | Product lifespan | Sharing financial system | Reshoring of producing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Medium-high | Excessive | Excessive | Low (+0%) |
Meals and land use: Local weather change impacts are nonetheless felt however are principally higher managed by way of adaptation measures. Areas have grow to be more practical at assembly the triple problem of balancing carbon discount, biodiversity enhancements and meals manufacturing upkeep by discovering the land use combine that works greatest in every panorama. Extra folks get pleasure from entry to protected nature zones. Extra meals is grown within the UK for home consumption. Maybe partially pushed by decrease incomes, meat consumption is low, and many individuals have transitioned to plant-based diets. Cultured meat has failed to realize traction with preliminary hesitance changing into widespread resistance that would not be overcome by companies in unfavourable financial circumstances.
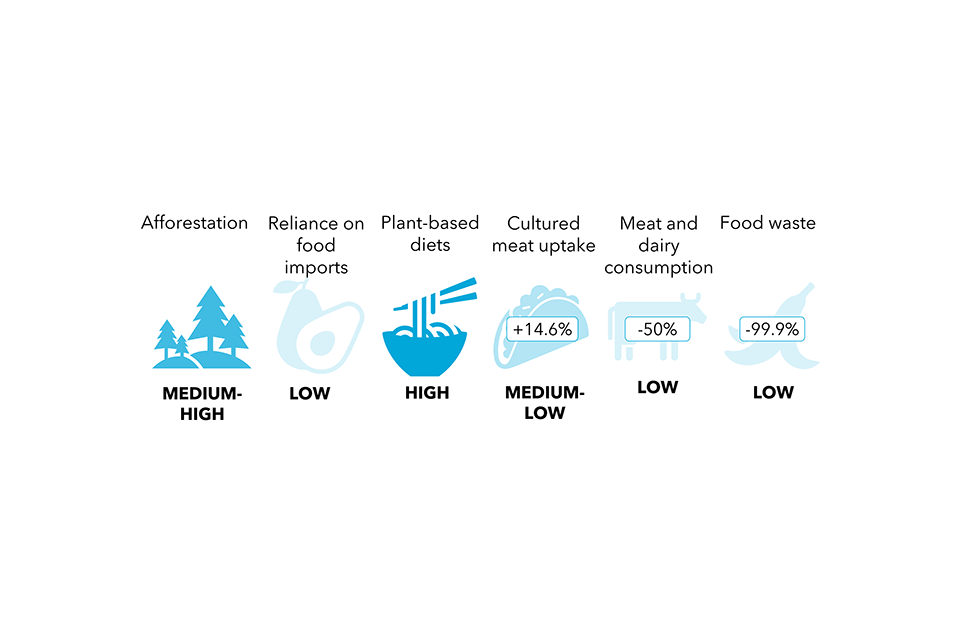
| Afforestation | Reliance on meals imports | Plant-based diets | Cultured meat uptake | Meat and dairy consumption | Meals waste |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-high | Low | Excessive | Medium-low (+14.6%) | Low (-50%) | Low (-99.9%) |
3.4 Sector comparisons

| The atomised society | The metropolitan society | The self-preservation society | The sluggish lane society |
|---|---|---|---|
| Many dwelling in gated communities in suburban and rural areas | Funding prioritises growth of city areas | Declining city funding drives folks out of cities | Inhabitants dispersed throughout city and rural areas |
| Fast house-building improves affordability | Extra folks dwelling in cities, these in rural areas really feel uncared for | Housing demand outstrips provide | Low funding in new properties |
| Extra folks dwelling alone | Compact dwelling in AI-enabled sensible properties | Extra multi-generational dwelling | Extra localised and compact existence |
| Higher reliance on on-line items and companies | Push for important companies near house | Give attention to ‘self-sufficient’ dwelling | Native facilities offering restore and sustainable dwelling companies |

| Insulation and vitality effectivity | Residence working | Information processing demand | Common family dimension | City/suburban inhabitants | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomised society | Medium-high | Excessive | Excessive | Low | Medium |
| Metropolitan society | Excessive | Medium-low | Medium-high | Medium-low | Excessive |
| Self-preservation society | Medium-low | Low | Low | Medium | Excessive |
| Sluggish lane society | Low | Medium-high | Medium-low | Excessive | Medium |

| The atomised society | The metropolitan society | The self-preservation society | The sluggish lane society |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flying overseas for leisure stays common | Zero-carbon choices keep recognition of flying | Flying is more and more costly | Prepare and boats used for long-haul journey |
| Lengthy-distance public transport has improved | Funding in low-cost city public transport | Reasonable funding in lively journey infrastructure | Energetic journey is the dominant mode of journey |
| Public transport costs exclude the poorest | Prepare journey cheaper and simpler between cities | Fragmented public transport outdoors of cities | Environment friendly public transport and clear air zones |
| Sturdy uptake of CAVs by the wealthy | CAVs obtainable as on-demand shared journey | CAVs obtainable for the wealthy | CAV use is much less widespread |

| CAVs uptake | Energetic existence | Shared journey | Street site visitors | Worldwide aviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomised society | Excessive | Low | Low | Excessive | Excessive |
| Metropolitan society | Medium-high | Medium-high | Medium-high | Medium | Medium-high |
| Self-preservation society | Medium-low | Medium-low | Medium-low | Medium-high | Medium-low |
| Sluggish lane society | Low | Excessive | Excessive | Low | Low |

| The atomised society | The metropolitan society | The self-preservation society | The sluggish lane society |
|---|---|---|---|
| Worldwide competitors and excessive ranges of reshoring | Native companies and low ranges of reshoring | Home competitors and reasonable ranges of reshoring costly | Smaller native companies thriving and low ranges of reshoring |
| Throwaway tradition partially offset by know-how enabled recycling | Rising round financial system | Throwaway tradition as a result of price of restore | Restore-first mannequin, shared items and companies |
| Crypto-currencies, financial system for digital items and companies | Tech is used to trace product provenance and lifecycles | Inbuilt obsolescence and ‘greenwashing’ commonplace | Some companies battle with lack of bodily infrastructure funding |
| Always creating know-how makes older merchandise out of date | AI permits correct carbon labelling of merchandise | Lack of traceability of carbon affect of merchandise | Client tech not as available |

| Useful resource consumption | Round financial system | Product lifespan | Sharing financial system | Reshoring of producing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomised society | Excessive | Medium-low | Low | Low | Excessive |
| Metropolitan society | Medium-high | Excessive | Medium-high | Excessive | Low |
| Self-preservation society | Medium-low | Low | Medium-low | Medium-low | Medium-low |
| Sluggish lane society | Low | Medium-high | Excessive | Excessive | Low |

| The atomised society | The metropolitan society | The self-preservation society | The sluggish lane society |
|---|---|---|---|
| Broad availability of cultured meat | Consumption of plant-based diets with cultured meat | Excessive availability of intensively farmed meat | Plant-based diets are common |
| City agriculture and vertical farming supply pricey native produce | Meals manufacturing combines high and low tech approaches | Some UK farmland has grow to be unviable | Give attention to defending biodiversity in meals manufacturing |
| Agriculture tech permits UK to take care of self-sufficiency | Tech reduces land and pesticide use and improves meals self-sufficiency | Little use of latest agricultural tech, however elevated reliance on imports | Some agricultural tech with emphasis on adaptation and self-sufficiency |
| Lowered biodiversity from environmental degradation | Ecosystem companies are valued, however tensions over rewilding | Rewilded farms, leisure use of rural land | Nature zones are protected and nationwide parks restored |

| Afforestation | Reliance on meals imports | Plant-based diets | Cultured meat uptake | Meat and dairy consumption | Meals waste | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomised society | Medium-low | Medium-high | Medium | Medium-high | Medium-high | Excessive |
| Metropolitan society | Medium-low | Medium-low | Excessive | Excessive | Medium-low | Medium |
| Self-preservation society | Medium-high | Excessive | Medium-low | Low | Excessive | Excessive |
| Sluggish lane society | Medium-high | Low | Excessive | Medium-low | Low | Low |
3.5 Translation into quantified ‘levers’
This part units out how the state of affairs narratives have been translated into quantified ‘levers’. Levers are inputs to sectoral fashions that may differ by state of affairs. These levers collectively decide every state of affairs’s demand and know-how availability. They permit our evaluation of how web zero might be met in every state of affairs, which is roofed within the subsequent chapter. This part is almost certainly to be of curiosity to readers with a technical curiosity within the element of the strategies and assumptions used within the challenge.
Beneath, we cowl a set of cross-cutting inputs, adopted by inputs into our 4 sectoral fashions: the constructed surroundings, journey and transport, work and {industry}, and meals and land use. For every sector, we additionally describe a number of the key sectoral mannequin ‘exercise’ outputs that feed into the vitality system mannequin, UKTM, as vitality calls for.
A word on the bottom 12 months for sectoral fashions
The selection of base 12 months for modelling knowledge just isn’t simple, given the disruptive results of the COVID-19 pandemic on society and the financial system in 2020 and 2021. It’s also not potential to make use of 2022 as knowledge are often finalised and revealed with a lag of a number of months. We’ve got subsequently opted to make use of 2019 as the bottom 12 months for many modelling knowledge. Nonetheless, financial indicators have been sourced from March 2022 OBR projections, which account for the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic. The state of affairs narratives and associated modelling enter trajectories additionally goal to account for the broader results of the pandemic indirectly (for instance, by explaining its results on future digital communication).
Cross-cutting levers
Some high-level points of 2050 had been assumed to remain in line with present predictions throughout all of the eventualities (for instance, inhabitants dimension). Nonetheless, there have been different essential overarching societal variations between the eventualities, which we translated right into a sequence of variable cross-cutting levers (reminiscent of GDP and earnings progress, and geographical inhabitants distribution). These cross-cutting levers had been utilized in all of the sectoral fashions and UKTM.
The tables under illustrate a number of the key levers for example our method. These tables cowl the excessive and low ‘settings’ for every lever, which eventualities had been chosen, a rationale for this selection, illustrative values, and a abstract of the proof used. The cross-cutting desk (Desk 3) additionally features a description of how every variable feeds by way of within the sectoral fashions. The total element is roofed in Annex 4.
Desk 3. Illustrative set of cross-cutting levers, used constantly throughout the sectoral fashions and UKTM (extra element is supplied in Annex 4)
Cross-cutting enter lever settings
(based mostly on OBR (2022) Financial and monetary outlook — March 2022; ONS inhabitants)
| Lever (Unit) | Present values | Highest | Lowest | Examples of how these feed into demand |
| Annual common GDP per capita (common annual change 2022–2050) | £31,793 (2021) | Situation: At Soc; Worth: +2.8%; Rationale: Increased financial progress is a defining function of this state of affairs, drawn from one of many two core state of affairs axes. | Situation: SL Soc; Worth: +0.3%; Rationale: Decrease financial progress is a defining function of this state of affairs, drawn from one of many two core state of affairs axes. | The constructed surroundings: Broadly, extra progress means extra building and extra emissions. Journey and transport: Progress continues to be coupled to freight and passenger transport, though there are limits. Work and {industry}: Broadly, extra progress means larger industrial output and extra emissions (all else being equal — round financial system measures might break this hyperlink). Meals and land use: GDP (and subsequently earnings) impacts family spending patterns on meals. |
| Common family dimension | 2.4 (2022) | Situation: SL Soc; Worth: 2.6 (+8.3%); Rationale: This state of affairs has larger ranges of belief and decrease incomes, with extra folks dwelling collectively in larger households. | Situation: At Soc; Worth: 2.1 (-13%); Rationale: This state of affairs has decrease ranges of belief and better incomes, with extra folks selecting to reside alone or in smaller households. | The constructed surroundings: Larger households use much less vitality and water per particular person than smaller households. Journey and transport: Extra single households enhance family automotive possession and use. Work and {industry}: Smaller households are related to the next floorspace construct fee. Meals and land use: Family dimension can have an effect on family spending patterns on meals. |
| Family disposable earnings per capita (common annual change 2022-2050) | £31,000 (2022) | Situation: At Soc; Worth: +2.1%; Rationale: THigher incomes linked to larger ranges of financial progress, which is a defining function of this state of affairs (see above). | Situation: SL Soc; Worth: +1.1%; Rationale: TLower incomes linked to decrease ranges of financial progress, which is a defining function of this state of affairs (see above). | The constructed surroundings: Elevated capability for funding and extra building. Journey and transport: Disposable earnings impacts family automotive possession and direct hyperlink to family automotive use. Elevated earnings has been a major driver of demand for aviation.26 Revenue influences automotive distance travelled and van site visitors. Work and {industry}: Family spending is the most important supply of consumption within the financial system, which pertains to emissions. Meals and land use: Adjustments in disposable earnings decide peoples’ potential to comply with more healthy diets. Inequality drives larger consumption of processed meals, and fewer consumption of fruit, greens, pink meat and oily fish. |
| Urbanised populations in 2050 (% of whole inhabitants in city and suburban areas) | 84% (2021) | Situation: Met Soc; Worth: 87%; Rationale: Funding and funding in city areas attracts many to compact city dwelling. | Situation: At Soc; Worth: 82%; Rationale: The inhabitants is extra dispersed, with the wealthy selecting to reside in suburban and rural areas. | The constructed surroundings: Altering demographics can have an effect on demand for brand spanking new properties. Journey and transport: Extra dispersed populations may be related to larger automotive possession and longer journey distances. Work and {industry}: As a inhabitants turns into more and more urbanised, demand for building will increase. Meals and land use: Urbanisation could be a key driver of agricultural demand, and lowered proportion of individuals dwelling in rural areas results in a scarcity of agricultural employees and will increase agricultural land conversion. |
The constructed surroundings
Key determinants of vitality demand in buildings embrace the interior temperature, and whole floorspace. Beneath are particulars of how these are assumed to differ throughout the eventualities.
Determine 13. Imply inside temperature (levels Celsius) for consolation in 2020–2050 within the 4 web zero society eventualities (high) and floorspace (million sq. metres) within the non-domestic buildings sector in 2020–2050 within the 4 web zero society eventualities (backside)
Please word: On this graph, the atomised society line is overwritten by the self-preservation society line

Determine 13 graph 1 knowledge: Imply inside temperature, ˚ C
| AT Soc | Met Soc | SP Soc | SL Soc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 18.6 | 18.6 | 18.5 | 18.4 |
| 2021 | 18.6 | 18.5 | 18.4 | 18.4 |
| 2022 | 18.7 | 18.5 | 18.3 | 18.3 |
| 2023 | 18.7 | 18.4 | 18.2 | 18.2 |
| 2024 | 18.8 | 18.4 | 18.1 | 18.2 |
| 2025 | 18.8 | 18.3 | 18 | 18.1 |
| 2026 | 18.9 | 18.2 | 17.9 | 18.1 |
| 2027 | 18.9 | 18.2 | 17.8 | 18 |
| 2028 | 19 | 18.1 | 17.7 | 18 |
| 2029 | 19 | 18 | 17.6 | 17.9 |
| 2030 | 19.1 | 18 | 17.5 | 17.9 |
| 2031 | 19.1 | 17.9 | 17.5 | 17.8 |
| 2032 | 19.1 | 17.9 | 17.4 | 17.8 |
| 2033 | 19.1 | 17.9 | 17.4 | 17.7 |
| 2034 | 19.1 | 17.9 | 17.4 | 17.6 |
| 2035 | 19.1 | 17.9 | 17.4 | 17.6 |
| 2036 | 19 | 17.9 | 17.4 | 17.5 |
| 2037 | 19.1 | 17.8 | 17.4 | 17.5 |
| 2038 | 19.1 | 17.8 | 17.4 | 17.4 |
| 2039 | 19.1 | 17.8 | 17.4 | 17.4 |
| 2040 | 19.1 | 17.8 | 17.4 | 17.3 |
| 2041 | 19.1 | 17.7 | 17.4 | 17.3 |
| 2042 | 19.1 | 17.7 | 17.4 | 17.2 |
| 2043 | 19.1 | 17.7 | 17.4 | 17.1 |
| 2044 | 19.1 | 17.7 | 17.4 | 17.1 |
| 2045 | 19.1 | 17.6 | 17.4 | 17 |
| 2046 | 19.1 | 17.6 | 17.4 | 17 |
| 2047 | 19.1 | 17.6 | 17.4 | 16.9 |
| 2048 | 19.1 | 17.6 | 17.4 | 16.8 |
| 2049 | 19.1 | 17.6 | 17.4 | 16.8 |
| 2050 | 19.1 | 17.5 | 17.4 | 16.7 |

Determine 13 graph 2 knowledge: Floorspace, million m2
| AT Soc | Met Soc | SP Soc | SL Soc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1000 | 1100 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2021 | 1000 | 1100 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2022 | 1000 | 1100 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2023 | 1000 | 1100 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2024 | 1000 | 1100 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2025 | 1000 | 1200 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2026 | 1000 | 1200 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2027 | 1000 | 1200 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2028 | 1000 | 1200 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2029 | 1000 | 1200 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2030 | 1000 | 1200 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2031 | 1000 | 1300 | 1000 | 1100 |
| 2032 | 1000 | 1300 | 1000 | 1200 |
| 2033 | 1000 | 1300 | 1000 | 1200 |
| 2034 | 1000 | 1300 | 1000 | 1200 |
| 2035 | 1000 | 1300 | 1000 | 1200 |
| 2036 | 1000 | 1400 | 1000 | 1200 |
| 2037 | 1000 | 1400 | 1000 | 1200 |
| 2038 | 1000 | 1400 | 1000 | 1200 |
| 2039 | 1000 | 1400 | 1000 | 1200 |
| 2040 | 1000 | 1400 | 1000 | 1200 |
| 2041 | 1100 | 1500 | 1100 | 1200 |
| 2042 | 1100 | 1500 | 1100 | 1200 |
| 2043 | 1100 | 1500 | 1100 | 1300 |
| 2044 | 1100 | 1500 | 1100 | 1300 |
| 2045 | 1100 | 1600 | 1100 | 1300 |
| 2046 | 1100 | 1600 | 1100 | 1300 |
| 2047 | 1100 | 1600 | 1100 | 1300 |
| 2048 | 1100 | 1600 | 1100 | 1300 |
| 2049 | 1100 | 1600 | 1100 | 1300 |
| 2050 | 1100 | 1700 | 1100 | 1300 |
Focussing on home buildings, the interior temperature is a perform of each the thermostat temperature and the warmth lack of the constructing. Poorly insulated buildings quiet down faster and so have a decrease imply inside temperature. We’ve got not made any particular assumptions in regards to the results of worldwide warming on indoor temperatures in every state of affairs, due to important uncertainties on how this might manifest throughout seasons, however it’s probably that this might have an effect on each heating and cooling demand within the UK.
Indoor temperature within the atomised society follows historic traits by rising to 19°C in 2050 (Determine 13, high), resulting in larger vitality calls for. The opposite eventualities see a lowered common indoor temperature by 2050, pushed by a mixture of environmental consciousness, price pressures, and ranges of insulation, various by state of affairs. The metropolitan society has larger common incomes, which reduces the inducement to show down thermostats, however that is offset by elevated environmental consciousness. The self-preservation society has comparatively excessive price pressures and decrease insulation, but in addition decrease environmental consciousness. The sluggish lane society has each excessive environmental consciousness and the bottom incomes, resulting in the bottom imply temperature by 2050.
The non-domestic floorspace expands in all 4 eventualities, though to completely different extents (Determine 13, backside). The most important enhance is noticed within the metropolitan society, by greater than 50% by 2050, as a result of a desire for face-to-face working that results in growth of metropolis centre workplace area. The atomised and self-preservation societies have excessive ranges of digital dwelling and dealing, and this results in them having the bottom progress in non-domestic floorspace, at slightly below 5% by 2050. The residential buildings sector just isn’t modelled based mostly on floorspace however makes use of assumptions in regards to the common family dimension, widespread throughout all sectors, to calculate family vitality use. Desk 4 units out additional particulars on a set of key levers and their settings for the constructed surroundings sector.
Desk 4. An illustrative set of levers for the constructed surroundings sector, which have been used within the sectoral mannequin (extra element is supplied in Annex 4)
Constructed surroundings enter lever settings
| Lever (Unit) | Most up-to-date values | Highest | Lowest |
| Complete non-domestic floorspace | 580.8 million m2 | Situation: Met Soc; Worth: 871.2 million m2 (+50%); Rationale: Choice of face-to-face working, resulting in a rise in growth of workplace area in metropolis centres.; Proof: CREDS report | Situation: At Soc / SP Soc; Worth: 608.1 million m2 (+4.7%); Rationale: Excessive ranges of digital dwelling and working, resulting in low progress in floorspace.; Proof: CREDS report |
| Residence working (Common variety of commuting and enterprise journeys per particular person) | 113 (2020) | Situation: At Soc; Worth: -20%; Rationale: Residence working extra widespread with larger availability of tech.; Proof: There’s a blended image on long run results on distance travelled. For instance, fewer common journeys for work might imply fewer general journeys however longer distances travelled to office. | Situation: SP Soc; Worth: -5%; Rationale: Some kinds of work have been automated, however a big proportion of the inhabitants continues to be working in face-to-face service and guide roles.; Proof: City planning influences the environmental impacts of teleworking, enabling teleworkers to journey much less to entry important amenities. |
| Common family vitality use (mixed gasoline and electrical energy use) | 15,400kWh/12 months (2017) | Situation: SL Soc; Worth: 9,086 kWh/12 months (-41%); Rationale: Funding in larger vitality effectivity measures.; Proof: UK Nationwide Family Mannequin[v] and CREDS | Situation: SP Soc; Worth: 13,090 kWh/12 months (-15%); Rationale: Extra folks selecting to reside off grid. Lack of funding in vitality effectivity measures.; Proof: UK Nationwide Family Mannequin and CREDS |
Journey and transport
Distance travelled by completely different automobile sorts is a key determinant of vitality demand within the transport sector. Beneath are particulars of how these are assumed to differ throughout the eventualities.
Determine 14. Demand for highway transport in billion vehicle-kilometres per 12 months within the 4 web zero society eventualities (high) and demand for aviation in billion passenger-kilometres per 12 months within the 4 web zero society eventualities (backside)

Determine 14. Graph 1 knowledge: Street transport demand billion vkm/12 months
| AT Soc | Met Soc | SP Soc | SL Soc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 450 | 450 | 450 | 450 |
| 2025 | 560 | 500 | 540 | 470 |
| 2030 | 590 | 470 | 550 | 380 |
| 2035 | 630 | 450 | 560 | 370 |
| 2040 | 680 | 440 | 570 | 360 |
| 2045 | 740 | 430 | 580 | 350 |
| 2050 | 800 | 420 | 580 | 350 |

Determine 14. Graph 2 knowledge: Aviation demand, billion pkm
| AT Soc | Met Soc | SP Soc | SL Soc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 |
| 2025 | 320 | 310 | 300 | 300 |
| 2030 | 350 | 340 | 310 | 300 |
| 2035 | 380 | 360 | 310 | 300 |
| 2040 | 410 | 380 | 310 | 300 |
| 2045 | 440 | 390 | 320 | 290 |
| 2050 | 470 | 410 | 320 | 290 |
Increased incomes, decrease automobile occupancy, and the provision of CAVs all result in the best demand for highway transport within the atomised society (Determine 14, high). Increased GDP can be related to extra freight needing to be moved on this state of affairs. The self-preservation society additionally has comparatively excessive ranges of journey by automotive, however primarily as a result of a scarcity of public transport and lively journey alternate options. The opposite two eventualities see a discount in journey by highway transport, as a result of a mix of environmental consciousness and good availability of alternate options to automotive journey, significantly in city areas within the metropolitan society. Decrease earnings progress and improved public transport and lively journey infrastructure additionally help reductions in automotive journey within the sluggish lane society, incentivising folks to make use of rail, bus companies, cycle or stroll the place potential.
Demand for aviation stabilises on the pre-pandemic ranges within the lower-growth societies (self-preservation and sluggish lane) however will increase considerably within the atomised society, almost doubling by 2050 (Determine 14, backside). Regardless of a rise in environmental consciousness within the metropolitan society, excessive incomes and an ongoing desire for international holidays result in comparatively excessive will increase in aviation demand on this state of affairs.
Desk 5 under units out additional particulars on a set of key levers and their settings for the journey and transport sector.
Desk 5. An illustrative set of levers for the journey and transport sector, which have been used within the sectoral mannequin (extra element is supplied in Annex 4)
Journey and transport enter lever settings
| Lever (Unit) | Most up-to-date values | Highest | Lowest |
| Worldwide journey and aviation (terminal passengers from UK airports) | 296,658 (2019 to account for pre-covid ranges) | Situation: At Soc; Worth: 400,488 (+35%); Rationale: Excessive incomes, sturdy attachment to worldwide holidays, and know-how that permits low carbon flying all contribute.; Proof: Assume an preliminary shift downwards as {industry} recovers adopted by continuation of pre-COVID journeys and journey lengths with a slight enhance in earnings elasticity (larger incomes, extra folks fly).; | Situation: SL Soc; Worth: 341,156 (+15%); Rationale: Comparatively low incomes, shifting societal preferences for UK holidays, and elevated environmental consciousness cut back flying. Increased pricing of aviation (particularly for frequent flyers) turns into acceptable through the 2020s.; Proof: Discount in air journey charges (folks fly much less however keep longer) thus lowering ‘hypermobility’ and ‘binge flying’. See CREDS Low Vitality Demand report for particulars.; |
| Change in highway site visitors (proportion change, 2015–2050) | 297.6 billion automobile miles pushed (2021) | Situation: At Soc; Worth: 0.57; Rationale: The non-public possession mannequin continues to dominate, with solely restricted traction for shared journey.; Proof: OECD knowledge, CREDS shared mobility inquiry and fee.; | Situation: Met Soc; Worth: -0.17; Rationale: Growth of unpolluted air zones and the event of extra environment friendly public transport made non-public possession much less engaging. Most individuals take up lively journey choices to guide more healthy existence.; Proof: OECD knowledge, CREDS shared mobility inquiry and fee.; |
| Automobile occupancy fee (common variety of folks per automobile) | 1.6 -2018 | Situation: Met Soc; Worth: 2 (+25%); Rationale: Large funding in shared and demand responsive transport (reminiscent of automotive golf equipment and experience sharing) result in larger automotive occupancy charges and decrease automotive possession.; Proof: OECD knowledge, CREDS shared mobility inquiry and fee.; | Situation: At Soc; Worth: 1.37 (-14%); Rationale: Particular person use most popular choice coupled with larger incomes means extra particular person possession, decrease automotive occupancy charges, and little mode shift to shared choices.; Proof: OECD knowledge, CREDS shared mobility inquiry and fee.; |
Work and {industry}
Vitality demand from work and {industry} are largely pushed by the output of these sectors, a proxy measure for which is Gross Worth Added (GVA). Beneath we give particulars of how that is assumed to differ throughout the eventualities.
Determine 15. Graphs exhibiting exercise in 4 key industrial subsectors, listed to 2010, in 2020 and in 2050 for the 4 web zero society eventualities

Determine 15 knowledge: GVA, listed to 2010
| Cement | Iron and metal | Non-ferrous metals | Chemical substances | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 0.88 | 0.74 | 0.7 | 0.48 | |
| 2050 | AT Soc | 1.08 | 1 | 0.62 | 0.45 |
| 2050 | Met Soc | 1.16 | 0.75 | 0.43 | 0.31 |
| 2050 | SP Soc | 1.06 | 0.6 | 0.32 | 0.23 |
| 2050 | SL Soc | 0.75 | 0.49 | 0.25 | 0.18 |
In comparison with 2010, to which the {industry} knowledge are listed within the sectoral mannequin, industrial exercise falls in all eventualities in addition to in 2020 as a result of ongoing offshoring of producing (besides within the atomised society) and enhancements in materials effectivity (Determine 15 illustrates 4 key industrial subsectors). For instance, by 2050 the sluggish lane society’s {industry} sector is halved in comparison with 2010 and within the self-preservation society it shrinks by round two thirds. By subsector, ammonia and high-value chemical substances dwindle most on common throughout all eventualities, to round a 3rd of their 2010 ranges. Whereas chemical substances is a big subsector when it comes to its vitality demand in 2010, its significance decreases by 2050 as its exercise ranges drop by between 55% (within the atomised society) and 82% (within the sluggish lane society) over that point interval.
The primary driver with the potential to offset the shrinking of the {industry} sector is reshoring. Within the atomised society this provides 20% to manufacturing sector outputs by 2050 (with corresponding reductions in imports), as a result of elevated automation and international battle, whereas within the self-preservation society this extra progress is smaller at 5%, with automation much less of a driver. Vital reshoring doesn’t happen within the different two eventualities. As well as, cement manufacturing will increase within the metropolitan, atomised and self-preservation societies due to expanded building, pushed by financial progress.
Desk 6. An illustrative set of levers for the work and {industry} sector, which have been used within the sectoral mannequin (extra element is supplied in Annex 4)
Work and {industry} enter lever settings
| Lever (Unit) | Most up-to-date values | Highest | Lowest |
| Sharing financial system: renting of clothes (proportion of market) | 2% (2022) | Situation: Met Soc; Worth: 0.28; Rationale: Increased use fee from sharing financial system kind approaches means fewer items required and emissions financial savings from lowered manufacturing.; Proof: Linked to earlier modelling of obtainable alternatives. | Situation: At Soc; Worth: 0.12; Rationale: Throwaway tradition is prevalent, partially offset by recycling.; Proof: Linked to earlier modelling of obtainable alternatives. |
| Product longevity | Common lifetime of enormous home equipment is 13 years (2020) | Situation: SL Soc; Worth: Common lifetime of enormous home equipment is 16 years (+23%); Rationale: Restore-first mannequin, with shared items and companies. Extending the lifetime of electrical home equipment.; Proof: Linked to earlier modelling of obtainable alternatives. | Situation: At Soc; Worth: Common lifetime of enormous home equipment is 14.1 years (+8.5%); Rationale: Always creating know-how makes older merchandise out of date. Throwaway tradition partially offset by technology-enabled recycling.; Proof: Linked to earlier modelling of obtainable alternatives. |
| Reshoring of producing (Output from UK manufacturing sector) | £183bn (2022) | Situation: At Soc; Worth: £219.6bn (+20%); Rationale: Worldwide competitors and excessive ranges of reshoring.; Proof: Decided by central GO-Science staff, suggested by Division for worldwide Commerce. | Situation: SL Soc; Worth: No or minimal change from present values.; Rationale: Home competitors and low ranges of reshoring. Smaller native companies thriving.; Proof: Decided by central GO-Science staff, suggested by Division for worldwide Commerce. |
Meals and land use
Calorific consumption by meals group, pushed by dietary preferences and meals availability, is a key metric figuring out vitality use and direct emissions from meals and land use.
Determine 16. Common calorific demand by meals group in 2020 and in 2050 for the 4 web zero society eventualities (kilocalories per capita per day

Determine 16 knowledge: Common calorie consumption per capita per day
| Meat (together with cultured) | Dairy | Cereals | Fish | Confectionary | Misc | Drinks | Greens | Fruit and nuts | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 430 | 370 | 720 | 86 | 370 | 120 | 250 | 360 | 170 | |
| 2050 | At Soc | 520 | 370 | 790 | 95 | 410 | 130 | 280 | 380 | 190 |
| 2050 | Met Soc | 460 | 240 | 720 | 86 | 370 | 120 | 250 | 450 | 170 |
| 2050 | SP Soc | 450 | 380 | 750 | 90 | 390 | 120 | 260 | 380 | 180 |
| 2050 | SL Soc | 340 | 160 | 630 | 75 | 330 | 100 | 220 | 510 | 150 |
Determine 17. Common calorific demand by meals group for meat in 2020 and in 2050 for the 4 web zero society eventualities (kilocalories per capita per day

Determine 17 knowledge: Common calorie consumption per capita per day
| Beef | Lamb | Pork | Processed pork | Poultry | Different processed meats | Cultured meat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 86 | 29 | 57 | 29 | 170 | 57 | 0 | |
| 2050 | At Soc | 87 | 29 | 63 | 32 | 190 | 63 | 55 |
| 2050 | Met Soc | 57 | 19 | 57 | 29 | 170 | 57 | 67 |
| 2050 | SP Soc | 90 | 30 | 60 | 30 | 180 | 60 | 0 |
| 2050 | SL Soc | 38 | 13 | 50 | 25 | 150 | 50 | 15 |
Pushed by larger incomes and high-consumption existence, the common calorific consumption within the atomised society grows by round 10% by 2050. The self-preservation society sees a smaller enhance, because of the decrease ranges of earnings progress. The sluggish lane society is the one state of affairs that sees a lowering whole common calorific consumption by 2050, by almost 13%. That is pushed largely by the discount in meat and dairy consumption (see under), but in addition due to lowered discretionary earnings. The sluggish lane society broadly follows the federal government suggestion of 2250 day by day energy (kcal) per particular person on common, with a ‘buffer’ of 250 kcal to account for added wants from extra lively existence in that state of affairs.
By meals group, the most important variations between eventualities are in meat and dairy and in cultured meat, the latter dealing with excessive technological uncertainty and untested buyer demand. Excessive ranges of technological growth within the metropolitan and atomised societies signifies that cultured meat begins to function in diets by 2050, however the contribution is modest. Meat and dairy consumption falls most within the sluggish lane society, by round 50% in comparison with 2020, due to environmental consciousness, a desire for wholesome existence, and decrease incomes (though the earnings relationship just isn’t explicitly modelled). There’s a smaller discount in meat and dairy consumption within the metropolitan society (of a 3rd from at present) with larger incomes stopping additional drops. Meat and dairy consumption stays at at present’s ranges within the self-preservation society.
Desk 7 units out a set of key levers and their settings for the meals and land use sector.
Desk 7. An illustrative set of levers for the meals and land use sector, which have been used within the sectoral mannequin (extra element is supplied in Annex 4)
Meals and land use enter lever settings
| Lever (Unit) | Most up-to-date values | Highest | Lowest |
| Meat consumption (proportion discount in meat consumption) | Pink and processed meat consumption met the utmost suggestion for adults of 66g per day (2020) | Situation: SL Soc; Worth: -0.5; Rationale: Meat consumption is low, and many individuals have transitioned to plant-based diets; Proof: CCC (2020) Sixth Carbon Price range Recommendation, Balanced Web Zero Pathway assumption. | Situation: SP Soc; Worth: No/minimal change from present values.; Rationale: Meat consumption has remained secure and alternate options, together with cultured meat, have didn’t take off.; Proof: Primarily based on Nationwide Food plan and Diet survey (proportion of calorific consumption from every meals group) with the belief that that is maintained to 2050. |
| Meals self-sufficiency (manufacturing to provide ratio for all meals in UK) | 60% (2020) | Situation: SL Soc; Worth: 0.75;Rationale: Extra meals is grown within the UK for home consumption; Proof: Primarily based on the final highest meals production-to-supply ratio of 75% in 1991. | Situation: SP Soc; Worth: No/minimal change from present values.; Rationale: Some farms have grow to be unviable (exacerbated by excessive climate occasions like drought and flooding), rising the UK’s reliance on imports.; Proof: Primarily based on present ranges of self-sufficiency. |
| Meals waste (% of avoidable meals waste fraction) | 9.5Mt per 12 months (2020) | Situation: SL Soc; Worth: 95,000t per 12 months (-99%); Rationale: Elimination of all avoidable meals waste.; Proof: Extrapolation of latest meals waste discount traits to 2050. | Situation: At Soc; Worth: No/minimal change from present values.; Rationale: Present charges of meals waste are maintained to 2050. No incentive to cut back.; Proof: Primarily based on present charges of meals waste. |
Methods pondering throughout sectors
Methods pondering is a method that may assist to grasp the interactions inside a posh system, and the potential penalties if there are modifications inside that system. It may be significantly useful to coverage makers when pondering by way of the broader implications of various coverage interventions, or the impacts of various eventualities. Methods pondering is already getting used throughout authorities within the UK, together with within the web zero technique.3 GO-Science has additionally revealed steerage on its use to assist promote extra widespread software in UK coverage making.
On this challenge, many such systemic relationships inside every sector are already dealt with by the sectoral fashions. Nonetheless, methods pondering was additionally used to discover the interactions between completely different sectors, significantly the place broader societal modifications might affect multiple sector. Right here we spotlight a number of examples for example the method. These are essential case research that had been explicitly utilized in our evaluation, representing the consequences of key drivers of change inside the eventualities, however there are lots of others that coverage makers might think about.
The instance in Determine 18 exhibits how digital interactions work together with journey and heating demand. Steerage on studying methods maps has been revealed by GO-Science.
Determine 18. The impacts of digital interplay on vitality use, through transport and constructing sectors

Since distant working elevated through the COVID-19 pandemic, a number of research have proven that reductions in transport vitality demand (as a result of much less commuting and enterprise journey) might be offset by will increase in house heating vitality demand. Whereas the web impacts on vitality use could also be small, representing such a change in web zero evaluation is probably going essential, as shifting vitality use from one sector to a different might imply a distinct vitality supply is used or that it’s used at a distinct time of day. These modifications might require completely different supportive insurance policies.
Determine 19 exhibits one other instance of how earnings progress and reshoring of producing might have an effect on each journey demand and the variety of automobiles produced within the UK, each of which might enhance general vitality demand.
Determine 19. The impacts of earnings progress and reshoring on vitality use, through transport and {industry} sectors

Determine 20 exhibits one other instance of how home meals manufacturing and ranges of meat consumption might have an effect on land availability within the UK, which might then each enhance residual emissions and cut back the potential for carbon removals from afforestation and bioenergy crop manufacturing. Taken collectively, this might considerably enhance the extent of direct air seize know-how that’s wanted.
Systemic relationships that contain competitors for a restricted provide of a selected vitality supply are additionally already captured inside UKTM (the vitality system mannequin used to calculate how web zero would probably be met in every state of affairs). The diagrams proven right here might be prolonged for example a few of these relationships. For instance, if there’s much less bioenergy obtainable, this might enhance the required quantity of electrical energy technology and hydrogen manufacturing.
Determine 20. The impacts of home meals manufacturing and meat consumption on direct air seize necessities, through meals and land use sectors

4. Implications for web zero
What do these potential future eventualities imply for the UK’s emissions in 2050? How will assembly web zero differ between eventualities? This part presents the outputs from the fashions and discusses the vitality system implications for reaching web zero. All our eventualities meet web zero, however some have a lot larger price and supply challenges than others. We additionally discover there’s variation within the wider impacts of assembly web zero (for instance, on well being), and within the dangers of lacking web zero between the eventualities.
4.1 Recap of modelling method
As described in Chapters 2 and 3, we translated the state of affairs narratives right into a set of modelling assumptions. Part 3.5 supplied key examples of how the variations between state of affairs narratives had been translated right into a set of cross-cutting assumptions and detailed ‘levers’ inside the 4 sectoral fashions. The total element on these assumptions is roofed in Annex 4.
Utilizing the UKTM mannequin, we then recognized how web zero and interim carbon budgets might be met by way of rollouts of know-how and vitality infrastructure, given the calls for and know-how availability in every state of affairs. UKTM calculates the bottom price method of assembly web zero and offers detailed perception on how the goal is met and what the prices are.
Unproven web zero applied sciences
Inside this chapter, we confer with commercially ‘unproven web zero applied sciences’, that are a set of applied sciences which are within the early levels of growth, and there’s a excessive diploma of uncertainty over how, whether or not and when they are often scaled-up and commercialised to ship cost-effective emissions reductions. Key examples of those, together with a really transient overview of the present state of growth, are supplied under:
- Carbon seize and storage (CCS): CCS is broadly recognised as enjoying a key position in assembly emissions discount targets, significantly within the context of commercial processes that straight emit CO2 and probably in electrical energy technology utilizing fossil fuels. CCS is technically mature for particular functions (reminiscent of enhanced oil restoration) however has not been deployed on a big scale. Value estimates for industrial CCS are extremely unsure, with estimates starting from £30/tCO2 to £330/tCO2, and these prices can differ by location and by web site.
- Bioenergy with carbon seize and storage (BECCS): Burning bioenergy fuels in a plant with CCS would offer unfavourable emissions because the carbon eliminated by the crop throughout its life is sequestered. Present biomass-to-power crops usually battle with sustaining constant home biomass provide with low life-cycle emissions, variable high quality of sourced biomass and low energy plant effectivity, that are among the many major boundaries to carbon unfavourable BECCS. , , , There’s appreciable variation in BECCS prices relying on location, dimension and feedstock prices, price of capital, and the power to retrofit present amenities.2 Some BECCS applied sciences are at larger ranges of readiness than others, which implies traders will see a few of them to be decrease threat.2 Nonetheless, larger technological maturity doesn’t relieve BECCS provide chain issues reminiscent of excessive life-cycle emissions of imported biomass145 and competitors with different land makes use of (reminiscent of for meals crops).
- Direct air seize (DAC): DAC know-how permits CO2 to be extracted straight from the air and saved utilizing a liquid or stable solvent. This course of requires important quantities of electrical energy and heating gasoline. The primary commercially prepared DAC plant, able to capturing 900tCO2 per 12 months, opened in 2017.140 Thus far, this know-how has had restricted funding, however there are drives to develop these applied sciences additional (see BEIS 2022). In keeping with the Local weather Change Committee’s sector abstract on greenhouse gasoline removals within the Sixth Carbon Price range (2020), in a extremely formidable state of affairs, deployment might begin in 2035 and prices might attain £120/tCO2 by 2050.1 In a much less formidable state of affairs, deployment might begin nearer to 2040 and prices might attain £180/tCO2 by 2050 (used because the CCC’s central assumption). The Worldwide Vitality Company highlights excessive uncertainty in estimating DAC prices, with a spread of between £80/tCO2 and £800/tCO2.
- Artificial fuels for aviation: Elevated use of power-to-liquid fuels is considered as a key longer-term technique for lowering carbon emissions from aviation, in comparison with short-term measures, reminiscent of curbing demand for flying. , , Nonetheless, key boundaries to widespread use embrace excessive prices and vitality necessities for manufacturing. In keeping with the US Nationwide Academies of Science report on Adverse Emissions Applied sciences and Dependable Sequestration (2019), there will probably be few alternate options to chemical fuels for business aviation by 2050.142 The Division for Transport launched the £15 million Inexperienced Fuels, Inexperienced Skies competitors in March 2021, targeted on sustainable aviation fuels (with winners introduced in December 2021). The 2021 Autumn Price range and Spending Overview additionally dedicated £180 million to kick-start growth of commercial-scale UK sustainable aviation gasoline. These, and different initiatives such because the £1 million Web Zero Transatlantic Flight Fund, might assist in creating gasification routes to jet gasoline and have the potential to create jobs within the sector.141 This funding helps the early-stage growth of those initiatives, and there’s nonetheless uncertainty round the way forward for these fuels.
Given the long run uncertainty of their feasibility, prices and believable scale, we pay explicit consideration to the position these applied sciences play in assembly web zero in every state of affairs.
4.2 Assembly web zero
Emissions
Determine 21. Greenhouse gasoline emissions by sector in 2020 and for the 4 web zero society eventualities in 2030 and 2050 (MtCO2e/12 months)

Determine 21 knowledge: Common calorie consumption per capita per day
| Beef | Lamb | Pork | Processed pork | Poultry | Different processed meats | Cultured meat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 86 | 29 | 57 | 29 | 170 | 57 | 0 | |
| 2050 | At Soc | 87 | 29 | 63 | 32 | 190 | 63 | 55 |
| 2050 | Met Soc | 57 | 19 | 57 | 29 | 170 | 57 | 67 |
| 2050 | SP Soc | 90 | 30 | 60 | 30 | 180 | 60 | 0 |
| 2050 | SL Soc | 38 | 13 | 50 | 25 | 150 | 50 | 15 |
UKTM was used to evaluate how all 4 eventualities might attain web zero by 2050, in addition to interim carbon budgets. This was achieved as proven in Determine 21, with a mean annual discount in greenhouse gasoline emissions of three% per 12 months between 2020 and 2050.
Determine 22. Greenhouse gasoline emissions by sector in 2050 for the 4 web zero society eventualities (MtCO2e/12 months)

Determine 22 knowledge: Greenhouse gasoline emissions, MtCO2e/12 months
| Energy | Trade | Gasoline provide | Warmth and buildings | Home transport | Worldwide aviation and transport | Agriculture and land use | Waste and F-gases | Removals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At Soc | -4 | 7 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 19 | 36 | 14 | -78 |
| Met Soc | 0 | 18 | 6 | 10 | 5 | 18 | 8 | 14 | -80 |
| SP Soc | 0 | 11 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 21 | 14 | -62 |
| SL Soc | 0 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 14 | -6 | 13 | -45 |
The extent of residual emissions in 2050 varies throughout sectors in every state of affairs (Determine 22), as does how a lot this must be balanced by carbon removals. Engineered removals are usually extra possible in technologically superior eventualities (such because the metropolitan society) whereas within the low progress eventualities (significantly the self-preservation society) even a small quantity of engineered carbon removals pushes the bounds of feasibility (see carbon seize and storage part under).
The atomised society has excessive ranges of residual emissions from agriculture, largely as a result of larger meat consumption, and from worldwide aviation and transport as a result of worldwide journey preferences on this state of affairs. Residual emissions in {industry} are low, regardless of excessive ranges of vitality use (see under), as a result of carbon seize applied sciences are used to sequester CO2 from this sector. Total, the comparatively excessive stage of residual emissions needs to be offset by excessive ranges of carbon elimination, requiring key unproven web zero applied sciences to be pushed above what are at the moment thought of to be believable ranges (see carbon seize and storage part under).
The metropolitan society has comparatively excessive ranges of residual emissions from {industry}, buildings and worldwide aviation. Residual {industry} and aviation emissions are pushed by larger GDP and earnings progress on this state of affairs. Residual buildings emissions come from excessive vitality use within the non-domestic sector. Agriculture and land use emissions are comparatively low on this state of affairs, partly as a result of afforestation offering some unfavourable emissions. Once more, excessive residual emissions have to be offset by excessive ranges of carbon elimination.
The sluggish lane society sees comparatively low ranges of residual emissions in all sectors, as a result of low ranges of vitality use and different societal modifications (reminiscent of lowered worldwide journey), which reduces residual emissions from aviation. As well as, the excessive ranges of afforestation and low ranges of meat consumption imply that emissions from agriculture and land use are web unfavourable. This implies this state of affairs wants the bottom stage of technologically eliminated carbon.
Our evaluation takes a territorial perspective on emissions, contemplating solely emissions produced inside the UK borders. In different phrases, emissions and vitality related to sourcing supplies and elements outdoors the nation usually are not modelled (for instance, for manufacturing EVs or wind generators). Equally, the place eventualities (such because the sluggish lane and metropolitan societies) depend on some imported biomass for decarbonisation, its lifecycle emissions are more likely to be larger than these of home biomass. Nonetheless, it’s value noting that the decrease imports within the atomised and self-preservation societies would cut back the UK’s consumption-based emissions.
Vitality use
All eventualities present reductions in whole ultimate vitality by 2050 (Determine 23), largely because of the electrification of sectors reminiscent of warmth and transport, which permits vitality for use extra effectively. Nonetheless, in some eventualities reductions in demand additionally play a task.
Determine 23. Complete ultimate vitality use in 2020–2050 (Petajoule/12 months) for the 4 web zero society state of affairs

Determine 23 knowledge: Complete ultimate vitality use, PJ/12 months
| 2020 | 2025 | 2030 | 2035 | 2040 | 2045 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At Soc | 5600 | 5500 | 5000 | 4600 | 4500 | 4500 | 4600 |
| Met Soc | 5600 | 5300 | 4700 | 4200 | 3900 | 3700 | 3500 |
| SP Soc | 5700 | 5300 | 4600 | 4000 | 3600 | 3400 | 3300 |
| SL Soc | 5700 | 5200 | 4500 | 3800 | 3300 | 3000 | 2800 |
Between 2020 and 2050, whole ultimate vitality use falls by 45% within the sluggish lane society and by 18% within the atomised society. It’s notable that demand reductions within the atomised society stage off round 2035 and vitality demand will increase slowly after 2045, as effectivity enhancements start to be offset by will increase in demand (significantly as a result of reshoring of producing). The self-preservation and metropolitan societies present comparable ranges of demand discount general, however for various causes: the metropolitan society has larger calls for (largely as a result of financial progress), offset by larger effectivity enhancements.
Whereas it could be helpful to have the ability to attribute variations in ultimate vitality calls for between the eventualities to particular sectoral levers, the advanced interactions between levers inside UKTM imply that it isn’t potential to hint this element by way of to the ultimate consequence. Instead, we current a disaggregation by sector of how effectivity modifications (for instance, house insulation or extra fuel-efficient automobiles) work together with modifications in exercise or outputs (reminiscent of distance travelled, or the amount of products manufactured) to supply a web change in vitality use. That is proven in Determine 24. Whereas it is just possible to hold out this evaluation for vitality use, is essential to notice that whole vitality use and the prices of assembly web zero are correlated, so the largest vitality reductions proven under will sometimes correspond to the largest price financial savings.
Determine 24. Decomposition of vitality demand modifications (2020-2050) by sector for the 4 web zero society eventualities

Determine 24 knowledge
| Sector exercise | Effectivity | Web vitality change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buildings- home | AT Soc | 5.40% | -18.00% | -12.00% |
| Buildings- home | Met Soc | -37.00% | -7.70% | -45.00% |
| Buildings- home | SP Soc | -4.10% | -22.00% | -26.00% |
| Buildings- home | SL Soc | -9.60% | -33.00% | -43.00% |
| Buildings- business | AT Soc | 3.80% | -38.00% | -34.00% |
| Buildings- business | Met Soc | 41.00% | -50.00% | -8.70% |
| Buildings- business | SP Soc | 3.70% | -39.00% | -35.00% |
| Buildings- business | SL Soc | 19.00% | -48.00% | -29.00% |
| Transport | At Soc | 50.00% | -79.00% | -29.00% |
| Transport | Met Soc | 23.00% | -65.00% | -42.00% |
| Transport | SP Soc | 17.00% | -67.00% | -50.00% |
| Transport | SL Soc | 2.00% | -56.00% | -54.00% |
| Work and {industry} | At Soc | 25.00% | -4.70% | 20.00% |
| Work and {industry} | Met Soc | -4.10% | -24.00% | -28.00% |
| Work and {industry} | SP Soc | -22.00% | -16.00% | -39.00% |
| Work and {industry} | SL Soc | -40.00% | -11.00% | -51.00% |
Key insights embrace:
- The constructed surroundings: Warmth pump and insulation rollouts in all eventualities present important effectivity enhancements. Within the buildings sector, exercise is a mix of common temperatures and floorspace, in addition to use {of electrical} units. The atomised society sees the most important output enhance general, however the lowest for business buildings largely as a result of excessive ranges of house working. Conversely, the metropolitan society sees comparatively excessive will increase in heating demand in business buildings, as office-based working sees a resurgence, however a big lower in residential heating demand as a result of the next proportion of individuals dwelling in flats and different dwellings with decrease floorspace.
- Journey and transport: All eventualities see massive effectivity enhancements, primarily from the rollout of electrical automobiles. Within the transport sector, modifications in exercise are basically modifications in distance travelled. All eventualities see will increase in distance travelled, however the enhance varies considerably. The rise within the sluggish lane society is primarily as a result of inhabitants progress, with distance travelled per particular person falling as a result of folks working and conducting leisure actions nearer to house. The big enhance within the atomised society is because of elevated long-distance journey attributable to an uptake of CAVs and an increase in international holidays.
- Work and {industry}: The atomised society is the one state of affairs that sees will increase in output, as a result of excessive GDP and family earnings progress, and reshoring of producing. The metropolitan society sees essentially the most substantial effectivity features, enabled by excessive ranges of analysis and growth funding, but in addition small web output reductions as round financial system measures offset calls for pushed by GDP and family earnings progress. Vitality use reductions within the sluggish lane and self-preservation societies are largely pushed by reductions in output as a result of decrease financial progress in each circumstances, and likewise due to round financial system measures within the sluggish lane society.
As an example which modifications make the largest distinction between the eventualities, we focus right here on the atomised and sluggish lane societies as these are the eventualities with the best and lowest vitality calls for general. Desk 8 exhibits the distinction between these two eventualities in activity-based change, efficiency-based change and whole vitality change (activity-based and efficiency-based mixed) for every sector. It additionally exhibits the proportion every sector contributes to the general distinction in vitality change between the atomised and sluggish lane societies.
Desk 8. Variations within the 2020–2050 vitality demand modifications within the atomised vs sluggish lane societies. A unfavourable quantity signifies a bigger discount in vitality use from 2020 to 2050 within the sluggish lane society in comparison with the atomised society
| Sector | Exercise-based vitality change, PJ | Effectivity-based vitality change, PJ | Complete vitality change, PJ | Share of whole, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trade | -553 | -57 | -610 | 37% |
| Home buildings | -293 | -300 | -593 | 36% |
| Transport | -892 | 433 | -459 | 28% |
| Business buildings | 122 | -99 | 23 | -1% |
| Meals and land use | -26 | 19 | -7 | 0% |
The {industry} sector makes the largest general distinction, as reshoring within the atomised society will increase vitality demand. Round financial system measures within the sluggish lane society have the other impact. That is mirrored in massive variations in exercise ranges versus effectivity inside this sector.
Home buildings are the sector with the second largest distinction general between the 2 eventualities, pushed by in depth use of hydrogen boilers within the atomised society versus rather more environment friendly warmth pumps within the sluggish lane society.
The transport sector exhibits the largest distinction in exercise ranges between the 2 eventualities. Nonetheless, this distinction is offset by the atomised society benefitting from extra environment friendly automobiles.
Lastly, variations within the meals and land use sector are low when it comes to vitality use however massive when it comes to emissions (see emissions part above). Within the atomised society, this sector has excessive residual emissions, largely as a result of livestock manufacturing to match excessive meat demand. In contrast, within the sluggish lane society, the meals and land use sector has web unfavourable emissions, as a result of low meat consumption and in depth tree-planting.
Vitality combine by state of affairs
Determine 25. Complete ultimate vitality use by vitality supply in 2020–2050 (Petajoules/12 months) for the 4 web zero society eventualities

Determine 25 knowledge: Complete ultimate vitality consumption, PJ/12 months
| Fuel | Coal | Oil | Non-energy use | Syn. kerosene | Ammonia | Wastes | Photo voltaic | Hydrogen | Biogas | Biofuels | Bioenergy | Electrical energy | Warmth | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At Soc | 2020 | 2200 | 200 | 2000 | 110 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0.88 | <0.01 | 49 | 1.8 | <0.01 | 1000 | 50 |
| At Soc | 2030 | 2000 | 93 | 1200 | 110 | 15 | 8 | 53 | 7.5 | 59 | 62 | 28 | 57 | 1300 | 80 |
| At Soc | 2040 | 670 | 73 | 400 | 99 | 67 | 37 | 52 | 27 | 690 | 69 | 23 | 53 | 2100 | 110 |
| At Soc | 2050 | 4.8 | 48 | 130 | 100 | 190 | 110 | 5.5 | 26 | 1700 | 27 | 13 | 9.5 | 2100 | 110 |
| Met Soc | 2020 | 2200 | 210 | 2000 | 110 | 0 | 0 | 64 | 0 | <0.01 | 48 | 1.8 | <0.01 | 1000 | 79 |
| Met Soc | 2030 | 1600 | 170 | 1300 | 97 | 8.5 | <0.01 | 67 | 0 | 2.6 | 57 | 35 | 38 | 1100 | 260 |
| Met Soc | 2040 | 1000 | 64 | 450 | 74 | 61 | <0.01 | 43 | <0.01 | 65 | 64 | 100 | 110 | 1400 | 460 |
| Met Soc | 2050 | 410 | 40 | 170 | 58 | 160 | <0.01 | 65 | <0.01 | 400 | 65 | 98 | 83 | 1600 | 500 |
| SP Soc | 2020 | 2100 | 200 | 2000 | 110 | 0 | 0 | 69 | 0.69 | <0.01 | 48 | 1.8 | <0.01 | 1000 | 51 |
| SP Soc | 2030 | 1700 | 170 | 1300 | 90 | 0 | 4.4 | 72 | 5.5 | 5.6 | 61 | 46 | 30 | 1100 | 75 |
| SP Soc | 2040 | 700 | 55 | 360 | 61 | 42 | 27 | 51 | 27 | 110 | 60 | 140 | 84 | 2100 | 110 |
| SP Soc | 2050 | 68 | 48 | 1.5 | 50 | 240 | 86 | 54 | 45 | 240 | 78 | 44 | 23 | 2500 | 110 |
| SL Soc | 2020 | 2200 | 210 | 2000 | 110 | 0 | 0 | 65 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 48 | 1.8 | <0.01 | 1000 | 93 |
| SL Soc | 2030 | 1700 | 150 | 1300 | 84 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 55 | 0.038 | 6.6 | 56 | 40 | 39 | 950 | 270 |
| SL Soc | 2040 | 890 | 40 | 410 | 52 | 26 | <0.01 | 36 | 0.69 | 68 | 65 | 170 | 140 | 1200 | 560 |
| SL Soc | 2050 | 180 | 36 | 230 | 34 | 65 | <0.01 | 63 | 12 | 190 | 66 | 120 | 140 | 1400 | 570 |
All eventualities see the usage of fossil fuels fall away by 2050, however the low carbon vitality sources used differ by state of affairs, significantly for house heating. Excessive ranges of hydrogen use within the atomised society is pushed by comparatively widespread use of hydrogen boilers, as on this state of affairs wealthier households in older homes had been prepared to pay extra for heating prices to keep away from the disruption of switching to a warmth pump. Warmth vitality is used within the district heating methods that see widespread deployment in city areas within the sluggish lane and metropolitan societies. Extra electrical energy is used within the self-preservation society, as a result of electrical boiler methods are utilized in some circumstances as a result of decrease ranges of warmth pump availability and demand on this state of affairs.
Biofuel and bioenergy use varies throughout the eventualities. Within the atomised and self-preservation societies, this drops considerably in the direction of 2050 as these eventualities have much less land obtainable as a result of extra livestock-focussed farming practices. These eventualities use artificial kerosene in aviation, as an alternative of biofuels, though it’s value noting that is an unproven web zero know-how.
Carbon seize and storage
This part covers engineered carbon unfavourable removals (reminiscent of BECCS and DAC), land-based options, in addition to fossil CCS the place whole emissions from energy and {industry} are considerably lowered by capturing and storing exhaust CO2.
Determine 26. Carbon dioxide sequestration by know-how in 2020–2050 (MtCO2/12 months) for the 4 web zero society eventualities

Determine 26 knowledge
Engineered removals, MtCO2/12 months
| Direct Air Seize (addition) | Direct Air Seize (DAC) | BECCS – Energy technology | BECCS – H2 manufacturing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At Soc | 2020 | 0 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 |
| At Soc | 2025 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| At Soc | 2030 | 0 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| At Soc | 2035 | 0 | -0.76 | -3.9 | -2.9 |
| At Soc | 2040 | -1.9 | -7.8 | -3.9 | -5.8 |
| At Soc | 2045 | -11 | -14 | -3.9 | -9.7 |
| At Soc | 2050 | -45 | -18 | -2.4 | -13 |
| Met Soc | 2020 | 0 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 |
| Met Soc | 2025 | 0 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| Met Soc | 2030 | 0 | -0.06 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| Met Soc | 2035 | >-0.01 | -0.18 | -0.69 | -6 |
| Met Soc | 2040 | >-0.01 | -3 | -11 | -12 |
| Met Soc | 2045 | >-0.01 | -23 | -11 | -23 |
| Met Soc | 2050 | >-0.01 | -29 | -11 | -40 |
| SP Soc | 2020 | 0 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 |
| SP Soc | 2025 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SP Soc | 2030 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SP Soc | 2035 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SP Soc | 2040 | -2 | 0 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SP Soc | 2045 | -11 | 0 | >-0.01 | -11 |
| SP Soc | 2050 | -46 | 0 | >-0.01 | -13 |
| SL Soc | 2020 | 0 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 |
| SL Soc | 2025 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SL Soc | 2030 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SL Soc | 2035 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SL Soc | 2040 | 0 | 0 | >-0.01 | -0.14 |
| SL Soc | 2045 | 0 | 0 | -9 | -8.8 |
| SL Soc | 2050 | 0 | 0 | -26 | -19 |
Fossil CCS, MtCO2/12 months
| Fossil CCS – Energy technology | Fossil CCS – H2 manufacturing | Fossil CCS – Trade | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At Soc | 2020 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| At Soc | 2025 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | -0.37 |
| At Soc | 2030 | >-0.01 | -3.7 | -1.3 |
| At Soc | 2035 | -2.5 | -9.9 | -3.7 |
| At Soc | 2040 | -2.5 | -24 | -7.4 |
| At Soc | 2045 | -1.6 | -51 | -11 |
| At Soc | 2050 | -3.5 | -71 | -10 |
| Met Soc | 2020 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| Met Soc | 2025 | >-0.01 | -0.11 | -0.49 |
| Met Soc | 2030 | >-0.01 | -0.11 | -2.4 |
| Met Soc | 2035 | -0.11 | -0.038 | -5.1 |
| Met Soc | 2040 | -1.6 | -0.038 | -8.3 |
| Met Soc | 2045 | -1.4 | -2.7 | -8.5 |
| Met Soc | 2050 | -2 | -4.6 | -7.1 |
| SP Soc | 2020 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SP Soc | 2025 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SP Soc | 2030 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | -0.27 |
| SP Soc | 2035 | -0.11 | >-0.01 | -0.79 |
| SP Soc | 2040 | -0.11 | -0.72 | -2 |
| SP Soc | 2045 | -1.4 | -0.24 | -4.3 |
| SP Soc | 2050 | -0.11 | -0.24 | -5.8 |
| SL Soc | 2020 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SL Soc | 2025 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SL Soc | 2030 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 | >-0.01 |
| SL Soc | 2035 | -0.11 | >-0.01 | -0.47 |
| SL Soc | 2040 | -0.11 | -1.8 | -1.5 |
| SL Soc | 2045 | -0.2 | -2 | -3.7 |
| SL Soc | 2050 | -0.11 | -0.67 | -5.5 |
Land-based removals, MtCO2/12 months
| Soil sequestration | Vitality forestry | Afforestation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At Soc | 2020 | -0.74 | -0.2 | -0.037 |
| At Soc | 2025 | -1.6 | -0.9 | -0.5 |
| At Soc | 2030 | -2.5 | -1.2 | -1.3 |
| At Soc | 2035 | -3 | -1.2 | -2 |
| At Soc | 2040 | -3.3 | -1.2 | -2.6 |
| At Soc | 2045 | -3.5 | -1.4 | -3 |
| At Soc | 2050 | -3.8 | -1.5 | -3.1 |
| Met Soc | 2020 | -0.74 | -0.12 | -0.037 |
| Met Soc | 2025 | -1.6 | -2.5 | -0.64 |
| Met Soc | 2030 | -2.5 | -6.2 | -3.2 |
| Met Soc | 2035 | -3 | -8.5 | -6.9 |
| Met Soc | 2040 | -3.3 | -8.8 | -10 |
| Met Soc | 2045 | -3.5 | -8.6 | -14 |
| Met Soc | 2050 | -3.8 | -8.4 | -18 |
| SP Soc | 2020 | -0.74 | -0.2 | -0.037 |
| SP Soc | 2025 | -1.6 | -2.5 | -0.57 |
| SP Soc | 2030 | -2.5 | -3.7 | -2.2 |
| SP Soc | 2035 | -3 | -4.2 | -4.5 |
| SP Soc | 2040 | -3.3 | -4.2 | -6.6 |
| SP Soc | 2045 | -3.5 | -4.4 | -8.8 |
| SP Soc | 2050 | -3.8 | -5.3 | -11 |
| SL Soc | 2020 | -0.67 | 0 | -0.037 |
| SL Soc | 2025 | -1.5 | 0.0017 | -0.71 |
| SL Soc | 2030 | -2.2 | -6.7 | -4.1 |
| SL Soc | 2035 | -3 | -12 | -9.4 |
| SL Soc | 2040 | -3.3 | -13 | -14 |
| SL Soc | 2045 | -3.5 | -12 | -19 |
| SL Soc | 2050 | -3.8 | -12 | -25 |
There are massive variations between the 4 eventualities in each the technique of capturing carbon dioxide, in addition to the quantities captured (Determine 26). These depend upon the scale of the vitality system, stage of technological growth, and availability of land for carbon sequestration.
One essential function of Determine 26 is the ‘direct air seize (addition)’ class, which was used as a backstop know-how to satisfy web zero after all the believable measures had been used up. For instance, within the atomised society, it was assumed that -18MtCO2 would plausibly be obtainable by 2050 on this state of affairs, however to satisfy web zero an extra -45MtCO2 (greater than 200% additional) was discovered to be required. The same stage of extra DAC is required within the self-preservation society and, given the low ranges of know-how growth on this state of affairs, this might probably be extraordinarily difficult to ship. That is an illustration of how difficult it could be to satisfy web zero in these eventualities.
The most important quantity of carbon eliminated by way of engineering in 2050 is within the atomised society, adopted by the metropolitan society. Land-based carbon elimination is most dominant within the sluggish lane society, and within the metropolitan society.
There’s little land obtainable for bioenergy and afforestation within the atomised society, a state of affairs that additionally has larger vitality demand than the opposite eventualities. For these causes, the atomised society sees fast deployment of hydrogen produced from fossil fuels and direct air seize (DAC). Moreover, because the vitality use by the {industry} sector within the atomised society stays excessive, this state of affairs depends closely on CCS, which is nearly twice the quantity of {industry} CCS within the sluggish lane and self-preservation societies.
The metropolitan society additionally makes use of important quantities of DAC, however the important thing engineered elimination answer on this state of affairs is bioenergy with carbon seize and storage (BECCS) for hydrogen manufacturing, accounting for round 40% of the state of affairs’s CO2 sequestration in 2050. The metropolitan society additionally advantages from an intensive tree-planting programme, in comparison with the atomised society.
The sluggish lane society doesn’t have the choice of utilizing DAC, due to decrease ranges of technological growth. There’s important land capability for reforestation however questions stay about how this might be paid for in a low-growth world. The self-preservation society, the place carbon removals are barely possible technologically and are available simply earlier than 2050 in an try to satisfy web zero, makes use of a extra even mixture of engineered removals and land-based removals, in comparison with the atomised and metropolitan societies.
Whereas the eventualities have 2050 as their endpoint, large quantities of carbon must be captured yearly after 2050 and saved indefinitely, until vitality demand is lowered and the vitality system is decarbonised by way of different measures. The danger of counting on unproven know-how (reminiscent of DAC) is important given the potential of unexpected technical boundaries. For applied sciences with a barely extra sure outlook (reminiscent of CCS), there stays a threat of related excessive prices and vitality use, even in 2050.
Within the meantime, extreme deal with such unsure applied sciences would possibly crowd out progress on emission reductions that may be achieved within the brief time period with extra confidence. That is mentioned in additional element in Part 4.4.
Land use
Most of the measures required to satisfy web zero will want a big quantity of land, together with for renewable electrical energy infrastructure, bioenergy crops, and afforestation. Land is a finite useful resource and there’s competitors for this useful resource from different actions (reminiscent of agriculture and housebuilding). Constructing vitality infrastructure additionally requires a planning course of, which may be time consuming and topic to problem (together with from native residents). The extra land wanted for infrastructure, the much less land is out there for different makes use of and the larger the chance of planning-related delays and challenges. Due to this fact, coverage makers might want to think about the general quantity of land required for measures to satisfy web zero in numerous future eventualities.
Coverage makers might also want to think about the precise land-use combine concerned in future eventualities. Some makes use of might have wider advantages (reminiscent of afforestation for biodiversity). This part offers illustrative, high-level estimates of the quantity of land taken up by completely different makes use of in every state of affairs and units out the probably implications.
Desk 9 exhibits the land taken up by agriculture, bioenergy crops and afforestation in every state of affairs in 2050, as a proportion of the full UK land space. For comparability, the proportion of UK land used for agriculture in 2022 is 71%.
Desk 9. Space taken up by agriculture, bioenergy crops and afforestation as a proportion of UK land in 2050
| Space taken up as a proportion of UK land space in 2050 | Atomised | Metropolitan | Self-preservation | Sluggish lane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | 82% | 73% | 79% | 66% |
| Bioenergy crops | 0% | 6% | 2% | 6% |
| Afforestation | 1% | 6% | 3% | 9% |
| Complete* | 83% | 84% | 84% | 80% |
*Constituent elements showing to not sum to totals is a results of rounding
Desk 10 exhibits the land taken up by the principle onshore and offshore renewable vitality sources in every state of affairs in 2050 , as a proportion of the full UK land space. That is proven individually to the opposite land makes use of above, as they are often mixed (for instance, onshore wind can be utilized alongside crops or livestock). Offshore infrastructure doesn’t compete for land used for different functions (reminiscent of agriculture or housing), however there’s a finite quantity of area within the waters across the UK, and there are some environmental impacts from constructing infrastructure offshore, so it is very important think about the amount required. Offshore floor space necessities are given as a proportion of UK land mass for ease of comparability.
Desk 10. Space taken up by key renewable electrical energy capability as a proportion of UK land in 2050
| Space taken up by renewables as a proportion of UK land space in 2050 | Atomised | Metropolitan | Self-preservation | Sluggish lane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onshore wind and photo voltaic | 3% | 2% | 5% | 2% |
| Offshore wind | 8% | 4% | 5% | 2% |
In all of the eventualities modelled, not less than 2% of land is required for renewable electrical energy. This end result might be prevented by, for instance, rising the quantity of nuclear technology (noting this might additionally include planning or supply challenges). As famous above, land-uses may also be mixed (for instance, rooftop photo voltaic or crops alongside wind generators).
The atomised society sees the best general agricultural land use as a result of excessive ranges of meat consumption, which limits the land obtainable for bioenergy crops and afforestation. Comparatively excessive quantities of land are wanted for onshore electrical energy technology, though this might be mixed with the agricultural land use. Probably the most important energy-related impacts are for offshore wind, wanted to satisfy the comparatively excessive vitality calls for on this state of affairs, requiring an space offshore equal to eight% of the UK’s land space.
The metropolitan society has comparatively low ranges of agricultural land use as a result of decrease meat consumption, which implies bioenergy crops and afforestation can take up comparatively more room. Low ranges of onshore electrical energy capability are wanted, with the electrical energy calls for pushed by larger financial progress on this state of affairs met by comparatively excessive ranges of offshore wind.
The self-preservation society sees the best onshore electrical energy capability as a result of it has a comparatively excessive vitality demand, however with out the technological progress to roll out offshore wind to the degrees seen within the atomised and metropolitan societies. This state of affairs additionally has the second highest agricultural land use as a result of excessive ranges of meat consumption.
The sluggish lane society has the bottom general land associated to satisfy web zero as a result of its low vitality use and meat consumption. This leads to there being extra land obtainable for different functions (reminiscent of for leisure or ecotourism makes use of).
Total, the excessive stage of land and offshore area required within the atomised and self-preservation societies is more likely to create heightened supply challenges in these eventualities. It isn’t potential to deduce the worth of getting larger amount of land obtainable for different functions (reminiscent of within the sluggish lane society). It’s because it could depend upon how this land was used (for instance, whether or not it was used to generate income and/or enhance wellbeing).
System prices
System prices cowl all funding and operational expenditure related to the vitality system, together with infrastructure, gasoline, and different working prices. Such prices are lined by a mix of personal funding from vitality corporations, vitality payments paid by shoppers, and authorities funding.
Determine 27 presents the system prices in every state of affairs through two comparisons:
- as a proportion of GDP (which varies by state of affairs), reflecting the truth that larger prices are extra inexpensive to a society with larger actual incomes and related tax income; and likewise
- relative to the system prices in a baseline state of affairs by which web zero just isn’t met , recognising that constructing, sustaining, and working an vitality system will at all times characterize a big nationwide expenditure.
The baseline state of affairs used right here is identical as for the federal government’s web zero technique and solely contains authorities insurance policies which had been carried out, adopted, or deliberate as of August 2019. These insurance policies are all assumed to be carried out as deliberate, however it’s acknowledged within the web zero technique that they don’t seem to be adequate to satisfy web zero. There are additionally variations within the macro-economic assumptions on this baseline and our eventualities, not least as a result of the baseline state of affairs makes use of GDP progress assumptions from the OBR’s March 2020 financial and monetary outlook. Because of this it’s vital to check the relative, reasonably than absolute, future price modifications. However, this evaluation does permit an illustrative comparability of the prices in every state of affairs, relative to a longtime baseline.
Determine 27. Annual system prices (2019 costs, undiscounted) as a proportion of GDP for the 4 web zero society eventualities, relative to these within the baseline state of affairs (expressed as a proportion level distinction)

Determine 27 knowledge: Annual vitality system price as a proportion of GDP, relative to baseline state of affairs
| The atomised society | The metropolitan society | The self-preservation society | The sluggish lane society | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | -0.0055 | -0.0055 | -0.0055 | -0.0055 |
| 2020 | -0.0084 | -0.0083 | -0.0084 | -0.0086 |
| 2021 | -0.0046 | -0.0059 | -0.0053 | -0.0072 |
| 2022 | -0.0026 | -0.0047 | -0.0028 | -0.0058 |
| 2023 | -0.0016 | -0.0042 | -0.00059 | -0.0044 |
| 2024 | -0.0014 | -0.0044 | 0.0011 | -0.0034 |
| 2025 | -0.0014 | -0.0047 | 0.0027 | -0.0025 |
| 2026 | -0.0019 | -0.0058 | 0.0033 | -0.0031 |
| 2027 | -0.0027 | -0.0071 | 0.0035 | -0.0041 |
| 2028 | -0.0036 | -0.0084 | 0.0037 | -0.005 |
| 2029 | -0.0044 | -0.0097 | 0.0039 | -0.0059 |
| 2030 | -0.0052 | -0.011 | 0.0041 | -0.0067 |
| 2031 | -0.0028 | -0.0099 | 0.0067 | -0.0049 |
| 2032 | -0.00058 | -0.009 | 0.0093 | -0.0031 |
| 2033 | 0.0015 | -0.0082 | 0.012 | -0.0013 |
| 2034 | 0.0034 | -0.0074 | 0.014 | 0.00043 |
| 2035 | 0.0052 | -0.0066 | 0.017 | 0.0022 |
| 2036 | 0.0031 | -0.0089 | 0.016 | 0.0014 |
| 2037 | 0.0011 | -0.011 | 0.016 | 0.00076 |
| 2038 | -0.00078 | -0.013 | 0.015 | 0.00021 |
| 2039 | -0.0026 | -0.015 | 0.015 | -0.00028 |
| 2040 | -0.0044 | -0.017 | 0.015 | -0.00073 |
| 2041 | -0.0044 | -0.017 | 0.016 | -0.00016 |
| 2042 | -0.0044 | -0.018 | 0.016 | 0.00044 |
| 2043 | -0.0045 | -0.018 | 0.017 | 0.001 |
| 2044 | -0.0046 | -0.019 | 0.018 | 0.0017 |
| 2045 | -0.0047 | -0.02 | 0.019 | 0.0023 |
| 2046 | -0.0033 | -0.02 | 0.024 | 0.0034 |
| 2047 | -0.002 | -0.02 | 0.03 | 0.0044 |
| 2048 | -0.0008 | -0.02 | 0.035 | 0.0055 |
| 2049 | 0.00031 | -0.02 | 0.041 | 0.0066 |
| 2050 | 0.0013 | -0.02 | 0.046 | 0.0077 |
Assembly web zero is discovered to be most inexpensive within the metropolitan society, the place 2050 system prices as a proportion of GDP are 2 proportion level decrease than within the baseline state of affairs, in different phrases extra inexpensive than not assembly web zero. Vitality demand and financial progress have been decoupled most importantly on this state of affairs, so although the metropolitan society wants a bigger vitality system than the sluggish lane society, the upper GDP makes this extra inexpensive.
Assembly web zero can be inexpensive within the sluggish lane and atomised societies, at solely 0–1% above the baseline state of affairs in 2050. Within the sluggish lane society it is because societal modifications have led to decrease ranges of vitality demand. Within the atomised society it is because larger GDP helps to pay for the excessive ranges of know-how adoption and infrastructure wanted to satisfy web zero on this state of affairs. In distinction, the self-preservation society has neither the societal modifications to cut back demand, nor the technological innovation and financial sources to pay for it. Consequently, the 2050 system prices are 5% larger than the baseline state of affairs.
It’s also helpful to check the system prices in every state of affairs to at least one one other in 2050:
- The best price state of affairs (self-preservation) is about 7% of GDP costlier than the bottom price state of affairs (metropolitan), because of the important variations in vitality demand and the way the web zero goal is met between these eventualities.
- The atomised and metropolitan societies have the same financial progress trajectory, so the principle variations between them relate to how society is organised and what this implies for vitality effectivity and demand. The metropolitan society has a price round 2% of GDP decrease than the atomised society, as vitality demand is lowered by way of measures just like the round financial system and larger use of lively journey and public transport.
- In absolute phrases, the metropolitan society has a 20% larger system price in comparison with the sluggish lane society, largely as a result of larger vitality calls for pushed by financial progress. However when expressed as a proportion of GDP, the metropolitan society has a system price about 3 proportion factors decrease than the sluggish lane society, which means that assembly web zero will probably be extra inexpensive on this larger progress state of affairs.
You will need to acknowledge some limitations of this evaluation of prices. This contains the truth that we now have not accounted for potential unit price reductions for brand spanking new applied sciences that would come about extra quickly in eventualities the place the UK is main technologically or the place international decarbonisation drives quicker innovation. We assume price reductions over time in all eventualities, however the charges of discount are more likely to be larger within the eventualities with larger ranges of technological growth (atomised and metropolitan). Given this, we is perhaps understating the affordability of assembly web zero in these eventualities. We’ve got not been capable of robustly quantify these variations as a result of excessive ranges of uncertainty.
Assembly web zero may also probably add to GDP in methods not quantified on this report. Modelling commissioned by the CCC means that, pushed by web zero, a mix of latest capital funding, lowered fossil gasoline imports and decrease vitality costs, might add about 0.1% extra GDP progress per 12 months to 2050.9 Nonetheless, GDP is an enter assumption in our eventualities and, whereas we now have not created an in depth breakdown of what drives the assumed progress in every case, it’s believable that this 0.1% might make up a part of the enter GDP progress assumptions throughout all our eventualities.
It also needs to be acknowledged {that a} ‘do-nothing’ state of affairs by which web zero just isn’t met on the international stage would result in extra pricey impacts from local weather change. For instance, the LSE’s Grantham Institute estimates that local weather change impacts would price the UK round 3.3% of GDP by 2050 and round 7.4% of GDP by the tip of the century. Situations with low ranges of worldwide belief (self-preservation and atomised) are more likely to be at larger threat of lacking international web zero and incurring larger adaptation prices.
As well as, a number of the well being co-benefits related to some eventualities (see Part 4.3), significantly the sluggish lane society, might contribute to a discount in general prices to society, which once more we’re not capable of quantify as a result of excessive ranges of uncertainty.
Lastly, this evaluation has explored vitality methods prices in every state of affairs and their comparatively affordability solely. We’ve got not thought of wider affordability questions, reminiscent of these for UK public companies, though that is more likely to be more difficult in each low-growth eventualities (sluggish lane and self-preservation).
Web zero technique comparisons
HM Authorities’s 2021 web zero technique included three eventualities for a way web zero is perhaps met, primarily focussed on which applied sciences is perhaps obtainable. Alongside this technique, some modelling output knowledge had been revealed, together with residual emissions by sector in 2050 throughout these three eventualities. Provided that we now have used the identical vitality system mannequin that was used for this technique (UKTM) we will make a direct comparability between the modelling outputs for the web zero society eventualities and these web zero technique eventualities. Determine 28 exhibits the total vary, from lowest residual emissions by sector in 2050 to highest, throughout the 2 units of eventualities.
Determine 28. Vary of residual emissions by sector in 2050 (lowest to highest) for the web zero technique eventualities and the 4 web zero society state of affairs

Determine 28 knowledge: Residual emissions, MtCO2e/12 months
| NZ technique vary | AT Soc | Met Soc | SP Soc | SL Soc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 1 — 3 | -3.5 | 0.41 | -0.05 | 0.12 |
| Gasoline provide and hydrogen | 3.2 — 7.5 | 5.35 | 6.35 | 1 | 4.85 |
| Work and {industry} | 3.2 — 10.2 | 6.5 | 17.7 | 11.3 | 6.67 |
| Warmth and buildings | 0 — 1.7 | 0 | 10.3 | 0.08 | 6.65 |
| Transport | 22.5 — 41 | 20 | 23 | 14 | 19 |
| Agriculture, land use, waste and F-gases | 26.2 — 33.8 | 50 | 22 | 35 | 7 |
| Greenhouse gasoline removals | -80.8 — 75.4 | -78.4 | -79.6 | -59.8 | -45.3 |
Key insights from this comparability are lined under. Typically, explanations for variations are speculative, as a result of the detailed assumptions underpinning the web zero technique haven’t been revealed.
- The web zero technique and our eventualities all assume the near-complete decarbonisation of the ability sector by 2050. Consequently, the societal modifications we now have modelled make little or no distinction to residual emissions from the ability sector. As mentioned above, they make an even bigger distinction to system prices.
- Had been a number of the modifications we’ve modelled to come back to go, residual emissions from {industry} might be as much as 73% larger than assumed within the web zero technique. This might current a threat to assembly web zero. Adjustments more likely to contribute to that embrace reshoring of producing and failure to put in CCS on industrial crops.
- Equally, our eventualities counsel residual emissions from warmth and buildings might be as much as 5 instances larger than assumed within the web zero technique. Adjustments related to this embrace an growth of non-domestic buildings within the metropolitan society, that are tougher to decarbonise.
- The modifications to weight loss plan and land use assumed within the sluggish lane society (and to a lesser extent the metropolitan society) counsel residual emissions might be as much as 73% decrease than assumed within the web zero technique. Had been this to occur, this might create important flexibility.
- Comparable, though much less considerably, in our eventualities the place there are extra important modifications to journey patterns, significantly decrease ranges of worldwide journey, residual transport emissions are as much as 38% decrease than assumed within the web zero technique.
- Taken collectively, our eventualities counsel the quantity of GHG removals wanted to satisfy web zero might be as little as 60% of that assumed within the web zero technique (within the sluggish lane society). Much less required GHG removals would imply much less price and fewer reliance on an unproven know-how. Nonetheless, it must be famous that this state of affairs just isn’t with out problem, significantly when it comes to low financial progress and its impacts on affordability. Nonetheless, it also needs to be famous that the sluggish lane society just isn’t the one solution to obtain such outcomes, and it could be possible to cut back reliance on GHG removals by way of vitality demand discount in the next progress state of affairs.
4.3 Wider evaluation and co-benefits
We explored a spread of impacts ensuing from the 4 state of affairs fashions, that are explored in larger element in Annex 5. Beneath we talk about what the broader evaluation exhibits in three areas: air high quality, wholesome life expectancy and vitality equality.
There are a lot of co-benefits regarding the transition to web zero, relying on the insurance policies chosen to underpin the lowering emissions. These potential co-benefits embrace elevated vitality safety, improved public well being, and higher water/air high quality. Evaluation means that the eventualities the place societal modifications have lowered demand have the best variety of potential co-benefits, whereas the atomised society has the least.
Air high quality
Air air pollution is related to burning a spread of fuels. Right here we deal with air pollution from fossil-fuelled automobiles as essentially the most important supply that the general public are uncovered to and also will be affected by attaining web zero. It must be famous that there are different important sources that may have an effect on public well being, reminiscent of wood-burning stoves, however these haven’t been thought of within the eventualities. As a result of deal with transport on this evaluation, and the very fact it makes use of nationwide common values, it isn’t potential to say definitively whether or not any of the eventualities meet the UK’s air air pollution targets, that are outlined at a neighborhood stage. However, it’s probably that the big reductions in roadside air air pollution from assembly web zero would make a big contribution to assembly these targets.
The primary levers that drive air pollution from automobiles are journey demand, the uptake of electrical automobiles, highway site visitors speeds, and the situation of emissions. Right here we estimate modifications in air air pollution with out translating them into impacts on morbidity and mortality. Nonetheless, well being advantages of lowered air air pollution are effectively documented. For instance, the Air High quality Life Index 2022 replace estimates that 2.2 years could be added to international common life expectancy if the World Well being Organisation’s new stringent targets on particulate matter had been met.
Air air pollution comes from direct emissions (from exhaust or particles from tyres/brakes carrying down) and from oblique emissions (from gasoline manufacturing and automobile manufacturing, upkeep and disposal). Direct Nitrogen Oxides (NOX) emissions (Determine 29, high) present downward traits for all 4 eventualities, largely as a result of decrease emission plug-in automobiles changing older, extra polluting ones.
Even by 2030, direct NOX emissions from highway transport could be anticipated to be half of these in 2019. In the long term, direct NOX emissions are lowest within the atomised society as a result of larger charges of car turnover and accelerated swap to EVs. Nonetheless, as soon as oblique emissions from gasoline manufacturing in addition to automobile manufacturing, upkeep and end-of-life are thought of, the atomised society has the best NOX emissions out of the 4 eventualities modelled right here, with whole lifecycle NOX persisting at excessive ranges into the 2050s (Determine 29, backside).
Whereas these excessive ranges of oblique emissions counterbalance any advantages from direct emissions within the atomised society, a big share of the automobile and gasoline lifecycle NOX emissions is emitted outdoors the UK, which isn’t thought of on this evaluation. In distinction, whole lifecycle NOX emissions lower furthest within the sluggish lane society as there are fewer automobiles and they’re travelling fewer miles. Each the sluggish lane and metropolitan societies might have points with larger NOX from bikes in city areas, given comparatively low electrification charges.
Determine 29. Direct NOX (high) and lifecycle NOX (backside) emissions from all highway transport (automobiles, vans, HGV, buses and coaches, bikes) in 2019 and for the 4 web zero society eventualities in 2030, 2040 and 2050

Determine 29 graph 1 knowledge: NOx emissions, tonnes/12 months
| Automobile | Bus and coach | Vans | HGV | Motorbike | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 58000 | 6600 | 15000 | 18000 | 1300 | |
| At Soc | 2030 | 22000 | 3900 | 7000 | 11000 | 1100 |
| At Soc | 2040 | 1100 | 1400 | 570 | 11000 | 1100 |
| At Soc | 2050 | 0 | 160 | 0 | 7300 | 1300 |
| Met Soc | 2030 | 17000 | 6500 | 7700 | 10000 | 3400 |
| Met Soc | 2040 | 1600 | 2300 | 3600 | 9300 | 3300 |
| Met Soc | 2050 | 2 | 380 | 61 | 4200 | 4000 |
| SP Soc | 2030 | 29000 | 4600 | 7700 | 10000 | 2500 |
| SP Soc | 2040 | 8200 | 2700 | 3800 | 9200 | 2800 |
| SP Soc | 2050 | 310 | 1400 | 140 | 6900 | 3700 |
| SL Soc | 2030 | 15000 | 9500 | 7000 | 9100 | 5500 |
| SL Soc | 2040 | 4900 | 5900 | 4500 | 7100 | 4700 |
| SL Soc | 2050 | 680 | 990 | 700 | 3400 | 5200 |

Determine 29 graph 2 knowledge: NOx emissions, tonnes/12 months
| Automobile | Bus and coach | Vans | HGV | Motorbike | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 150000 | 8800 | 29000 | 33000 | 1600 | |
| At Soc | 2030 | 110000 | 5800 | 25000 | 28000 | 1700 |
| At Soc | 2040 | 90000 | 2800 | 20000 | 39000 | 1600 |
| At Soc | 2050 | 85000 | 1100 | 19000 | 45000 | 1900 |
| Met Soc | 2030 | 90000 | 11000 | 23000 | 26000 | 4900 |
| Met Soc | 2040 | 57000 | 5900 | 18000 | 29000 | 4900 |
| Met Soc | 2050 | 48000 | 3200 | 13000 | 29000 | 5800 |
| SP Soc | 2030 | 110000 | 7000 | 22000 | 25000 | 3500 |
| SP Soc | 2040 | 67000 | 4700 | 17000 | 30000 | 4100 |
| SP Soc | 2050 | 51000 | 3100 | 11000 | 32000 | 5200 |
| SL Soc | 2030 | 62000 | 15000 | 20000 | 23000 | 7700 |
| SL Soc | 2040 | 37000 | 10000 | 15000 | 21000 | 6600 |
| SL Soc | 2050 | 29000 | 3900 | 9200 | 19000 | 7300 |
Extremely-fine particulate matter (PM2.5) stems from each tailpipe and non-tailpipe sources (tyre and brake put on, highway abrasion) and is very poisonous to people. As with NOX, the eventualities explored right here could be anticipated to speed up reductions in tremendous particulate matter (PM2.5) emissions within the brief to medium time period, and considerably cut back them in the long run. As Determine 30 (high) exhibits, by 2030, direct PM2.5 emissions are about half of the 2019 ranges in all eventualities. PM2.5 emissions in 2030 are barely larger within the sluggish lane and metropolitan societies, reflecting elevated use of buses and categorical coaches. By 2050, PM2.5 emissions are highest within the self-preservation society, reflecting slower automobile turnover and transition to zero tailpipe emission buses and HGVs.
Determine 30. Direct PM2.5 (high) and lifecycle PM2.5 (backside) emissions from all highway transport (automobiles, bikes, vans, HGVs, buses, and coaches) in 2019 and for the 4 web zero society eventualities in 2030, 2040 and 2050

Determine 30 knowledge graph 1: Direct PM2.5 emissions, tonnes/12 months
| Automobile | Bus and coach | Vans | HGV | Motorbike | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 1900 | 2700 | 2200 | 12000 | 96 | |
| At Soc | 2030 | 860 | 1700 | 1300 | 6600 | 86 |
| At Soc | 2040 | 45 | 550 | 68 | 4400 | 80 |
| At Soc | 2050 | 0 | 49 | 0 | 630 | 98 |
| Met Soc | 2030 | 700 | 2400 | 1600 | 6300 | 260 |
| Met Soc | 2040 | 75 | 810 | 540 | 4600 | 260 |
| Met Soc | 2050 | 0 | 93 | 7 | 410 | 310 |
| SP Soc | 2030 | 1100 | 1800 | 1500 | 6100 | 190 |
| SP Soc | 2040 | 320 | 1000 | 750 | 3400 | 220 |
| SP Soc | 2050 | 12 | 670 | 25 | 940 | 280 |
| SL Soc | 2030 | 630 | 3100 | 1400 | 5600 | 440 |
| SL Soc | 2040 | 210 | 1800 | 810 | 3500 | 370 |
| SL Soc | 2050 | 28 | 280 | 85 | 510 | 410 |

Determine 30 knowledge graph 2: Lifecycle PM2.5 emissions, tonnes/12 months
| Automobile | Bus and coach | Vans | HGV | Motorbike | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 3100 | 2800 | 2400 | 12000 | 100 | |
| At Soc | 2030 | 1800 | 1700 | 1600 | 6900 | 95 |
| At Soc | 2040 | 700 | 570 | 330 | 4700 | 88 |
| At Soc | 2050 | 660 | 58 | 190 | 850 | 110 |
| Met Soc | 2030 | 1500 | 2400 | 1700 | 6500 | 290 |
| Met Soc | 2040 | 490 | 840 | 690 | 4900 | 280 |
| Met Soc | 2050 | 350 | 120 | 140 | 580 | 340 |
| SP Soc | 2030 | 2000 | 1800 | 1700 | 6200 | 210 |
| SP Soc | 2040 | 860 | 1000 | 880 | 3600 | 240 |
| SP Soc | 2050 | 420 | 690 | 130 | 1100 | 310 |
| SL Soc | 2030 | 1200 | 3100 | 1600 | 5700 | 470 |
| SL Soc | 2040 | 510 | 1900 | 940 | 3700 | 400 |
Taken collectively, air air pollution and its hostile affect on well being could be decrease in all eventualities we modelled. It’s minimised within the eventualities the place we now have assumed larger ranges of societal change within the transport sector the place variety of automobiles and miles travelled are each lowered.
Dietary impacts on wholesome life expectancy
This part focuses solely on the impacts on wholesome life expectancy as a result of dietary modifications, as these had been essentially the most readily quantifiable within the meals and land use sector mannequin used on this challenge. Many different modifications within the eventualities, together with bodily exercise and funding of healthcare companies might even have impacts (as talked about within the state of affairs narratives). Nonetheless, these are much less simple to quantify and past the scope of this work.
All 4 eventualities have a web constructive well being affect as a result of dietary modifications, in response to our modelling. In each the sluggish lane and metropolitan societies, we assumed massive substitutions of meat and dairy consumption in comparison with the opposite two eventualities. Consequently, they see the largest well being enhancements. Life expectancy features are largest in sluggish lane society (36 extra minutes of wholesome life expectancy per day of consuming that weight loss plan). The metropolitan society assumes barely much less important shifts in weight loss plan, primarily because of the larger incomes assumed. Consequently, the well being advantages are smaller. Nonetheless, there is no such thing as a technical cause the upper dietary shift couldn’t be achieved on this state of affairs. Moreover, the metropolitan society doesn’t have the general public spending and innovation constraints that would offset a number of the acquire modelled within the sluggish lane society. In fact, particular person outcomes would differ based mostly on private dietary composition. Between 2019 and 2050, life expectancy will increase within the atomised and self-preservation are lower than half that seen within the metropolitan society.
Desk 11. Life expectancy implications of common diets in 2050 per state of affairs (in minutes gained per capita per day of consuming the weight loss plan)
| Atomised | Metropolitan | Self-preservation | Sluggish lane | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra minutes of wholesome life from dietary modifications (per capita, per day of consumption) | 12 | 25 | 12 | 36 |
4.4 Threat of lacking web zero
The eventualities are simply 4 examples of many potential methods by which the long run might play out. It’s simple to consider different believable futures that look similar to our eventualities however are lacking a key ingredient required within the modelling to satisfy web zero. For instance, it’s potential that efforts to develop commercially viable, carbon impartial aviation fuels usually are not profitable by 2050 within the metropolitan society. Or within the sluggish lane society, ranges of journey might begin to enhance between 2030 and 2050 as a result of a societal shift or an uptick in family incomes. Given such dangers exist for all eventualities, it is very important think about the extent of contingency measures obtainable in every state of affairs to have the ability to adapt and nonetheless meet web zero.
The desk under offers a qualitative evaluation of essentially the most important dangers in every state of affairs, and the mitigations obtainable. This evaluation was undertaken by the GO-Science challenge staff and reviewed by a panel of specialists.
| Situation | Dangers of lacking web zero | Mitigations if a key web zero ingredient is lacking | Total threat evaluation after mitigations |
|---|---|---|---|
| At Soc | Assembly web zero on this state of affairs is very depending on unproven web zero applied sciences. Assembly the goal is subsequently susceptible to unexpected technical or price boundaries to creating these applied sciences, though the excessive ranges of funding in analysis and growth on this state of affairs cut back the chance of this occurring. Vitality demand is already very excessive on this state of affairs in comparison with the opposite eventualities, however there stays a chance it might drift larger. | Unproven web zero applied sciences are already deployed at very excessive ranges on this state of affairs, so stretching it additional could be difficult. If DAC just isn’t obtainable, it could be extraordinarily tough to seek out one other know-how to bridge the emissions hole. There’s a prioritisation of particular person consumption on this state of affairs, significantly for folks with larger incomes, which could make persuading folks to make use of much less vitality tougher than in different eventualities. One mitigation on this state of affairs might be to benefit from the societal desire for interacting digitally, serving to to cut back journey demand. | Medium |
| Met Soc | This state of affairs makes use of unproven web zero applied sciences, however at decrease ranges than within the atomised society, so any failure to develop these would depart a smaller emissions hole to bridge. Demand for vitality and items is comparatively excessive on this state of affairs, and there’s a threat this might drift even larger. | Unproven web zero applied sciences usually are not deployed on the highest ranges, so failure of one in all these might be offset by will increase in others. As particular person sustainable selections aren’t the first driver of some societal shifts, any efforts to incentivise folks to cut back vitality use may not be absolutely profitable. Nonetheless, lots of the societal modifications are supported by structural and systemic modifications (for instance, the round financial system and concrete infrastructure), which could make them simpler to broaden to offset underperformance in different areas. | Low |
| SP Soc | This state of affairs depends on unproven web zero applied sciences, however the lack of technological growth signifies that price reductions and supply challenges are unlikely to have been absolutely resolved, so the chance of failure is excessive. Moreover, persons are drawn in the direction of outdated methods of doing issues, so there’s a threat that some behavioural modifications are sluggish to be absolutely rolled out (reminiscent of the usage of low carbon heating). | This state of affairs has each restricted know-how availability and a society that’s much less amenable to alter, so scope for mitigating any surprising web zero boundaries is low. Due to this fact, the chance of lacking web zero is excessive. | Excessive |
| SL Soc | Unproven web zero applied sciences usually are not obtainable at business scale on this state of affairs. The state of affairs manages to satisfy web zero with out them, due to the extra important societal shifts that help emissions and vitality demand reductions. The primary threat on this state of affairs is that a number of of those societal shifts doesn’t absolutely materialise or reverses. | The dearth of technological growth on this state of affairs considerably reduces the scope for mitigating this threat. Society is amenable to creating modifications for the larger good on this state of affairs, and additional behavioural change is more likely to be the principle mitigation that might be used to keep away from lacking web zero. Nonetheless, society has already undergone important shifts on this state of affairs, so there’s uncertainty of whether or not this might be pushed additional as a mitigation. | Medium |
4.5 Key messages from modelling
The 4 eventualities have been designed to spotlight completely different challenges and alternatives to assembly web zero that would come up from societal shifts. Not one of the eventualities is with out its challenges, and so they shouldn’t be seen as a menu of choices. These eventualities present coverage makers with a software to consider potential societal modifications that would current alternatives and dangers for assembly web zero, in addition to potential co-benefits. Anticipating these modifications, deciding which to foster or keep away from, which to trace and what our contingency is perhaps in the event that they did or didn’t occur, will make web zero coverage extra resilient.

| Atomised | Metropolitan | Self-preservation | Sluggish lane | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New vitality infrastructure wanted to satisfy demand: Extra land for vitality infrastructure will compete with different land makes use of (reminiscent of pure habitats, housing, or agriculture). | Excessive | Medium-high | Medium-high | Low |
| Prices of delivering vitality infrastructure, relative to GDP: Rising prices of supply will have to be paid for, e.g. by way of taxation (pushed by amount and unit price reductions) | Medium-low | Low | Excessive | Medium-low |
| Dangers to assembly web zero: If a web zero measure doesn’t work out, how simple is it to cut back emissions in one other method? | Medium | Low | Excessive | Medium |
This determine summarises the important thing findings of our quantitative and qualitative evaluation of the implications of every state of affairs for assembly web zero. This abstract exhibits that every one eventualities have some downsides.
For instance, the sluggish lane society requires the least infrastructure however has a comparatively excessive threat of assembly web zero, and the metropolitan society has decrease threat, however wants a big quantity of land for vitality infrastructure. These eventualities are supposed to characterize comparatively excessive outcomes, and with the appropriate planning, coverage makers might have contingency measures in place to minimise the downsides of various societal modifications.
Additional key messages are summarised under.
- Web zero may be met in all of the eventualities we modelled. Even in eventualities the place societal modifications result in larger ranges of vitality demand, there are pathways to web zero. Nonetheless, these larger demand eventualities depend on in depth use of carbon elimination applied sciences which are but to be confirmed at scale, which might be tough and/or costly to roll out on the tempo required, introducing larger threat to this path to web zero.
- Societal change will have an effect on the long run stage of demand for vitality and items and what applied sciences can be found. There’s round a 65% distinction in 2050 vitality demand between our eventualities. However precisely how society will change is, after all, unsure. Many equally believable eventualities exist, however ours characterize a number of the key potential modifications that governments ought to concentrate on as they plan.
- If societal modifications cut back vitality demand, assembly web zero might be cheaper than failing to take action. In comparison with a baseline state of affairs, which fails to satisfy web zero and has restricted societal modifications, our state of affairs with larger financial progress and demand-reducing societal modifications has 2050 vitality system prices which are decrease by 2% of GDP. On this state of affairs, modifications to journey patterns and new fashions for consuming items cut back vitality demand. This in flip reduces the scale, complexity and funding wants of the vitality system.
- In eventualities the place societal modifications cut back vitality demand, reliance on carbon elimination applied sciences is lowered, much less land is required for infrastructure, and well being co-benefits are larger. Situations that see decrease vitality demand and consumption, as a result of components reminiscent of these outlined within the earlier discovering, have lowered reliance on direct air seize (DAC) know-how to deal with residual emissions. These eventualities additionally require much less land for vitality infrastructure, which might make the vitality system simpler to ship and permit the land for use for different functions. Vital well being advantages might additionally circulation from lowered meat consumption and elevated bodily exercise.
- In distinction, in eventualities the place societal modifications do little to cut back demand, assembly web zero will probably be tougher to ship. That is partially because of the want for a bigger vitality system to be constructed quickly to satisfy the demand. It’s also because of the elevated reliance on costly know-how reminiscent of DAC to compensate for larger vitality use and emissions. Such massive vitality methods may be extra inexpensive in eventualities with stronger financial progress. Nonetheless, if financial progress is weak then this will likely imply web zero is much less inexpensive (as much as 5% of GDP costlier than the baseline).
- Financial progress and technological innovation are correlated. There’s a threat {that a} low progress, low innovation world would have fewer technological choices for assembly web zero. It’s potential to satisfy web zero with out additional technological breakthroughs. Nonetheless, with out them, the path to web zero would require extra important societal modifications, reminiscent of larger reductions within the ranges of flying and lowered consumption of meat and dairy. We’ve got not explicitly estimated the potential financial advantages of the UK being a frontrunner in inexperienced know-how in our evaluation. Nonetheless, this might plausibly additional improve the relative price discount in some eventualities.
- Financial progress and vitality demand may be additional decoupled if different societal modifications reminiscent of useful resource effectivity and different ‘round financial system’ measures happen in parallel. Our evaluation means that assembly web zero in a excessive financial progress state of affairs with such societal modifications might be round 2% of GDP less expensive in 2050 than in a excessive financial progress state of affairs with out them. All else being equal, financial progress is more likely to enhance general vitality demand, rising the scale and complexity of the vitality system, with related supply challenges. With bettering financial progress as a constant authorities aim, web zero planning ought to account for a way web zero may be met in a world with larger progress.
- Excessive ranges of innovation might result in extra quickly falling unit price reductions than assumed right here. Value reductions for key web zero applied sciences might come about extra quickly in eventualities the place the UK is main technologically or the place international decarbonisation drives quicker innovation. This can be extra more likely to occur within the eventualities with larger ranges of technological growth, by which case we is perhaps understating the affordability of assembly web zero in these eventualities.
- The trail to web zero will probably be affected by a variety of societal components that might be tracked as a part of planning for web zero, together with earnings distribution, sectoral combine within the financial system, adoption of digital applied sciences, the extent of city versus rural dwelling, and ranges of cohesion between completely different social teams. Authorities will greatest have the ability to adapt its method to web zero — seizing alternatives and mitigating a number of the prices — with early alerts of the course of journey. To enhance the resilience of its web zero technique, the federal government might observe these developments and adapt its method to web zero accordingly.
5. Public dialogue
We held a public dialogue to grasp what the general public would possibly take into consideration the completely different future eventualities and the implications for a way the UK might attain web zero. Reflections included that people would discover making sustainable selections tougher with out enabling infrastructure. Contributors had been additionally aware of the tensions concerned in choice making round web zero, noting that involving the general public might guarantee trade-offs had been higher understood and addressed. In addition they raised cross-cutting themes they believed had been essential throughout all of the eventualities, in addition to their ideas on every particular person state of affairs.
5.1 Dialogue introduction
What are public dialogues?
Our method on this report encompasses each a high-level overview of potential societal change (by way of our critiques and our modelling work) and a close-focus investigation on how people would possibly expertise societal change sooner or later. For the latter, we selected to carry a public dialogue. Public dialogues carry members of the general public collectively to deliberate on policy-relevant points. They don’t seem to be a brand new method for understanding public views on science and know-how points, with the Sciencewise programme having existed to help dialogue since 2004.
Higher public engagement in formal choice making processes has been recommended as a way to enhance the acceptability and success of ensuing laws and insurance policies. For instance, in its progress report back to Parliament on the web zero goal, the CCC advocated for larger use of public dialogues in choice making.2 The Home of Lords Setting and Local weather Change Committee carried out an inquiry exploring the position of behaviour change in assembly local weather and environmental objectives. The ensuing inquiry report recommended that public engagement work might enhance the effectiveness of interventions for reaching web zero. The report additionally known as for a public engagement technique by April 2023 to fill the information gaps across the modifications required to satisfy web zero, and to provoke dialogues with the general public to grasp which insurance policies can greatest allow these modifications.
What did we wish to talk about by way of this work?
The overwhelming majority of the UK inhabitants are involved about local weather change. Nonetheless, analysis has proven that the general public’s response to potential societal modifications is dependent upon the perceived affect on their existence, the potential price implications and the framing.170, There have been numerous public dialogues on points regarding web zero. Though a few of these had been tangentially related to our work, we needed to study folks’s reactions to the precise eventualities we had developed. To this finish, the general public dialogue documented right here took a distinct method to earlier work because it immersed contributors in 4 believable future eventualities the place web zero has been reached to grasp their reactions to potential future societal modifications. The web zero society challenge staff, with help from Sciencewise, commissioned the analysis firm Ipsos to hold out a public dialogue based mostly on the 4 eventualities laid out above. The goal of the general public dialogue was to collect:
- attitudes in the direction of the 4 eventualities and the underlying values/ideas that influenced them,
- suggestions on the plausibility of the 4 eventualities,
- options for the societal modifications that would set the UK on a path to the completely different eventualities, and
- reflections on the perceived tensions offered within the eventualities.
5.2 Dialogue method
A gaggle of 29 contributors from throughout the UK (Determine 31) took half within the public dialogue. This group was broadly reflective of UK inhabitants demographics (together with age, earnings stage, geographical location, ethnicity, and gender). The dialogue initially launched contributors to the method and the problems pertinent to the eventualities by way of a webinar. Following the webinar, contributors participated in 4 three-hour on-line workshops (workshops 1–4) that every thought of a person state of affairs. Then they took half in a ultimate three-hour on-line workshop (workshop 5) the place they mirrored on all of the eventualities. The workshops included the usage of numerous stimuli, together with the 4 wealthy image illustrations proven in Chapter 3 and ‘future artefacts’, that are supplies that mirror the tradition and day by day lifetime of an imagined future (see Annex 6 for the total set of artefacts used).
All workshops had been recorded and each breakout room had a skilled notetaker who made notes through the periods. The transcripts of the recordings and the notes had been then coded and thematically analysed.
The general public dialogue outcomes are offered in abstract under, as follows:
- Plausibility and pathways, specializing in the points of the eventualities that contributors felt had been least believable and the modifications they believed could be wanted between now and 2050 to make the state of affairs believable.
- Cross-cutting themes, which had been the 4 key matters that contributors constantly raised throughout all of the workshops.
- Reactions to the person eventualities, together with a brief reminder of the modelling outputs for every state of affairs adopted by contributors’ reactions to every society as a complete and the sectors inside it.
- Tensions and trade-offs, which covers essentially the most tough points that contributors recommended that call makers engaged on web zero would want to think about when occupied with future societies.
Determine 31. Areas of contributors on a map of the UK (places in massive cities, reminiscent of London, characterize multiple participant)

5.3 Plausibility and pathways
Most contributors had been anxious about local weather change and the dangers it posed to present and future society. There have been some contributors who had been sceptical about the potential of reaching web zero by 2050, with some stating particular technological points (reminiscent of zero carbon flying) that appeared unrealistic to them. Others expressed sturdy doubts in regards to the way of life modifications proven within the eventualities, suggesting that the ‘establishment’ wouldn’t change within the implied timescales.
Though contributors had been inspired in workshops 1–4 to just accept the premise of the eventualities even the place they could discover some points implausible, there was a chance in workshop 5 to debate plausibility. Contributors usually referenced the current day when contemplating plausibility, suggesting that some eventualities confirmed both an excessive amount of or little distinction between now and 2050.
When contemplating the eventualities general, contributors thought that the self-preservation society and the atomised society had been essentially the most believable (usually suggesting this was the trail that UK society was already on). In different phrases, contributors discovered the eventualities with decrease social cohesion and fewer dramatic societal modifications extra believable. Some recommended that the metropolitan society and the sluggish lane society had been theoretically potential however had been extra aspirational than lifelike.
[The self-preservation society] does seem to be it might occur. […]. But additionally, [the slow lane society] if we’re optimistic, we might get to a spot like that. Making do with what we now have and never shopping for a lot
The place contributors expressed that they didn’t see a pathway from present society to a future state of affairs, they had been requested what they thought would want to alter and why they thought that change was unlikely. Beneath are the modifications that they recommended might happen that might transfer society onto the pathway to a number of the eventualities.
Elevated funding
Key message for coverage makers: Societal change is considerably contingent on the infrastructure obtainable to help it (reminiscent of accessible public transport and lively journey infrastructure). Contributors expressed the need to make modifications of their existence however had been involved that this was not believable with out funding within the infrastructure to permit them to take action. Framed in reverse, funding in low carbon infrastructure was seen as a key to unlocking acceptable modifications to satisfy web zero.
What the contributors mentioned: For all eventualities, besides the self-preservation society, there was a common sense that for them to happen there would have to be important funding in future applied sciences to bridge the hole between the place applied sciences at the moment are and the place they might have to be to understand the eventualities. Contributors significantly highlighted that worldwide journey doesn’t have an environment friendly, low-carbon international transport community, which leaves no viable different to flying in some cases. This highlights that assembly web zero in a method that maximised public help would probably require both low carbon flight or viable alternate options. Each would require substantial funding.
To take action, we have to make investments extra in public transport in each rural and concrete areas. The extra we’re linked by public transport the higher for the entire neighborhood.
Contributors additionally recommended considerably extra funding in making UK public transport choices extra environment friendly and dependable could be wanted if the eventualities with elevated reliance on public transport had been to come back about. Rural contributors additional highlighted that for any eventualities with lowered entry to personal automobiles to be workable, there would have to be a far-reaching growth of public transport networks and entry to native facilities (colleges, for instance) into at the moment poorly linked areas.
Reskilling
Key message for coverage makers: Contributors solely discovered eventualities with massive societal modifications (reminiscent of will increase in automation or a larger emphasis on the round financial system) believable if there have been supporting efforts to reskill people. Clearly modifications reminiscent of automation usually are not straight linked to web zero targets however might have an effect on emissions. With out the deal with schooling and coaching, supporting the general public to navigate large financial shifts, contributors believed that such societal modifications had been unlikely to happen or could be met with resistance.
What the contributors mentioned: When discussing eventualities that offered an elevated deal with repairing items reasonably than changing them, contributors highlighted that there’s a massive hole in most people’s information of learn how to restore sure gadgets. They recommended that if these eventualities had been to come back about then there would have to be extra upskilling to facilitate the broader societal change of losing much less and repairing extra.
Reskilling was additionally referenced when contributors mentioned eventualities with excessive ranges of automation. Whereas most contributors had been involved that individuals might lose their jobs, a number of contributors argued that eventualities with elevated automation would possibly current a chance to facilitate upskilling and retraining, however that this wanted to be finished cautiously and with sensitivity to these unwilling or unable to make these modifications.
There would be the automation of peoples’ jobs, however I believe authorities and different organisations must assist folks to reskill and retrain.
Some eventualities recommended a rise in people or native communities rising their very own meals. Contributors had been eager on this idea however once more indicated that this was a giant change from present society, the place persons are usually separated from agricultural processes. Once more, it was recommended that for these eventualities to be lifelike, people would have to be educated in learn how to produce their very own meals.
Altering meals preferences
Key message for coverage makers: Contributors assumed that the pattern for residents lowering their meat and dairy consumption would proceed and plenty of expressed a want to cut back their very own consumption. They had been averse to having fewer meals choices obtainable sooner or later however had been usually supportive of incentivising folks to decide on much less emissions-intensive choices. Future coverage makers might want to rigorously navigate between the expressed dietary preferences of the day, decarbonising meals manufacturing, and sustaining public help for a number of the technical choices to realize this. Ongoing public engagement on that is more likely to be vital.
What the contributors mentioned: Most contributors acknowledged that lowering meat and dairy consumption would cut back carbon emissions. This was additionally the case amongst contributors working in agriculture. Though all contributors needed to maintain meat and dairy as choices for people in future societies, some had been eager to encourage lowered meat and dairy consumption and incentivise folks to decide on much less emissions-intensive choices (for instance, by making plant-based alternate options cheaper).
Contributors struggled to just accept the premise that different proteins (reminiscent of cultured meat) or novel agricultural strategies (reminiscent of vertical farming) could be broadly accepted sooner or later. They usually recommended that individuals would view this as much less fascinating than meals grown or reared historically. Most contributors believed that meals produced utilizing novel applied sciences (significantly cultured meat) was inherently much less wholesome than meals grown in a conventional method. This affected how believable they considered eventualities with elevated consumption of cultured meat. Just a few contributors mentioned that if the appropriate checks had been performed to make sure cultured meat was protected for consumption, they might purchase it. Others additionally acknowledged that their response might have been pushed by a lack of know-how of the know-how utilized in these processes. Reservations round shifting in the direction of merchandise that relied on novel applied sciences have an effect on the metropolitan and atomised societies to a larger extent. Issues in regards to the reliance on imports impacts the self-preservation society most, whereas issues about lowered meals selection impacts the sluggish lane society barely greater than the others.
We’ve got the accountability to do the appropriate factor for the planet, however the authorities have to incentivise that selection as effectively.
Incentivising companies
Key message for coverage makers: As famous beforehand, contributors expressed that some societal modifications could be much less more likely to happen with out modifications in different sectors. For instance, contributors recommended that establishing a round financial system would require companies to cut back inbuilt obsolescence, enhance repairability and cut back waste related to manufacturing. Contributors recommended that companies would probably want incentivising to develop these practices as a result of the modifications required might come into battle with their profitability.
If corporations are rewarded for producing issues which are higher for the planet, that might be a greater method of attracting funding into that stream.
What the contributors mentioned: Just a few contributors flagged that to facilitate the broader societal change outlined in a number of the eventualities (particularly these with a larger emphasis on the round financial system), companies at the moment producing merchandise with inbuilt obsolescence would have to be incentivised to alter their working mannequin. Options included requirements for repairability and utilizing the total lifecycle of merchandise. This was significantly true for eventualities suggesting important modifications to how merchandise are made, used and disposed of (such because the sluggish lane society or the metropolitan society).
5.4 Cross-cutting themes
All through discussions, contributors explored what they noticed as the benefits and challenges within the 4 eventualities offered to them and the way these might affect their lives and people of others. 4 major themes emerged within the contributors’ discussions throughout the 5 workshops. These cross-cutting themes (know-how, equality, well being, and involvement) are outlined under. The themes that emerged throughout this dialogue additionally carefully match these which have been present in earlier public engagement work.175, 176
Know-how
Key message for coverage makers: In web zero pathways that depend on a excessive stage of know-how adoption, particularly know-how which is very seen to residents (reminiscent of novel meals applied sciences or modifications to work environments), coverage makers might want to work to make sure public help. Contributors counsel that selling fairness of entry to (and impacts from) know-how, stopping job losses, and cautious regulation had been essential to making sure public help. From stem cells to mitochondrial DNA transfers, successive UK governments have been capable of craft coverage positions that commanded broad help, partially by way of public dialogue. The rollout of client dealing with web zero applied sciences might profit from comparable work.
What the contributors mentioned: Many contributors expressed wariness of superior applied sciences, how they had been used and who benefitted from their use. Contributors indicated that important technological innovation was anticipated by 2050 and had been constructive about much less seen technological development (reminiscent of know-how to facilitate a round financial system). Nonetheless, they expressed concern about relying disproportionately on know-how to cut back emissions. They had been additionally extremely crucial of applied sciences they noticed as automating jobs or contributing to social isolation.
I’m all for know-how, however is it going to begin controlling all the pieces I do?
Self-preservation society
Contributors sometimes exhibited low ranges of belief within the agenda and priorities of enormous know-how corporations. This concern additionally got here by way of within the opinions expressed round the usage of superior applied sciences in meals manufacturing, the place some contributors expressed concern that a number of influential corporations might find yourself controlling the means of manufacturing meals.
You’ll be able to’t belief large tech, it’s about their shareholders, not their world.
Metropolitan society
Contributors had been additionally involved in regards to the social and financial implications of technological improvements. They questioned whether or not know-how could be inexpensive for all and if some applied sciences might cut back social contact between completely different teams. Nonetheless, in addition they noticed some advantages, regarding potential constructive well being outcomes and comfort, that would come up by way of the efficient use of applied sciences. This theme was most frequently raised in relation to the atomised and metropolitan societies, which contain the best uptake of novel applied sciences.
As simple as it’s to submerge your self on this digital bubble, it might probably’t change actuality and it by no means ought to.
Atomised society
Equality
Key message for coverage makers: Perceived equity was extraordinarily essential to contributors. If narratives had been to emerge round a scarcity of equity in how web zero is being delivered, whether or not by authorities motion or because of this wider modifications, it could probably create resistance and maintain again progress. Future governments will have to be alert to, and tackle, issues expressed by the general public round equity in relation to web zero pathways.
What the contributors mentioned: The theme of equality was introduced up by contributors in each workshop. All contributors had been deeply involved by potential inequalities within the 4 eventualities. The issues expressed round inequality may be broadly grouped into three classes:
- Revenue inequality: Contributors had been involved that those that had been much less effectively off sooner or later might be excluded from sure points of society. For instance, they had been involved that some people may not have the ability to entry inexpensive transport choices or is perhaps at larger threat of shedding their jobs to automation. There was a pervasive sense that there was a threat that these with much less cash might be ‘left behind’.
-
Place-based and geographic inequality: Contributors had been anxious that there might be a widening of inequalities between city and rural areas sooner or later. This sentiment was expressed most strongly by these from rural areas. There have been two major issues raised. Firstly, that rural areas wouldn’t have entry to the facilities and funding loved by city areas. Secondly, that these at the moment dwelling in rural areas would want to maneuver into city areas, leading to a lack of entry to nature or lack of livelihoods for these working in agriculture.
“If [food is] grown in a lab, they received’t want farmers anymore. Farmers will lose out.”
- Accessibility: Contributors advocated strongly for elevated accessibility in future eventualities and had been constructive about cases the place they noticed alternatives for elevated accessibility. Contributors recommended that that extra disparate constructed environments wouldn’t adequately meet the wants of these with completely different accessibility wants. Usually, non-public automobiles had been seen as being most advantageous for these with restricted mobility, though a number of contributors highlighted the chance that public transport advances might end in larger independence for these with completely different accessibility necessities.
Metropolitan society
The issues round elevated earnings equality most impacts the atomised society (which has elevated earnings equality) and to a lesser extent, the self-preservation and metropolitan societies (the place inequality was assumed to remain roughly at at present’s stage). The priority across the widening divide between city and rural areas principally impacts the metropolitan society, the place funding has targeted on city areas for effectivity causes.
Well being
Key message for coverage makers: As explored within the earlier chapter, there are potential co-benefits to insurance policies aimed toward lowering emissions, together with longer wholesome life expectations and improved air high quality. Contributors favoured eventualities that gave equal precedence to public and planetary well being. Given this, emphasising the well being co-benefits related to a web zero transition ought to profit residents and, in so doing, bolster help for the transition itself.
[I like the idea of] the pure fruit and veg, the well being advantages and low meat consumption.
Sluggish lane society
What the contributors mentioned: Contributors usually explored the impacts that future societal modifications might have on human well being. Discussions about weight loss plan and meals centred on the implications for well being. Basically, contributors expressed the view that helpful local weather outcomes must be aligned with helpful well being outcomes.
Contributors had been significantly involved with the well being implications of the diets that completely different eventualities put ahead, and plenty of contributors’ views on the well being implications of individuals’s diets had been contingent on the standard and kind of meals completely different folks had been capable of entry.
One other key focus was the affect of social isolation on people’ psychological well being. There have been issues that reliance on know-how would end in larger isolation. Contributors highlighted this with the constructed surroundings too, noting that lack of entry to greenery or nature can have unfavourable impacts on psychological and bodily well being. Issues round isolation and loneliness significantly affected responses to the atomised and metropolitan societies.
I’ve issues not nearly well being however psychological well being on this state of affairs.
Atomised society
Involvement
Key message for coverage makers: Contributors had been conscious that assembly web zero would probably come from folks making modifications to their existence and weren’t averse to doing so. Nonetheless, they expressed the sturdy want to be consulted if coverage makers had been on the lookout for methods to expedite these modifications. In addition they famous that for insurance policies to work, folks needed to belief the establishments designing and implementing them. Coverage makers will probably discover it simpler to chart a course to web zero by working with and listening to residents.
It’s nice when you’re doing it voluntarily, however when you’re pressured into it with out another choice, it’s not so good.
Self-preservation society
What the contributors mentioned: Contributors usually emphasised the significance for people to be concerned within the choices that affected their lives and to have the ability to make their very own, knowledgeable selections. Most contributors recognised the significance of societal modifications to cut back emissions. Some contributors expressed constructive views about modifications in client behaviour, reminiscent of elevated desire for plant-based diets or lowering consumption of products. Basically, there was emphasis on the significance for folks and communities to take larger particular person and collective accountability, and for sustainable selections to be inspired and incentivised. Issues round low ranges of involvement and institutional belief significantly have an effect on the atomised and self-preservation societies.
5.5 Reactions to the eventualities
On this part there’s a brief reminder of the modelling outputs for every state of affairs adopted by an outline of what challenges coverage makers on this imagined future state of affairs would face. That is adopted by larger element on contributors’ reactions to every society as a complete and the sectors inside it.
Atomised society
Reminder of what the modelling tells us: As a proportion of GDP, the price of delivering this vitality system in 2050 is roughly the identical a baseline state of affairs the place web zero just isn’t met, largely as a result of GDP is larger on this state of affairs. Due to its excessive vitality demand and low obtainable land area, this state of affairs depends closely on direct air seize, carbon seize and storage, and hydrogen produced from fossil fuels. The inhabitants imagined on this world has a desire for top ranges of consumption. The excessive vitality demand and reliance on unproven applied sciences place this state of affairs at a medium threat of lacking web zero if the traits don’t comply with our assumptions.
Key challenges for coverage makers within the atomised society: In a future like this, excessive financial progress and technological innovation affords selection for coverage makers and most people. Though this selection is more likely to be fascinating for a lot of residents (who might worth having a spread of transport choices or meals selection), there could also be discontent amongst these on decrease incomes who might discover some choices unaffordable. Societal divisions (together with bodily separation of various social teams) might make this future a tough surroundings by which to create and implement coverage, particularly provided that residents could also be extra involved about potential disproportionate impacts of any coverage choices. Coverage making round agriculture and land use could also be significantly advanced, with residents probably being reluctant to just accept the big modifications to rural landscapes and inexperienced areas wanted to stability meals manufacturing and carbon seize know-how.
Society as a complete
Contributors’ general reactions: Contributors’ preliminary reactions centred on issues round earnings inequality. Whereas some did word know-how might be used to realize constructive outcomes (for instance, to make healthcare more practical and environment friendly), many contributors expressed issues in regards to the frequent use of digital actuality and different immersive applied sciences in contributing to the isolation. Even contributors who welcomed the usage of applied sciences for the discount of emissions and larger comfort expressed issues about know-how getting used to displace human interplay and communities.
[People] will probably be extra disconnected and impersonal of their dealings, like indifferent robots. I discover that basically unhappy.
Atomised society
Sector-specific reactions
The constructed surroundings
Reminder of the constructed surroundings within the atomised society: Persons are more and more dwelling in self-contained ‘bubbles’ in suburban and rural areas, with extra folks dwelling alone. New properties in dispersed places have improved affordability. Nonetheless, there are fewer native facilities.
It seems to be just like the poorer are excluded from all kinds of transports Atomised society
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors shared a dislike for the perceived insularity of this society, expressing discomfort with the dispersed inhabitants and the excessive variety of folks dwelling alone. They had been additionally anxious that these on larger incomes would transfer into gated communities or in another method bodily separate themselves from these on decrease incomes, rising segregation and lowering the sense of neighborhood.
Journey and transport
Reminder of journey and transport within the atomised society: On this world, long-distance public transport is environment friendly and handy. Nonetheless, the price of utilizing it’s comparatively excessive. There’s a sturdy uptake of CAVs by these with larger incomes. Worldwide flights for holidays and leisure stay common.
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors famous that there have been many transport choices for the best earners on this society (for instance, CAVs and public transport) however restricted choices for these on the bottom incomes. There have been issues that this might successfully exclude some folks from numerous actions outdoors of the house.
Work and {industry}
Reminder of labor and {industry} within the atomised society: Excessive consumption and elevated technological obsolescence have created a throwaway tradition. Nonetheless, there are additionally higher recycling options for some merchandise. Cryptocurrency is more and more used to buy companies in each the bodily and digital world.
Contributors’ reflections: There was concern from contributors about inbuilt obsolescence on this society. Challenges round inequalities had been additionally raised, particularly issues about whether or not there was equal entry to digital infrastructure. Some contributors had been involved in regards to the jobs obtainable on this society, noting that top ranges of automation might end in some folks shedding their jobs. Different contributors disagreed, suggesting that innovation would generate jobs and create alternatives to reskill.
I perceive the concerns of how some jobs are being taken over by know-how, however I believe with tech, that may generate extra job alternatives for folks to allow them to develop extra skillsets.
Atomised society
Meals and land use
Reminder of meals and land use within the atomised society: There is a rise within the availability and affordability of cultured meat. City agriculture and vertical farming supply native produce for these with larger incomes. Genome-edited crops and robotic pollinators permit the UK to realize self-sufficiency. Nonetheless, environmental degradation has lowered biodiversity.
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors expressed reticence round elevated agricultural know-how on this society, significantly for genome-edited meals, cultured meat and vertical farming (there have been fewer issues expressed about robotic pollinators). There have been additionally issues that rural landscapes and inexperienced areas may not exist on this society, which was seen as undesirable.
Metropolitan society
Reminder of what the modelling tells us: The price of delivering the vitality system in 2050 is 2% of GDP decrease than a baseline state of affairs the place web zero just isn’t met. In different phrases, this state of affairs is extra inexpensive than not assembly web zero. Vitality demand and financial progress have been decoupled most importantly on this state of affairs. This state of affairs makes use of unproven applied sciences to achieve web zero, though it additionally makes use of nature-based removals. Demand for vitality and items is reasonably excessive, pushed partially by larger financial progress, however offset by useful resource effectivity. The vitality calls for on this state of affairs imply a comparatively massive space is required to construct the required vitality infrastructure. The danger to lacking web zero on this state of affairs is comparatively low, as there’s scope to push know-how change or demand discount additional if wanted.
Key challenges for coverage makers within the metropolitan society: On this future, excessive financial progress, alongside excessive social cohesion and institutional belief, have created a comparatively benign surroundings for rolling out new applied sciences and implementing new insurance policies. Nonetheless, there’s more likely to be continued reticence in the direction of applied sciences seen to be infringing on folks’s private lives and coverage makers would probably have to proceed reassuring the general public on the protection of latest applied sciences so as to not lose help. Explicit resistance could also be obvious in meals manufacturing, the place the general public could also be least comfy with applied sciences enjoying a significant position with out cautious analysis and regulation. Rural populations might categorical dissatisfaction with insurance policies seen to favour city areas or to create divisions between city and rural areas. Basically, residents’ want for inexperienced areas and rural landscapes might come into battle with rising urbanisation and land getting used for meals manufacturing and/or nature-based carbon elimination.
Society as a complete
Contributors’ general reactions to the metropolitan society: Contributors’ preliminary ideas on this state of affairs usually revolved across the excessive use of know-how in 2050. Some contributors felt the state of affairs offered futuristic and thrilling improvements, however others expressed some discomfort round elevated use of some applied sciences (particularly AI and agricultural know-how). Many contributors had been involved that heavy reliance on know-how would possibly exclude some teams, particularly older folks and people in rural areas. In addition they expressed common concern in regards to the rural and concrete divide. Contributors from rural areas had been anxious about being ‘left behind’, with restricted entry to the enhancements in public transport efficiencies obtainable in city areas and with the perceived side-lining of their existence and livelihoods (for instance, by way of meals manufacturing changing into divorced from rural areas).
I believe individuals who don’t have an city way of life have been forgotten about.
Metropolitan society
Sector-specific reactions
The constructed surroundings
Reminder of the constructed surroundings within the metropolitan society: Many individuals reside in cities and fewer reside in rural areas. Funding is channelled to city areas. There’s compact dwelling in small households and a push for important companies near house.
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors had been constructive about the potential of inexperienced cities and excessive financial progress on this society. Nonetheless, they raised some issues about potential isolation, with small or single-person households usually being considered negatively. They had been additionally involved about bodily separation and a scarcity of interplay between completely different teams (particularly between these on larger incomes and people on decrease incomes and between these in city and people in rural areas).
Journey and transport
Reminder of journey and transport within the metropolitan society: There was larger funding in low-cost city public transport and prepare journey is cheaper and simpler between cities. CAVs can be found as on-demand shared journey. There are zero carbon worldwide flights obtainable however much less home flying.
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors welcomed the advantages that lively journey and public transport might have on lowering air pollution and bettering air high quality. Nonetheless, some had been involved with what a rise in public transport (and to a sure extent, elevated use of CAVs) would imply for transport infrastructure. Particularly, they had been involved in regards to the funding that might be required and whether or not new inter-city infrastructure would impinge on inexperienced areas.
Work and {industry}
Reminder of labor and {industry} within the metropolitan society: There’s a thriving marketplace for items and companies alongside a rising round financial system. An elevated deal with sustainability supported with know-how assists folks in making sustainable selections.
I fairly like the best way that it’s making an attempt to eradicate consumerism and the throwaway tradition we now have, reminiscent of quick style.
Metropolitan society
Contributors’ reflections: The round financial system was seen as a constructive facet of this society. Nonetheless, some contributors had been involved that there could be a rise in automation within the workforce, which might end in folks’s jobs altering or being misplaced. Others famous that it was potential for folks to reskill to work within the new jobs that technological innovation would possibly supply.
Meals and land use
Reminder of meals and land use within the metropolitan society: There was a rise in plant-based diets and cultured meat. Organically farmed meat is a uncommon luxurious. Genome modifying and robotics have lowered land and pesticide use.
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors had been usually averse to the usage of novel applied sciences in meals manufacturing on this society, significantly cultured meats and, to a lesser extent, genome-edited meals. Nonetheless, others noticed potential positives in lowering pesticide use and decreasing emissions.
In agriculture, we at the moment use a number of pesticides and chemical substances, so lowering these might be constructive for the pure world and biodiversity.
Metropolitan society
Self-preservation society
Reminder of what the modelling tells us: The price of delivering this vitality system in 2050 is the best proportion of GDP of all of the eventualities and is 5% of GDP larger than a baseline state of affairs the place web zero just isn’t met. Extra land will probably be wanted to accommodate demand-led infrastructure in addition to for elevated livestock and agriculture. The extent of carbon elimination required necessitates each technological and nature-based approaches. There’s additionally a comparatively excessive reliance on unproven web zero applied sciences, mixed with a society much less amenable to alter; these challenges are unlikely to be resolved and the chance of failure in assembly web zero is excessive.
Key challenges for coverage makers within the self-preservation society: On this future, low progress and technological progress have left fewer choices for coverage makers to achieve web zero. This has meant counting on comparatively high-cost unproven applied sciences to cut back emissions. Decrease progress additionally presents wider challenges to earnings and public companies. Coverage makers might discover a inhabitants pissed off by a scarcity of innovation, alternatives, and sense of neighborhood. Nonetheless, the comparatively low use of seen know-how might imply that coverage makers have to make fewer choices on regulation. The preservation of ‘conventional’ jobs and existence might also imply coverage makers have to sort out fewer points round reskilling the inhabitants. Decrease progress has resulted in comparatively little new infrastructure or housing. Coverage makers might discover, subsequently, that the main points they face are round housing provide and dependable transport choices. Though new constructing initiatives haven’t affected the agricultural panorama, coverage makers might face discontent in rural areas the place unviable agricultural land has been used for technological and nature-based carbon elimination.
Society as a complete
Contributors’ general reactions: There was a powerful feeling held by most contributors that this society was ‘going backwards’ and confirmed no progress between the present day and 2050. Some expressed disappointment within the lack of the web zero applied sciences that they believed had been essential to cut back emissions. Contributors had been involved in regards to the earnings equality on this society and had been anxious that some points of day by day dwelling could be unaffordable for these on decrease incomes. Just a few contributors recommended that this society could be the least jarring for older folks or for individuals who had been strongly averse to alter because it felt essentially the most just like the present day.
Sector-specific reactions
The constructed surroundings
Reminder of the constructed surroundings within the self-preservation society: Much less funding in cities has pushed folks out to the suburbs and rural areas. Housing demand outstrips provide and there’s extra multigenerational dwelling because of this. There’s additionally a deal with ‘self-sufficient’ dwelling.
I come from an already segregated society and gated communities will do nothing to combine folks from various backgrounds.
Self-preservation society
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors had been anxious that the mixture of a scarcity of a way of neighborhood and what they perceived as low dwelling requirements would result in elevated crime. They recommended this might end in these with the best incomes shifting into gated communities, exacerbating the social divisions they already felt had been prevalent on this society. Some contributors had been pretty constructive in regards to the enhance in multi-generational dwelling, suggesting that this would cut back emotions of isolation. Nonetheless, others expressed concern that this pattern could be pushed by financial circumstances reasonably than an elevated want to carry households nearer collectively.
Journey and transport
I reside in a small hamlet. The closest large store is over an hour’s drive away. It wouldn’t be potential for me to get round in all places on a motorcycle with younger kids.
Self-preservation society
Reminder of journey and transport within the self-preservation society: Public transport is out there however is fragmented outdoors of cities and has obtained little funding. There was reasonable funding in lively journey infrastructure. CAVs usually are not widespread however can be found for the wealthy. Flying is more and more costly.
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors had been involved about how individuals who didn’t personal a personal automobile would journey on this society, noting that an unreliable and fragmented public transport system would make life very tough. There have been additionally issues that costly flights would imply that international holidays would solely be potential for the best earners and that most individuals couldn’t afford to go to household or pals they could have overseas.
Work and {industry}
Reminder of labor and {industry} within the self-preservation society: Many items are nonetheless designed with inbuilt obsolescence. ‘Greenwashing’ by corporations is widespread. Basically, there’s a throwaway tradition. Nonetheless, these dwelling ‘off grid’ have a ‘make do and mend’ angle. There are additionally service trade or mutual items trade methods.
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors disliked the throwaway tradition on this society and expressed concern for a way the waste could be managed. There have been constructive reactions in the direction of teams who repaired their items and in the direction of mutual items trade methods. Contributors additionally recommended that this society had the potential for the best variety of ‘conventional’ and face-to-face jobs, which they expressed help for.
Meals and land use
Reminder of meals and land use within the self-preservation society: Meat is available by way of intensive farming. Natural choices can be found however are unaffordable for most individuals. Some UK farmland has grow to be unviable, which means there’s an elevated reliance on imported meals. Some former farmland has been rewilded. There’s little superior agricultural know-how obtainable.
Contributors’ reflections on meals and land use within the self-preservation society: Contributors had been unfavourable in regards to the elevated reliance on imports, noting a want for self-sufficiency and meals safety. Many additionally advocated for guaranteeing that there was equal entry to wholesome meals for all teams sooner or later. They had been involved that high quality produce would solely be inexpensive for these on larger incomes and that these on decrease incomes might find yourself having decrease high quality meals and fewer selection in what they consumed. Though contributors had been usually constructive in the direction of rewilding, some had been involved that it might be detrimental to ‘conventional’ rural existence.
I prefer to be self-sufficient in what we develop […] When you don’t produce your personal reserves, you’re held captive by outdoors forces.
Self-preservation society
Sluggish lane society
Reminder of what the modelling tells us: The price of delivering this vitality system in 2050 is 1% of GDP larger than a baseline state of affairs the place web zero just isn’t met. It makes use of considerably much less new vitality infrastructure than different eventualities to satisfy the demand, and important societal shifts have lowered vitality demand and lowered the necessity for unproven web zero applied sciences. This features a shift to a round financial system and nature-based carbon elimination. Nonetheless, the dearth of know-how availability means that there’s a comparatively excessive threat of not reaching web zero if demand reductions are short-lived. The society is amenable to creating important modifications, and that is more likely to be the principle mitigation in case of dangers.
Key challenges for coverage makers within the sluggish lane society: On this future, low financial progress has meant fewer know-how choices can be found for coverage makers to achieve web zero. Decrease progress additionally presents wider challenges to earnings and public companies. Nonetheless, shifts in consumption have stored prices for assembly emissions targets low. Though there’s excessive societal cohesion, coverage makers might face a inhabitants that’s liable to changing into dissatisfied with a scarcity of progress in dwelling requirements, a scarcity of comfort, and restricted selections (for instance, in what to eat or learn how to journey). Challenges for coverage makers on this society are more likely to be about guaranteeing that public companies can proceed to satisfy demand in a future with comparatively restricted public funds. Nonetheless, they could face fewer challenges round perceived inequalities and land use, with this future having excessive social cohesion and safety of rural areas (together with for conventional agriculture and preservation of pure landscapes).
Society as a complete
Contributors’ general reactions: Most contributors highlighted that the deal with communities on this society was very constructive. The provision of domestically grown meals was additionally common, as was the in depth use of public transport, the shrinking earnings inequality, and the ‘restore and mend’ tradition. Some contributors had been anxious a few slow-down in manufacturing and new merchandise being much less continuously obtainable. Most issues centred on lowered comfort and perceived decrease dwelling requirements.
I really like the thought of getting us onto a extra stage enjoying discipline.
Sluggish lane society
Sector-specific reactions
The constructed surroundings
Reminder of the constructed surroundings within the sluggish lane society: Inhabitants is unfold throughout city and rural areas. There was low funding in new properties. Persons are dwelling extra localised and compact existence and counting on elevated native facilities.
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors had constructive reactions to the elevated sense of neighborhood on this society. The transfer in the direction of native facilities and close-knit communities unfold throughout city and rural areas was additionally seen positively. Nonetheless, some feared the countryside could be essentially modified by the brand new infrastructure and housing that might be wanted to facilitate inhabitants dispersal from cities and cities.
Journey and transport
Reminder of journey and transport within the sluggish lane society: Strolling and biking are widespread, and folks can entry an environment friendly and well-maintained public transport system. Non-public automotive possession is much less frequent and there are few CAVs in use. Flying domestically or internationally is much less widespread with extra choices for slower and fewer emissions-intensive choices (reminiscent of high-speed trains or boats).
If everyone seems to be taking the identical mode of transport, you could create extra railway traces, trains and routes. They have to be extra dependable.
Sluggish lane society
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors had been pretty constructive in regards to the excessive use of lively journey and public transport on this society, noting this might be helpful for public well being and the surroundings. In addition they recommended that having adequate infrastructure for lively journey would create extra flexibility in journey than both non-public or public transport. Some contributors had been unconvinced by alternate options to aviation for long-distance journey, suggesting it could be inconvenient and impractical for these working in jobs with restricted go away. There have been issues that each non-public and public transport may not be inexpensive for these on low salaries.
Work and {industry}
Reminder of labor and {industry} within the sluggish lane society: Small companies are thriving and benefiting from localisation. Huge companies are selling constructive societal values to draw clients. There’s an elevated in shared items and companies. The price of items is excessive and there is a rise in repairing reasonably than changing gadgets.
Contributors’ reflections: Most contributors had been very constructive in the direction of the ideas of a round financial system and sharing items in a neighborhood (reminiscent of by way of a ‘library of issues’). Some contributors additionally argued that this shift would create jobs and result in new expertise to be developed. A small variety of contributors expressed concern that there could be restricted alternatives to purchase new items on this society and recommended that this would cut back the comfort that they expertise at the moment.
Meals and land use
Reminder of meals and land use within the sluggish lane society: There is a rise in plant-based diets and decrease meat consumption. Little agricultural know-how is out there. Extra meals is grown within the UK for home consumption. There are protected nature zones and restored nationwide parks.
I do eat meat, however I do like a plant-based weight loss plan. To me, it appears fairly good. I’m completely satisfied to not have the identical selection as on the minute. I’d survive.
Sluggish lane society
Contributors’ reflections: Contributors had been constructive about domestically grown meals, consuming seasonal produce and lowering reliance on imports. Nonetheless, some expressed that this might make the UK much less resilient if there have been excessive climate occasions that affected home manufacturing. Contributors additionally highlighted that there would probably be regional variations within the potential to develop meals, which means some areas could be reliant on meals from different areas or on dearer imports. Some contributors additionally famous that comfort meals could be lacking from this society, which was seen as unfavourable for individuals who at the moment depend on it (reminiscent of working mother and father).
5.6 Tensions and trade-offs
Key message for coverage makers: Contributors had been aware of the tensions concerned in choice making round web zero. When exploring inherent trade-offs, they famous that there was no solution to resolve them absolutely. Nonetheless, by way of exploring them, they often turned extra receptive to a wide range of choices. In future, as governments articulate the subsequent levels in our path to web zero, residents could also be most receptive to modifications the place they really feel the tensions or trade-offs have been thought of and never disguised. Involving residents early might present sustainable routes by way of any thorny trade-offs that future governments would possibly face.
What the contributors mentioned: Contributors usually raised the tensions they noticed inside the completely different eventualities they had been discussing. Some key themes emerged that contributors recommended that call makers engaged on web zero would want to think about when occupied with future society.
- Infrastructure and value: Contributors recognized a pressure across the funding wanted in societies with massive infrastructure modifications and the place the funding would come from. Contributors usually agreed that larger prices could be tolerable if it could imply assembly local weather targets, lowering inequalities, and sustaining a way of neighborhood. For some, there was concern that infrastructure growth would deal with city areas as a result of the price of the identical developments in rural areas could be deemed too excessive.
- Sustainability and selection: Contributors recognised the necessity for people to make sustainable selections to cut back emissions by 2050. Nonetheless, they famous that sustainable and fewer wasteful selections typically got here with trade-offs (reminiscent of being much less handy or inexpensive). Contributors usually needed choices for folks sooner or later in order that they might select what labored for them. Some recommended that these with larger wealth who’ve the best emissions wanted to be incentivised to take accountability too. Different contributors recommended there was a task for incentivising and educating folks to make extra sustainable selections. Contributors had been prepared to just accept substantial and widespread modifications as long as this didn’t happen on the expense of particular person freedoms and end in people being mandated to reside their lives in a sure method.
“We’ve got to place the constructing blocks into it, which could imply paying extra. However in the long term, it could imply a cleaner, greener nation.” - Innovation and custom: Contributors had been usually hesitant round societies with elevated use of know-how in ways in which appeared to threaten what they deemed as ‘conventional’ methods of life. Some contributors had been accepting of the usage of superior know-how supplied there have been the appropriate checks and balances in place. These contributors tended to be those that self-identified as earlier adopters of latest know-how. Nonetheless, there have been tensions recognized round elevated use of know-how and jobs. For instance, some contributors had been anxious that if know-how undermines conventional farming, it might imply the tip of ‘conventional’ rural existence.
“Incentivise folks, reasonably than power and push folks […] Training is perhaps a key issue when it comes to folks’s choice making.”
5.7 Key messages from public dialogue
After immersing themselves within the 4 future web zero eventualities, the important thing messages that might be drawn from the discussions of the general public dialogue contributors are:
- Contributors recognised that societal change is considerably contingent on the infrastructure obtainable to help it (reminiscent of accessible public transport and lively journey infrastructure). Residents might wish to make modifications of their lives however want the infrastructure to permit them to take action.
- Contributors believed that a number of the massive societal modifications (reminiscent of will increase in automation or a larger emphasis on the round financial system) might solely occur if there are supporting efforts to reskill people.
- Having fewer meals choices obtainable sooner or later could be unwelcome. Contributors favoured incentivising folks to decide on much less emissions-intensive choices. There’s probably an ongoing want to have interaction the general public in balancing dietary preferences, decarbonising meals manufacturing, and creating public help for potential technical options for this.
- Residents are more likely to be attentive to the perceived equity of pathways to web zero. Future governments are more likely to have to be alert to, and tackle, narratives round equity. Contributors favoured eventualities that gave equal precedence to public and planetary well being. Due to this fact, emphasising the well being co-benefits related to a web zero transition ought to profit residents and, in so doing, bolster help for the transition itself.
- People are conscious that individuals making modifications to their existence may help cut back emissions and usually are not averse to doing so. Nonetheless, contributors expressed the have to be consulted in regards to the way of life modifications they might favour and to not have modifications imposed on them.
- Residents could also be extra receptive to insurance policies the place they really feel the tensions or trade-offs have been thought of and never disguised.
6. Subsequent steps
The analysis, insights and instruments offered on this report are supposed to assist coverage makers think about the position of societal change in each web zero technique and a wider vary of coverage areas. This work has proven how the believable societal modifications might considerably have an effect on the best way that the UK will attain web zero by 2050. It has additionally explored the general public notion of the chance and acceptability of societal modifications. This ultimate part considers how coverage makers can use the outputs of the challenge to make their coverage and technique extra resilient. Different organisations, reminiscent of companies and native authorities, might also discover these approaches useful.
The best way to use the eventualities
The outputs of the challenge present strategic insights into some essential dangers and alternatives related to completely different pathways to web zero, however the proof and eventualities may also be utilized by coverage makers to assist develop and refine particular web zero insurance policies with extra detailed and particular evaluation. Approaches that might be used are described under.
Coverage stress-testing
Stress-testing is a technique for testing coverage, technique, or challenge aims in opposition to a set of eventualities to see how effectively they stand as much as a spread of exterior circumstances.
Goal: The method is used to:
- discover how completely different eventualities would possibly have an effect on strategic coverage aims, and
- establish which points of the coverage are sturdy throughout the total vary of eventualities and which is able to have to be modified if circumstances change sooner or later.
Output: Suggestions on how a brand new or present coverage, technique, or challenge is perhaps affected in numerous eventualities and the way it would possibly have to be tailored within the close to time period to make sure resilience throughout a spread of future circumstances.
Consequence: A extra resilient coverage, technique or challenge.
Strategy
- Work by way of the grid under (Desk 12), discussing how your coverage performs within the longer-term underneath the completely different circumstances of every state of affairs.
- Take a step again to look throughout the total grid: What’s crucial for us to do within the close to time period? What do we have to adapt or observe to make sure the effectiveness of this coverage throughout a spread of potential futures?
Desk 12. Instance coverage stress-testing train
| Coverage proposal (That we do X to realize Y) | Situation 1 | Situation 2 | Situation 3 | Situation 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| What points of this state of affairs make delivering this coverage simpler or tougher? (Suppose when it comes to enablers and boundaries) | ||||
| In 2050, is that this coverage intervention thought of successful or a failure? Why? (What would possibly successful narrative seem like?) | ||||
| Who advantages from this intervention on this state of affairs? Who doesn’t? Who or what’s adversely affected? | ||||
| What would we have to begin, cease, change, or proceed doing now/within the close to time period for this coverage to realize its goal on this state of affairs? |
The method may also be used to assist select between numerous competing coverage selections; an choice which is assessed as performing effectively in most eventualities could also be preferable to at least one that experiences extra boundaries.
Testing implications of wider objectives
Among the societal modifications represented within the eventualities overlap with wider coverage objectives that present or future governments might select to deal with, together with boosting financial progress, strengthening UK manufacturing, and bettering city infrastructure to help inhabitants progress in cities.
Web zero planning doesn’t sometimes think about how the UK’s method to web zero would want to alter if such objectives had been efficiently achieved, however this challenge has illustrated that this might have essential implications for the trail to web zero.
If a set of agreed long-term objectives may be recognized, coverage makers might translate these into a brand new future societal state of affairs utilizing the approaches set out on this report, take a look at the efficiency of their web zero technique in opposition to this state of affairs, after which establish any modifications in method that is perhaps wanted.
As an illustrative instance, this might permit coverage makers to establish how they might meet web zero in a world the place any targets for elevated financial progress had been efficiently achieved or in a world the place UK manufacturing is flourishing.
Methods pondering
The challenge has demonstrated that making use of methods pondering and modelling when planning for the long run is crucial to reveal connections between elements of our vitality system that will not be salient to coverage makers working in particular person sectors. For instance, important will increase in digital communication might cut back demand for journey however enhance demand for house heating and electrical energy use in knowledge centres.
Authorities is already making use of methods pondering in its web zero technique, however this work might be constructed on to consider wider societal connections and cross-sector results.3 This might be significantly essential if evaluation of a selected sector is dealt with by a person authorities division that’s not actively contemplating oblique results from different sectors. To resolve this, growth of cross-sector methods maps to tell methods pondering ought to contain folks working in numerous authorities departments.
Chapter 3 of this report described how methods pondering was used on this challenge to establish cross-sector results that might have implications for vitality demand and emissions. For example, Determine 32 exhibits a methods map illustrating how earnings progress and reshoring of producing might have an effect on each journey demand and the variety of automobiles produced within the UK, each of which might enhance general vitality demand. Improvement of such a map ought to contain coverage makers engaged on progress, transport, and manufacturing to make sure all of the connections are absolutely explored.
Determine 32. The impacts of earnings progress and reshoring on vitality use, through transport and {industry} sector

Horizon scanning
Authorities already tracks a spread of web zero indicators. Additional societal indicators may be tracked to evaluate whether or not the UK is headed in the direction of one or different of the eventualities, offering intelligence on whether or not web zero is perhaps tougher or simpler to satisfy than at the moment assumed, or if the technique might have to adapt in another method.
Indicators for uptake of web zero applied sciences and behaviours are already tracked by authorities, reminiscent of EV gross sales or properties insulated. New societal indicators essential for web zero (a few of which have already got available knowledge), might embrace:
- Public attitudes to web zero and willingness to take particular actions to assist meet UK targets.
- GDP progress and its relationship to vitality demand (in addition to emissions) to grasp the tempo of decoupling of those metrics.
- Diets, together with the share of meat and dairy, in addition to attitudes to new meat and dairy substitutes.
- Uptake of latest digital communications applied sciences and their impact on journey patterns.
- Willingness to make use of shared companies (reminiscent of automotive golf equipment or a ‘library of issues’).
- Availability of repairable merchandise and public attitudes to repairing merchandise.
- Adjustments in city versus rural populations and the ensuing affect on journey and residential vitality use.
- Information on uptake of rising applied sciences and their probably impact on vitality use, together with CAVs, digital currencies, AI, vertical farms and cultured meat.
The information for a lot of of those indicators have been or are being collected to tell coverage makers (for instance, public well being insights from knowledge on diets). Such knowledge might be monitored from a web zero perspective to offer intelligence on altering trajectories in societal components which may enhance or lower emissions, affecting the trail to web zero.
Acknowledgements
GO-Science wish to thank everybody who contributed to the work of this challenge and generously supplied their recommendation and steerage.
This challenge was led by Rowena Bermingham, Jack Snape and Tom Wells. The GO-Science staff included Heather Ballard, Helen Blackbourn, Nina Grassmann, Cara Nicol, Maria Sharmina, Mattie Taylor and Emily White.
We’re grateful to the people and organisations listed under for his or her time, effort, and invaluable contributions.
- GO-Science employees from a wide range of groups who gave help at completely different levels within the challenge, together with: Matthew Ball, Zach Banks, Jessica Bode, Mieke Buckley, Nuala Burnett, Mel Carlin, Kharug Cheema, Helen Doran, Kenneth Hawthorn, Carrie Heitmeyer, Melissa Jackson, Owen Jackson, Felix Langley, Maddi Mackay, Bee Morgan, Mary Phelan and Nathan Roberts.
- Authorities officers who contributed to the working group, steering group and state of affairs workshops, together with the chair of the steering group Paul Monks (Chief Scientific Adviser, BEIS) and representatives from the Cupboard Workplace, Defra, DfT, DHSC, DLUHC, FCDO, Meals Requirements Company, HM Treasury, Nationwide Infrastructure Fee, Pure England, Quantity 10, Workplace for Life Sciences, Ofgem and Scottish Authorities.
- The CREDS modelling staff: John Barrett (College of Leeds), Christian Model (College of Oxford), Oliver Broad (College Faculty London), Alice Garvey (College of Leeds), Elliott Johnson (College of Leeds), Harry Kennard (College Faculty London), Jonathan Norman (College of Leeds), Tadj Oreszczyn (College Faculty London), James Worth (College Faculty London), Steve Pye (College Faculty London) and Paul Ruyssevelt (College Faculty London).
- Exterior specialists who took half in our eventualities workshops and/or who supplied recommendation and steerage at numerous levels of the challenge: Emma Adler (Wildlife and Countryside Hyperlink), Friederike Andres (Federation of Small Companies), James Asfa (Residents UK), William Blomefield (Mars), James Bullock (UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology), Richard Carmichael (Imperial Faculty London), Duncan Cass-Beggs (OECD), Dexter Docherty (OECD), Michael Fell (UCL), Lía Flattery (E3G), Gabrielle Ginér (BT Group), Fay Holland (Groundwork UK), Kamila Izykowicz (John Lewis Partnership), Tim Lord (Phoenix Group), Rob Macquarie (Grantham Analysis Institute), Theresa Marteau (College of Cambridge), Ana Musat (Aldersgate Group), Emily Nurse (CCC), Kathy Peach (Nesta), Jonathan Rennie (Natwest), Olivia Rex (Centre for Web Zero), Andrew Richmond (Native Authorities Affiliation), Amiera Sawas (Local weather Outreach), Hugh Simpson (KPMG), John Fluctuate (John Lewis Partnership) and Sarah Whitmee (London Faculty of Hygiene and Tropical Drugs).
- Ipsos, Sciencewise and UKRI for his or her help and supply of the web zero society public dialogue, the 29 members of the general public who took outing of their busy lives to contribute to this challenge, and our professional advisory group: Jacob Ainscough (Lancaster College), Mette Excessive (College of St Andrews), Justin Macmullan (Which?), Jonathan Marshall (Decision Basis), Theresa Marteau (College of Cambridge), Stuart McKinnon (Vitality Methods Catapult), Doug Parr (Greenpeace UK), Jonatan Pinkse (College of Manchester), Nem Vaughan (College of East Anglia), Lorraine Whitmarsh (College of Tub) and Rebecca Willis (Lancaster College).
- The authors of the societal change proof evaluate, Simone Abram (Durham College) and Silvia Pergetti (College of Edinburgh), and the societal change workshop contributors/reviewers: Anna Carlsson (BEIS), David Edgerton (King’s Faculty London), Stephen Evans (College of Cambridge), Frank Geels (College of Manchester), Alyssa Gilbert (Imperial Faculty London), Chris Langdon (Suppose Unthinkable Ltd), David Newbery (College of Cambridge), Ralitza Nikolaeva (College of St Andrews), Ruth Pugh (College of Studying) and Charlie Wilson (College of Oxford).
We recognize the immense pool of experience we had been capable of entry throughout this challenge and hope that the ultimate report will probably be helpful to those contributors and a good wider group.
Glossary
| Time period | Definition |
|---|---|
| Afforestation | The method of artificially changing non-forest land into forest, usually for carbon sequestration. |
| AI | Synthetic intelligence. |
| Air high quality life index | A measure of the affect of air air pollution on life expectancy. |
| Assumptions | A set of conventions and selections made when creating and working a computational mannequin. |
| At Soc | The atomised society. |
| BECCS | Bioenergy with carbon seize and storage; a course of for producing vitality from biomass whereas extracting carbon dioxide from the ambiance. |
| BEIS | Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique. |
| Bioenergy with carbon seize and storage | Capturing and completely storing carbon dioxide from bioenergy emissions, in order that it turns into a supply of unfavourable emissions. |
| Blockchain | A shared decentralised system that can be utilized to underpin cryptocurrencies or comparable initiatives requiring a decentralised ledger. |
| Bnpkm | Billion passenger kilometre; a unit of measurement representing a passenger travelling one kilometre. |
| Bnvkm | Billion automobile kilometre; a unit of measurement representing a automobile travelling one kilometre. |
| Carbon seize and storage | Capturing carbon dioxide earlier than it enters the ambiance after which storing it. |
| CAV | Related and autonomous automobile; a automobile that may perform some or all its the driving duties, rather than the driving force. |
| CC | Local weather change. |
| CCC | Local weather Change Committee; an unbiased non-departmental public physique that advises the UK on tackling and getting ready for local weather change. |
| CCS | Carbon seize and storage; capturing carbon dioxide earlier than it enters the ambiance after which storing it. |
| CCU | Carbon seize and utilisation; the method of capturing carbon dioxide to be recycled for additional utilization (together with for biofuels). |
| CCUS | Carbon seize, utilisation and storage; a set of applied sciences for capturing carbon dioxide both for storage or for additional utilization. |
| Related and autonomous automobile | A automobile that may perform some or all its the driving duties, rather than the driving force. |
| COP | United Nations Convention of Events; a sequence of annual conferences, which have been working since 1995, to carry collectively members of the United Nations Framework Conference on Local weather Change (UNFCCC) to evaluate progress made on commitments to restrict local weather change. |
| CREDS | Centre for Analysis into Vitality Demand Options |
| Crucial uncertainties | Extremely essential however extremely unsure potential future modifications. |
| DAC | Direct air seize; the method of capturing carbon straight from the ambiance. |
| Defra | Division for Setting, Meals and Rural Affairs. |
| Direct air seize | The method of capturing carbon straight from the ambiance. |
| DIT | Division for Worldwide Commerce. |
| Drivers of change | Occasions or shifts that will trigger a societal pattern to change or change tempo. |
| Ecotourism | A type of tourism that includes visiting pure areas through sustainable strategies of transport. There’s usually a deal with environmental schooling. |
| Vitality forestry | Forestry by which fast-growing bushes or woody shrubs are grown with the aim of offering biomass for vitality use. |
| ETS | Emissions Buying and selling Scheme; a market-based method to controlling web emissions by offering financial incentives for lowering the emission ranges. Additionally know as ‘cap and commerce’ as a result of emissions ranges are capped for particular person polluters however unused limits may be traded between polluters. |
| Fossil CCS – H2 manufacturing | Capturing carbon dioxide that outcomes from the burning of fossil fuels utilized in hydrogen manufacturing. |
| Fossil CCS – {industry} | Capturing carbon dioxide that outcomes from the burning of fossil fuels in industrial processes, reminiscent of metal and cement manufacturing. |
| Fossil CCS – energy technology | Capturing carbon dioxide that outcomes from the burning of fossil fuels for energy technology. |
| GDP | Gross home product; a financial measure of the market worth of products/companies produced and bought in a rustic in a selected time interval. |
| GHG | Greenhouse gases (together with carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and others); gases within the earth’s ambiance that take in and emit radiant vitality, inflicting the worldwide warming. |
| International commons | Useful resource domains which are shared the world over (such because the oceans, the ambiance or outer area). These domains are outdoors of nationwide jurisdictions and may be accessed by all nations. |
| GM | Genetically modified; any organism whose genetic materials has been altered utilizing genetic engineering strategies. |
| Greenwashing | A type of advertising and marketing used to influence the general public that an organisation’s merchandise or insurance policies are environmentally pleasant when they don’t seem to be. |
| Warmth pump | A tool that heats buildings by transferring in thermal vitality from an outdoor supply. |
| HGV | Heavy items automobile (any truck over 3.5 tonnes). |
| Web of issues | The community of on a regular basis objects which are linked to the web. The objects can join and share knowledge with one another and are embedded with sensors and software program that allow them to do that. |
| Cultured meat | Meat produced by culturing cells outdoors of the animal’s physique, by way of tissue engineering strategies. |
| Levers | Quantitative mannequin settings that may be adjusted to match the descriptions of an imagined state of affairs, permitting computational modelling to happen. |
| Library of issues | An organisation that owns gadgets (reminiscent of tools for gardening or house enchancment) that may be lent to clients. |
| Met Soc | The metropolitan society. |
| Metaverse | A hypothesised future technology of the web, in which there’s a shared immersive and protracted 3D digital actuality area, performing as an extension to the bodily world and permitting people to work together with a computer-generated surroundings. |
| MtCO2e | Megatonne of carbon dioxide emissions. |
| NDNS | Nationwide Food plan and Diet Survey. |
| NOx | Nitrogen oxides; poisonous gasoline molecules contributing to air pollution. |
| NTS | UK Nationwide Journey Survey. |
| OBR | Workplace for Price range Accountability. |
| OECD | Organisation for Financial Co-operation and Improvement. |
| ONS | Workplace for Nationwide Statistics. |
| Parameters | A numerical worth knowledgeable by knowledge that can be utilized in a mannequin. |
| PJ | Peta joule. |
| PM2.5 | Particulate matter lower than 2.5 micrometres in diameter. |
| R&D | Analysis and growth. |
| Reshoring | The method of shifting manufacturing of a product from overseas to the nation the place it’s bought. |
| Rewilding | The method of restoring land to its pure, uncultivated state. |
| SL Soc | The sluggish lane society |
| Soil sequestration | The method by which carbon dioxide is captured from the ambiance and saved within the soil carbon retailer. |
| SP Soc | The self-preservation society. |
| Telepresence | Know-how that enables folks to hold out duties from a digital location, as in the event that they had been in a state of affairs bodily. |
| The atomised society | A stretching but believable future societal state of affairs, by which financial progress and technological progress are excessive, and social cohesion and institutional belief are low. |
| The metropolitan society | A stretching but believable future societal state of affairs, by which financial progress and technological progress are excessive, and social cohesion and institutional belief are additionally excessive. |
| The self-preservation society | A stretching but believable future societal state of affairs, by which financial progress and technological progress are low, and social cohesion and institutional belief are additionally low. |
| The sluggish lane society | A stretching but believable future societal state of affairs, by which financial progress and technological progress are low, and social cohesion and institutional belief are excessive. |
| Tendencies | Basic actions throughout society in an identifiable course. |
| UK NHM | UK Nationwide Family Mannequin. |
| UK TIMES mannequin | A mannequin for the vitality system of the UK, developed by UCL and BEIS. |
| UKTM | UK Instances Mannequin. |
| VR | Digital Actuality. |
| Weak alerts | Early indicators of change or rising points that will grow to be extra important. |
References
CCC (2020). The sixth carbon budget: the UK’s path to net zero. Local weather Change Committee
CCC (2022). Progress in reducing emissions: 2022 report to parliament. Local weather Change Committee
BEIS (2021). Net zero strategy: build back greener. Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique
Stark, C. & Thompson, M. (2019). Net zero: the UK’s contribution to stopping global warming. Local weather Change Committee
Nationwide Grid ESO (2022). Future energy scenarios. Nationwide Grid ESO
BEIS (2021). Impact assessment for the sixth carbon budget. Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique
OECD (2020). Tax policy reforms. Group for Financial Cooperation and Improvement
Barrett, J., Pye, S., Betts-Davies, S., Broad, O., Worth, J., Eyre, N., Anable, J., Model, C., Bennett, G., Carr-Whitworth, R., Garvey, A., Giesekam, J., Marsden, G., Norman, J., Oreszczyn, T., Ruyssevelt, P. & Scott, Ok. (2022). Energy demand reduction options for meeting national zero-emission targets in the United Kingdom. Nature Vitality, 7(8), 726–735.
Chewpreecha, U. & Summerton, P. (2020). Economic impact of the sixth carbon budget. Cambridge Econometrics
GO-Science (2018). Futures toolkit for policy-makers and analysts. Authorities O ffice for Science
BGS (2023). The greenhouse effect. British Geological Survey
BEIS (2022). UK greenhouse gas emissions: other technical reports. Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique
IEA (2022). Global energy review: CO2 emissions in 2021. Worldwide Vitality Company
Bhanumati, P., de Haan, M. & Tebrake, J. (2022). Greenhouse emissions rise to record, erasing drop during pandemic. Worldwide Financial Fund
The Climate Change Act 2008 (2050 Target Amendment) Order 2019.
CCC (2021). Progress in reducing emissions: 2021 report to parliament. Local weather Change Committee
Schultz, P. (2022). Secret agents of influence: leveraging social norms for good. Present Instructions in Psychological Science, 31(5), 443–450.
Yamin, P., Fei, M., Lahlou, S. & Levy, S. (2019). Using social norms to change behavior and increase sustainability in the real world: a systematic review of the literature. Sustainability, 11(20), 5847.
Kinzig, A. P., Ehrlich, P. R., Alston, L. J., Arrow, Ok., Barrett, S., Buchman, T. G., Each day, G. C., Levin, B., Levin, S., Oppenheimer, M., Ostrom, E. & Saari, D. (2013). Social norms and global environmental challenges: the complex interaction of behaviors, values, and policy. Bioscience, 63(3), 164–175.
Rothstein, B. & Stolle, D. (2008). The state and social capital: an institutional theory of generalized trust. Comparative Politics, 40(4), 441–459.
Sparkman, G., Howe, L. & Walton, G. (2021). How social norms are often a barrier to addressing climate change but can be part of the solution. Behavioural Public Coverage, 5(4), 528–555.
Brown, A., Moodie, C. & Hastings, G. (2009). A longitudinal study of policy effect (smoke-free legislation) on smoking norms: ITC Scotland/United Kingdom. Nicotine and Tobacco Analysis, 11(8), 924–932.
BEIS (2021). Net zero societal change analysis project. Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique
Barrett, J., Pye, S., Betts-Davies, S., Eyre, N., Broad, O., Worth, J., Norman, J., Anable, J., Bennett, G., Model, C., Carr-Whitworth, R., Marsden, G., Oreszczyn, T., Giesekam, J., Garvey, A. Ruyssevelt, P. & Scott, Ok. (2021). The role of energy demand reduction in achieving net-zero in the UK. Centre for Analysis into Vitality Demand Options
ONS (2023). GDP expenditure components – real-time database. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics
Airports Fee (2013). Airports commission: interim report. Airports Fee
DfT (2022). Statistical data set: aviation (TSGB02). Division for Transport
Pillai, U. (2015). Drivers of cost reduction in solar photovoltaics. Vitality Economics, 50, 286–293.
Bryant, C. (2019). We can’t keep meating like this: attitudes towards vegetarian and vegan diets in the United Kingdom. Sustainability, 11(23), 6844.
Jaciow, M., Rudawska, E., Sagan, A., Tkaczyk, J. & Wolny, R. (2022). The influence of environmental awareness on responsible energy consumption—the case of households in Poland. Energies, 15(15), 5339.
Fehér, A., Gazdecki, M, Véha, M., Szakály, M. & Szakály , Z. (2020). A comprehensive review of the benefits of and the barriers to the switch to a plant-based diet. Sustainability, 12(10), 4136.
Maggin, T. (2016). Vegan society poll. Ipsos
Johnson, G-R. (2022). How many vegetarians and vegans are in the UK?. Finder
ONS (2022). Families and households in the UK: 2021. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics
ONS (2019). The cost of living alone. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics
Marteau, T., Chater, N. & Garnett, E. (2021). Changing behaviour for net zero. BMJ, 375, n2293.
Shone, A. & Wilkinson, P. (2015). Corporate political engagement index 2015. Transparency Worldwide UK
ONS (2022). Trust in government, UK: 2022. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics
OBR (2022). Economic and fiscal outlook: November 2022. Workplace for Price range Accountability
Lopez, R., Pastén, R. & Gutiérrez Cubillos, P. (2022). Climate change in times of economic uncertainty: A perverse tragedy of the commons?. Financial Evaluation and Coverage, 75, 209–225.
Lloyds Financial institution (2020). Business In Britain 2020. Lloyds Financial institution
Successful, M. & Willan, C. (2020). Towards net zero in UK manufacturing. College Faculty London & HSBC
Development-Monitor (2020). The structure of families and households in the UK. Development-Monitor
ONS (2022). Is hybrid working here to stay?. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics
PWC (2022). State of climate tech 2021: scaling breakthroughs for net zero. PricewaterhouseCoopers
Preston, I., Banks, N., Hargreaves, Ok., Kazmierczak, A., Lucas, Ok., Mayne, R., Downing, C. & Road, R. (2014). Climate change and social justice: an evidence review. The Joseph Rowntree Basis
Approach, R., Ives, M., Mealy, P. & Farmer, J. (2021). Empirically grounded technology forecasts and the energy transition. Joule, 6(9), 2057– 2082.
DfT (2018). Road traffic forecasts 2018. Division for Transport
Wadud, Z. Mackenzie, D. & Leiby, P. (2016). Help or hinderance? The travel, energy and carbon impacts of highly automated vehicles. Transportation Analysis Half A: Coverage and Follow, 86, 1–18.
Ahmad, T., Zhang, D., Huang, C., Zhang, H., Dai, N., Track, Y. & Chen, H. (2021). Artificial intelligence in sustainable energy industry: status quo, challenges and opportunities. Journal of Cleaner Manufacturing, 289, 125834.
Rainie, L., Anderson, J. & Vogels, E. (2021). Experts doubt ethical AI design will be broadly adopted as the norm within the next decade. The Pew Analysis Centre
Setzer, J. & Higham, C. (2022). Global trends in climate change litigation: 2022 snapshot. Grantham Analysis Institute.
Thomas-Peter, H. (2021). Fossil fuel firms sue governments across the world for £13bn as climate policies threaten profits. Sky Information
EA (2022). Climate change civil penalties. Setting Company
Agbugba, G., Okoye, G., Giva, M. & Marlow, J. (2019). The decoupling of economic growth from carbon emissions: UK evidence. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics
Partington, R. (2019). Britain now G7’s biggest net importer of CO2 emissions per capita, says ONS. The Guardian
Antunes, M., Barroca, J. & Oliveira, D. (2021). Urban future with a purpose: 12 trends shaping human living. Deloitte Insights
Beltrán, A., Maddison, D. & Elliott, R. (2018). Is flood risk capitalised into property values?. Ecological Economics, 146, 668–685.
Jenson, J. (2011). Defining and measuring social cohesion. Commonwealth Secretariat
Delhey, J., Boehnke, Ok., Dragolov, G., Ignácz, Z., Larsen, M., Lorenz, J. & Koch, M. (2018). Social cohesion and its correlates: a comparison of western and Asian societies. Comparative Sociology, 17(3–4), 426–455.
Charron, N. & Rothstein, B. (2018). Regions of trust and distrust: how good institutions can foster social cohesion. In: Bridging the Prosperity Hole within the EU (Eds. U. Bernitz, M. Mårtensson, L. Oxelheim & T. Persson, 220–242).
Janmaat, J. (2011). Social cohesion as a real-life phenomenon: assessing the explanatory power of the universalist and particularist perspectives. Social Indicators Analysis, 100(1), 61–83.
Andrews, R., Jilke, S., van de Walle, S. (2014). Economic strain and perceptions of social cohesion in Europe: does institutional trust matter?. European Journal of Political Analysis, 53(3), 559–579.
Arguedas, A. R., Robertson, C. T., Fletcher, R. & Nielsen, R. Ok. (2022). Echo chambers, filter bubbles, and polarisation: a literature review. The Reuters Institute for the Research of Journalism
Sønderskov, Ok. & Dinesen, P. (2016). Trusting the state, trusting each other? The effect of institutional trust on social trust. Political Behaviour, 38(1), 179–202.
Spadaro, G., Gangl, Ok., van Prooijen, J., van Lange, P. & Mosso, C. (2022). Enhancing feelings of security: how institutional trust promotes interpersonal trust. PLoS One, 15(9), e0237934.
Clair, R., Gordon, M., Kroon, M. & Reilly, C. (2021). The effects of social isolation on well-being and life satisfaction during pandemic. Humanities & Social Sciences Communications, 8(28).
Lieberz, J., Shamay‐Tsoory, S., Saporta, N., Esser, T., Kuskova, E., Stoffel‐Wagner, B., Hurlemann, R. & Scheele, D. (2021). Loneliness and the social brain: how perceived social isolation impairs human interactions. Superior Science, 8(21), e2102076.
Rotenberg, Ok. (1994). Loneliness and interpersonal trust. Journal of Social and Medical Psychology, 13(2), 152–173.
Rapolienė, G. & Aartsen, M. (2022). Lonely societies: low trust societies? Further explanations for national variations in loneliness among older Europeans. European Journal of Ageing, 19(3), 485–494.
Yang, J. & Moorman, S. (2021). Beyond the individual: evidence linking neighborhood trust and social isolation among community-dwelling older adults. The Worldwide Journal of Ageing and Human Improvement, 92(1), 22–39.
Mitsch, F., Lee, N. & Ralph Morrow, E. (2021). Faith no more? The divergence of political trust between urban and rural Europe. Political Geography, 89, 102426.
Kenny, M. & Luca, D. (2021). The urban-rural polarisation of political disenchantment: an investigation of social and political attitudes in 30 European countries. Cambridge Journal of Areas, Financial system and Society, 14(3), 565–582.
Xu, C. (2021). Effects of urbanization on trust: evidence from an experiment in the field. Journal of Financial Psychology, 87, 102450.
Ligthart, J. & van Oudheusden, P. (2015). In government we trust: the role of fiscal decentralization. European Journal of Political Financial system, 37, 116–128.
Kim, S., Lee, Y. & Kim, T. (2022). The relationship between fiscal decentralization and trust in government: evidence from the South Korean case. Worldwide Overview of Administrative Science, 88(2), 373–389.
Kaldor, N. (1957). A model of economic growth. The Financial Journal, 67(268), 591–624.
Pakes, A. & Sokoloff, Ok. (1996). Science, technology, and economic growth. PNAS, 93(23),12655–12657.
Maradana, R., Pradhan, R., Sprint, S., Gaurav, Ok., Jayakumar, M. & Chatterjee, D. (2017). Does innovation promote economic growth? Evidence from European countries. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 6(1).
Chen, M., Zhang, H., Liu, W. & Zhang, W. (2014). The global pattern of urbanization and economic growth: evidence from the last three decades. PLoS One, 9(8).
Nguyen, H. & Nguyen, L. (2018). The relationship between urbanization and economic growth: an empirical study on ASEAN countries. Worldwide Journal of Social Economics, 45(2), 316–339.
Brunt, L. & García-Peñalosa, C. (2022). Urbanisation and the onset of modern economic growth. The Financial Journal, 132(642), 512–545.
Miller, H. (2014). What are the features of urbanisation and cities that promote productivity, employment and salaries?. Division for Worldwide Improvement & EPS PEAKS
Quigley, J. (2008). Urbanization, agglomeration, and economic development. The World Financial institution
Fang, C. & Yu, D. (2017). Urban agglomeration: an evolving concept of an emerging phenomenon. Panorama and City Planning, 162, 126–136.
Wu, L., Jiang, Y., Wang, L. & Qiao, X. (2022). The two faces of urbanisation and productivity: enhance or inhibit? New evidence from Chinese firm‐level data. Asian-Pacific Financial Literature, 36(1), 126–142.
Turok, I. & McGranahan, G. (2019). Urbanisation and economic growth: the arguments and evidence for Africa and Asia. Urbanisation, 4(2), 109–125.
Venables, A., Laird, J. & Overman, H. (2014). Transport investment and economic performance. Division for Transport
Chen, M., Zhang, H., Liu, W. & Zhang, W. (2014). The global pattern of urbanization and economic growth: evidence from the last three decades. PLoS One, 9(8).
Roser, M., Ortiz-Ospina, E. & Ritchie, H. (2022). Life expectancy. Our World in Information
Preston, S. (1975). The changing relation between mortality and level of economic development. Inhabitants Research, 29(2), 231-248.
Euromonitor Worldwide (2014). Economic growth and life expectancy: do wealthier countries live longer?. Euromonitor Worldwide.
Lutz, W. & Kebede, E. (2018). Education and health: redrawing the Preston curve. Inhabitants and Improvement Overview, 44(2), 343–361.
Ecob, R. & Davey Smith, G. (1999). Income and health: what is the nature of the relationship?. Social Science & Drugs, 48(5), 693–705.
Rea, M. & Tabor, D. (2022). Health state life expectancies by national deprivation deciles, England: 2018 to 2020. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics.
Lichtenberg, F. (2015). The impact of biomedical innovation on longevity and health. Nordic Journal of Well being Economics, 5(1), 45–57.
Aperion Care (2022). Inventions that drive modern life expectancy. Aperion Care
DfID (2010). Fair society, healthy lives: the Marmot Review: strategic review of health inequalities in England post-2010. Division for Worldwide Improvement
Kondo, N., Sembajwe, G., Kawachi, I., van Dam, R. M., Subramanian, S. & Yamagata, Z. (2009). Income inequality, mortality, and self-rated health: meta-analysis of multilevel studies. BMJ, 339, b4471–b4471.
Onofrei, M., Vatamanu, A. & Cigu, E. (2022). The relationship between economic growth and CO2 emissions in EU countries: a cointegration analysis. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10.
Acheampong, A. (2018). Economic growth, CO2 emissions and energy consumption: what causes what and where?. Vitality Economics, 74, 677–692.
Osadume, R. & College, E. (2021). Impact of economic growth on carbon emissions in selected West African countries, 1980–2019. Journal of Cash and Enterprise, 1(1), 8–23.
Yusuf, A., Abubakar, A. & Mamman, S. (2020)Relationship between greenhouse gas emission, energy consumption, and economic growth: evidence from some selected oil-producing African countries. Environmental Science and Air pollution Analysis, 27, 15815–15823.
Ritchie, H. (2021). Many countries have decoupled economic growth from CO2 emissions, even if we take offshored production into account. Our World in Information
Agarwala, M. & Martin, J. (2022). Environmentally-adjusted productivity measures for the UK: working paper 28. The Productiveness Institute
BEIS (2022). National statistics: energy consumption in the UK. Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique
Topolewski, Ł. (2021). Relationship between energy consumption and economic growth in European countries: evidence from dynamic panel data analysis. Energies, 14(12), 3565.
Odugbesan, J. & Rjoub, H. (2020). Relationship among economic growth, energy consumption, CO2 emission, and urbanization: evidence From MINT countries. SAGE Open,10(2).
Diacon, P. & Maha, L. (2015). The relationship between income, consumption and GDP: a time series, cross-country analysis. Procedia Economics and Finance, 23, 1535–1543.
Osuntuyi, B. & Lean, H. (2022). Economic growth, energy consumption and environmental degradation nexus in heterogeneous countries: does education matter?. Environmental Sciences Europe, 34(1).
OBR (2022). Economic and fiscal outlook: March 2022. Workplace for Price range Accountability
ONS (2022). Population projections. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics
ONS (2023). Gross domestic product (average) per head, CVM market prices: SA. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics
NIC (2016). The impact of population change and demography on future infrastructure and demand. Nationwide Infrastructure Fee
CCC (2018). Reducing UK emissions: 2018 progress report to parliament. Local weather Change Committee
Maguire, E. & Monsivais, P. (2015). Socio-economic dietary inequalities in UK adults: an updated picture of key food groups and nutrients from national surveillance data. British Journal of Diet, 113(1),181–189.
World Financial institution (2022). Urban population (% of total population) United Kingdom. World Financial institution Group
DIT (2022). Analysis of trends in industrial sectoral demand. Division for Worldwide Commerce
VOA (2022). Non-domestic rating: stock of properties including business floorspace. Valuation Workplace Company
DfT (2022). National travel survey. Division for Transport
Shi, Y., Sorrell, S.R. & Foxon, T.J. (2022). Do teleworkers have lower transport emissions? What are the most important factors?. SSRN
BEIS (2021). Energy follow up survey (EFUS) 2017. Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique
BEIS (2017). National household model. Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique
Büchs, M. & Mattioli, G. (2021). Trends in air travel inequality in the UK: from the few to the many?. Journey Behaviour and Society, 25, 92–101.
Cohen, S. & Gossling, S. (2015). A darker side of hypermobility. Setting and Planning A: Financial system and Area, 47(8),166–1679.
Cohen, S., Higham, J. & Cavaliere, C. (2011). Binge flying: behavioural addiction and climate change. Annals of Tourism Analysis, 38(3), 1070–1089.
DfT (2022). Road traffic estimates in Great Britain: 2021. Division for Transport
Marsden, G., Anable, J., Bray, J., Seagriff, E. & Spurling, N. (2019). Shared mobility: Where now? Where next? Second report of the commission on travel demand. Centre for Analysis into Vitality Demand Options
OECD (2021). Exploring the impact of shared mobility services on CO2. Group for Financial Cooperation and Improvement
Make UK (2022). UK manufacturing the facts: 2022. Make UK
PHE (2016). Government dietary recommendations: government recommendations for food energy and nutrients for males and females aged 1–18 and 19+ years. Public Well being England
PHE (2021). NDNS: diet and physical activity a follow-up study during COVID-19. Public Well being England
Defra (2021). United Kingdom food security report 2021: theme 2 UK food supply sources. Division for Setting, Meals and Rural Affairs
Parry, A., LeRoux, S., Quested, T. & Parfitt, J. (2014). UK food waste: historical changes and how amounts might be influenced in the future. WRAP
Defra (2022). Food statistics in your pocket. Division for Meals, Setting and Rural Affairs
GO-Science (2022). Systems thinking for civil servants. Authorities Workplace for Science
Hook, A., Courtroom, V., Sovacool, B. & Sorrell, S. (2020). A systematic review of the energy and climate impacts of teleworking. Environmental Analysis Letters, 15(9).
O’Brien, W. & Yazdani Aliabadi, F. (2020). Does telecommuting save energy? A critical review of quantitative studies and their research methods. Vitality Construct, 225.
Kikstra, J. S., Vinca, A., Lovat, F., Boza-Kiss, B., van Ruijven, B., Wilson, C., Rogelj, J., Zakeri, B., Fricko, O. & Riahi, Ok. (2021). Climate mitigation scenarios with persistent COVID-19-related energy demand changes. Nature Vitality, 6(12), 1114–1123.
Bui, M., Adjiman, C., Bardow, A., Anthony, E., Boston, A., Brown, S., Fennell, P., Fuss, S., Galindo, A., Hackett, L., Hallett, J., Herzog, H., Jackson, G., Kemper, J., Krevor, S., Maitland, G., Matuszewski, M., Metcalfe, I., Petit, C., Puxty, G., Reimer, J., Reiner, D., Rubin, E., Scott, S., Shah, N., Smit, B., Trusler, J., Webley, P., Wilcox, J. & Mac Dowell, N. (2018). Carbon capture and storage (CCS): the way forward. Vitality & Environmental Science, 11(5), 1062–1176.
Pershad, H., Standen, E., Durusut, E. & Slater, S. (2013). Carbon capture and storage (CCS) costs for UK industry: high level review. Division for Enterprise Innovation and Abilities & Division of Vitality and Local weather Change
Nationwide Academies of Science, Engineering and Drugs (2019). Negative emissions technologies and reliable sequestration: a research agenda. Nationwide Academies of Science, Engineering and Drugs
Gough, C., Garcia-Freites, S., Jones, C., Mander, S., Moore, B., Pereira, C., Röder, M., Vaughan, N. & Welfle, A. (2018). Challenges to the use of BECCS as a keystone technology in pursuit of 1.5⁰C. International Sustainability, 1, e5.
Fajardy, M. & Mac Dowell, N. (2017). Can BECCS deliver sustainable and resource efficient negative emissions?. Vitality & Environmental Science, 10(6), 1389–1426.
Welfle, A., Gilbert, P. & Thornley, P. (2014). Increasing biomass resource availability through supply chain analysis. Biomass and Bioenergy, 70, 249–266.
Muscat, A., de Olde, E., de Boer, I. & Ripoll-Bosch, R. (2020). The battle for biomass: a systematic review of food-feed-fuel competition. International Meals Safety, 25, 100330.
BEIS (2022). Direct air capture and other greenhouse gas removal technologies competition. Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique
IEA (2022). Direct air capture. Worldwide Vitality Company.
Scheelhaase, J., Maertens, S. & Grimme, W. (2019). Synthetic fuels in aviation: current barriers and potential political measures. Transportation Analysis Procedia, 43, 21–30.
Bows-Larkin A., Mander S., Traut M., Anderson Ok. & Wooden F. (2016). Aviation and climate change: the continuing challenge. Encyclopaedia of Aerospace Engineering
Sharmina, M., Edelenbosch, O., Wilson, C., Freeman, R., Gernaat, D., Gilbert, P., Larkin, A., Littleton, E., Traut, M., van Vuuren, D., Vaughan, N., Wooden, F. & Le Quéré, C. (2021). Decarbonising the critical sectors of aviation, shipping, road freight and industry to limit warming to 1.5–2°C. Local weather Coverage, 21 (4), 455–474.
The Royal Society (2019). Sustainable synthetic carbon based fuels for transport. The Royal Society
DfT (2021). Green fuels, green skies competition: winners. Division for Transport
HM Treasury (2021). Autumn budget and spending review 2021. HM Treasury
DfT (2022). Net zero transatlantic flight fund. Division for Transport
Defra (2022). Research and analysis: farming and environment evidence packs latest editions. Division for Setting, Meals and Rural Affairs
Bailey, H., Brookes, Ok. & Thompson, P. (2014). Assessing environmental impacts of offshore wind farms: lessons learned and recommendations for the future. Aquatic Biosystems, 10(1), 8.
OBR (2019). Economic and fiscal outlook: March 2019. Workplace for Price range Accountability
Rising, J., Dietz, S., Dumas, M., Khurana, R., Kikstra, J., Lenton, T., Linsenmeier, M., Smith, C., Taylor, C. & Ward, B. (2022). What will climate change cost the UK? Risks, impacts and mitigation for the net-zero transition. Grantham Analysis Institute on Local weather Change and the Setting.
Greenstone, M., Hasenkopf, C. & Lee, Ok. (2022). Air quality life index (AQLI) annual update. Vitality Coverage Institute on the College of Chicago
Stylianou, Ok.S., Fulgoni, V. & Jolliet, O. (2021). Small targeted dietary changes can yield substantial gains for human health and the environment. Nature Meals, 2(8), 616–627.
Sciencewise (2023). Welcome to Sciencewise. Sciencewise
King, M., Padmanabhan, C. & Rose, Ok. (2021). Engaging the public on climate change: a literature review. Centre for Public Impression
Demski, C. (2021). Net zero public engagement and participation. Division for Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique
Willis, R., Curato, N. & Smith, G. (2022). Deliberative democracy and the climate crisis. Wiley Interdisciplinary critiques: Local weather Change, 13(2), e759.
Wells, R., Howarth, C. & Model-Correa, L. (2021). Are citizen juries and assemblies on climate change driving democratic climate policymaking? An exploration of two case studies in the UK. Local weather Change, 168(1–2), 5.
College of Lancaster (2022). The role of deliberative public engagement in climate policy development A report for the Climate Change Committee. Local weather Change Committee
Home of Lords Setting and Local weather Change Committee (2022). In our hands: behaviour change for climate and environmental goals. UK Parliament
ONS (2021). Three quarters of adults in Great Britain worry about climate change. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics
Thompson, S. (2022). UK public still broadly supports most net zero policies. Ipsos
Flynn, C., Yamasumi, E., Fisher, S., Snow, D., Grant, Z., Kirby, M., Browning, P., Rommerskirchen, M. & Russell, I. (2021). People’s climate vote. United Nations Improvement Programme
Local weather Outreach (2022). Net zero, fairness and climate politics. Local weather Outreach
Mellier-Wilson, C. & March S. (2020). UK climate change citizens’ assemblies and citizens’ juries. Contain
Lucien, M. (2021). What a citizen-led low carbon vision looks like. Shared Future
Local weather Meeting UK (2020). Climate assembly UK: The path to net zero. Home of Commons & Contain
Deloitte (2021). Futures we want. UN Local weather Change Convention UK 2021
ONS (2021). Measuring UK greenhouse gas emissions. Workplace for Nationwide Statistics
PHE (2016). National diet and nutrition survey. Public Well being England
[ad_2]
Source link







